Abstract
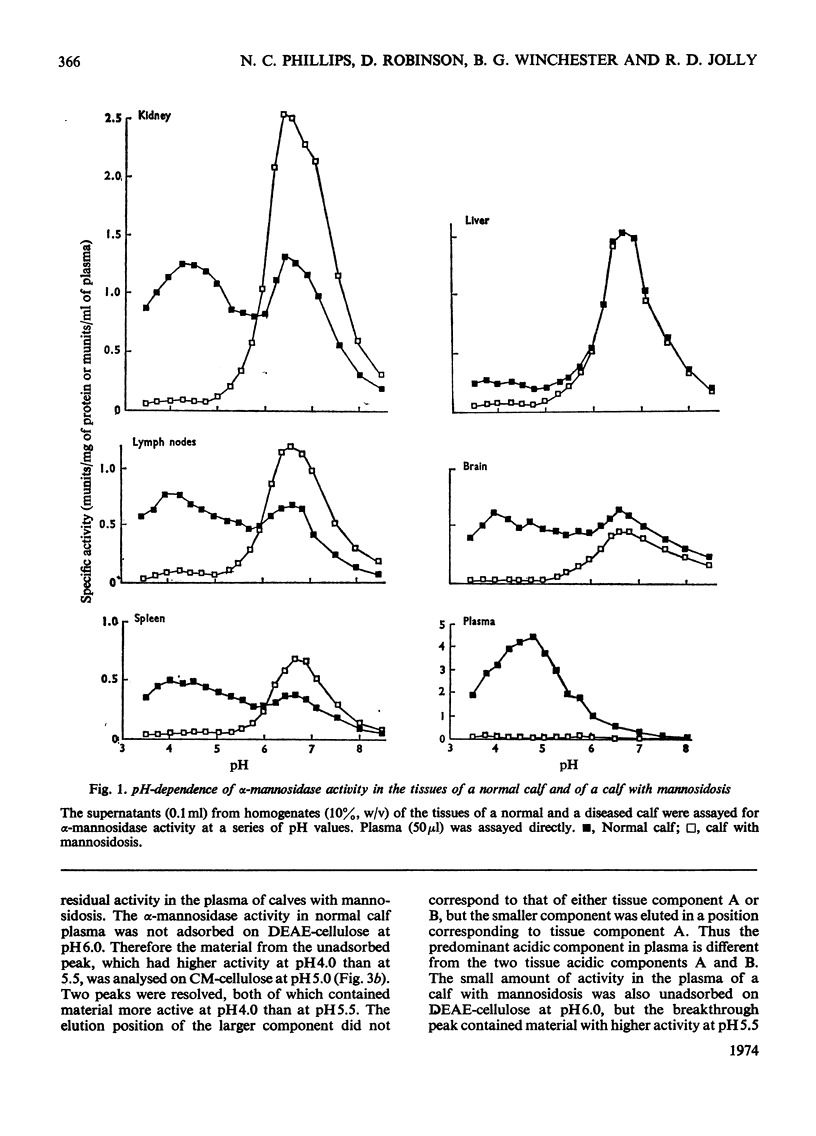
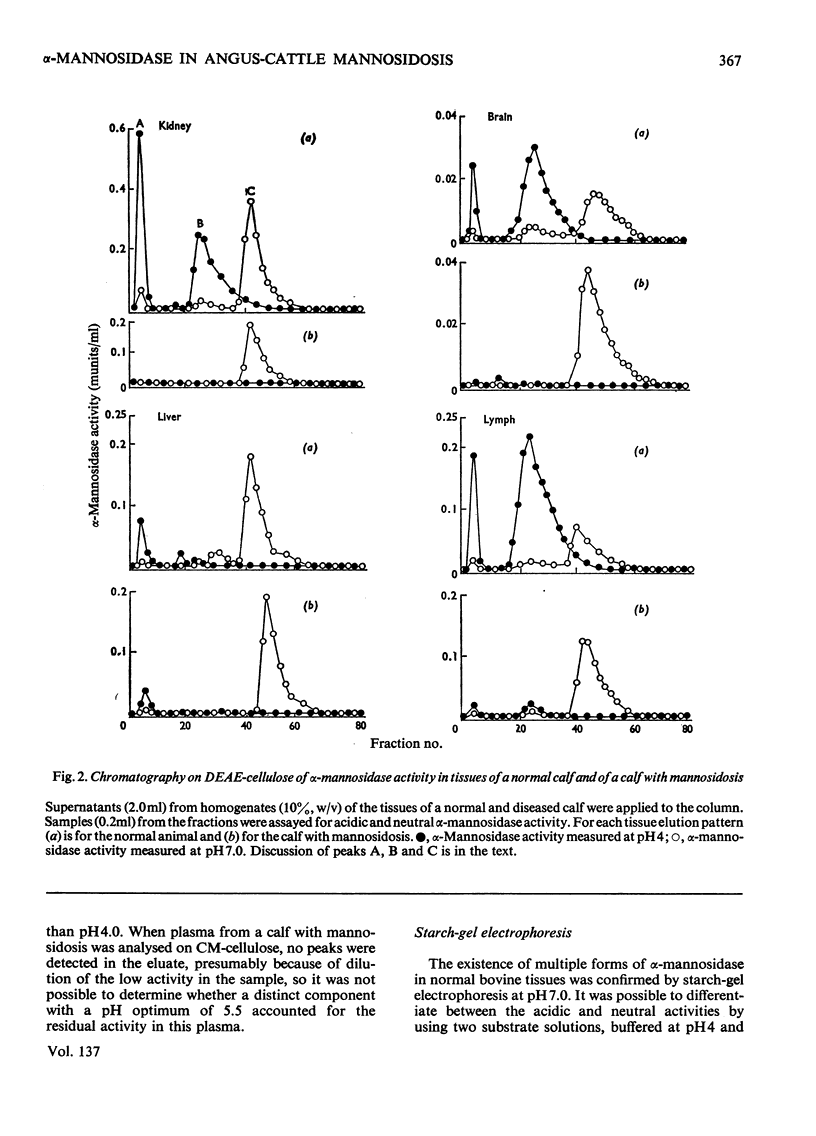
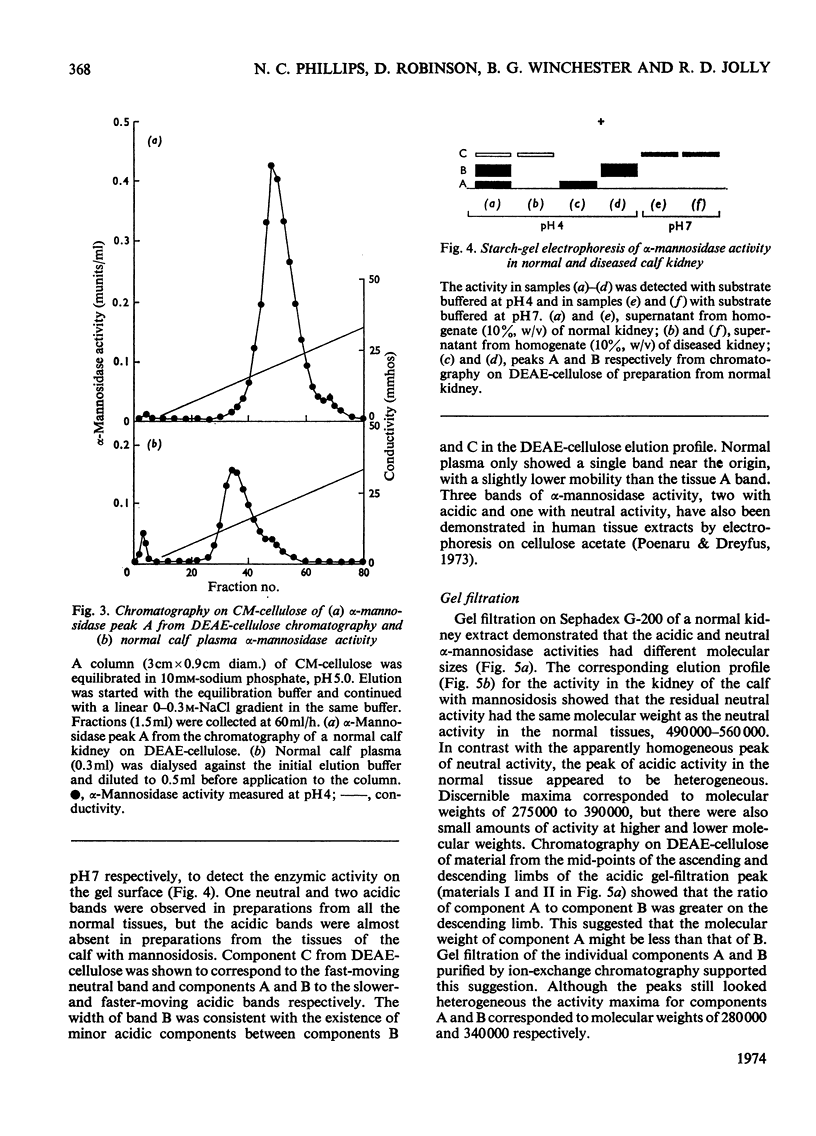
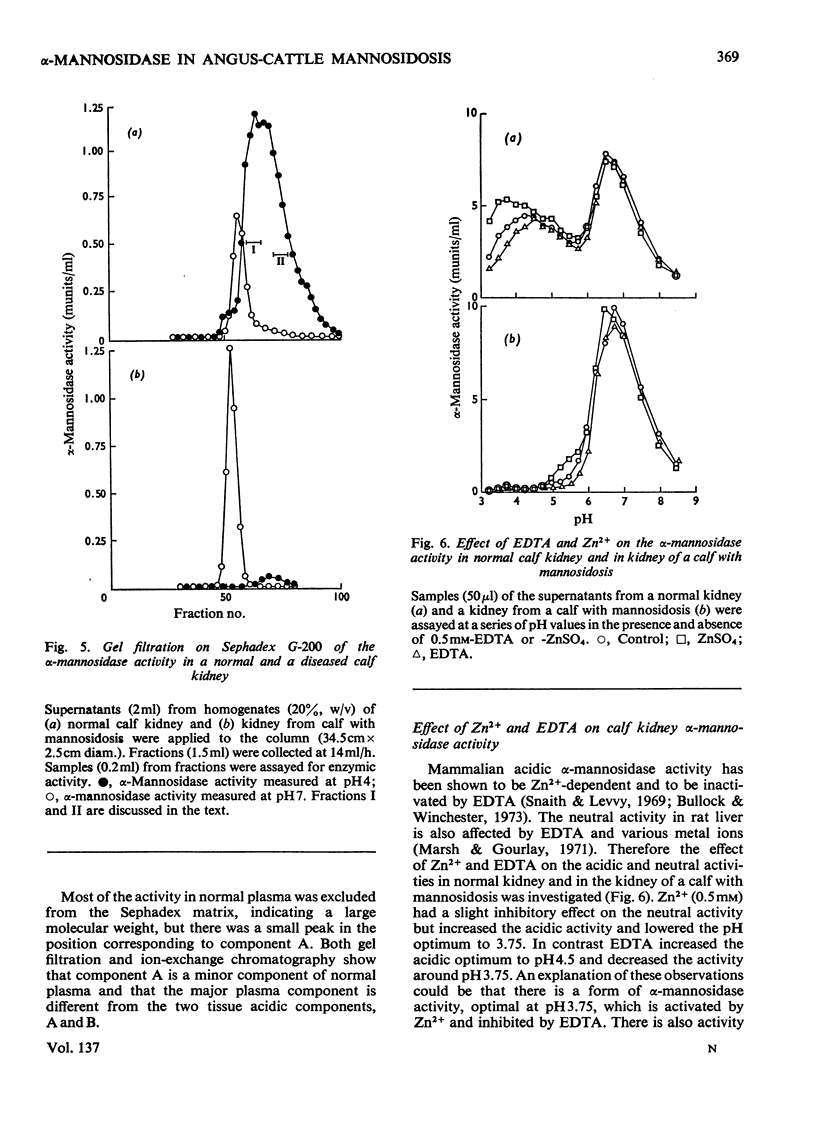
Normal calf α-mannosidase activity exists in at least three forms separable by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose and by starch-gel electrophoresis. Two components, A and B, have optimum activity between pH3.75 and 4.75, but component C has an optimum of pH6.6. Components A and B are virtually absent from the tissues of a calf with mannosidosis and the residual activity is due to component C. The acidic and neutral forms of α-mannosidase differ in their molecular weights and sensitivity to EDTA, Zn2+, Co2+ and Mn2+. An acidic α-mannosidase component (pH optimum 4.0) accounts for most of the activity in normal plasma but it is absent from the plasma of a calf with mannosidosis. Although the acidic α-mannosidase component is probably related to tissue components A and B, it can be distinguished from them by ion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration. The optimum pH of the low residual activity in the plasma from a calf with mannosidosis is pH5.5–5.75. The results support the hypothesis that Angus-cattle mannosidosis is a storage disease caused by a deficiency of lysosomal acidic α-mannosidase activity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CONCHIE J., MANN T. Glycosidases in mammalian sperm and seminal plasma. Nature. 1957 Jun 8;179(4571):1190–1191. doi: 10.1038/1791190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M., Dance N., Masson P. K., Robinson D., Winchester B. G. Human mannosidosis--the enzyme defect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):579–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois J. E., Mangeot M. Sur quelques caractéres de l'alpha-mannosidase du sérum. Son activation par les sels de cobalt. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1972;30(1):49–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G. INBORN LYSOSOMAL DISEASES. Gastroenterology. 1965 May;48:625–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking J. D., Jolly R. D., Batt R. D. Deficiency of alpha-mannosidase in Angus cattle. An inherited lysosomal storage disease. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):69–78. doi: 10.1042/bj1280069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultberg B. Properties of alpha-mannosidase in mannosidosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1970 Sep;26(2):155–159. doi: 10.3109/00365517009049228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly R. D. The pathology of the central nervous system in pseudolipidosis of Angus calves. J Pathol. 1971 Feb;103(2):113–121. doi: 10.1002/path.1711030206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellman B., Gamstorp I., Brun A., Ockerman P. A., Palmgren B. Mannosidosis: a clinical and histopathologic study. J Pediatr. 1969 Sep;75(3):366–373. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley T. J., Jevons F. R. Characterization of beef-liver glycosidases possibly involved in glycoprotein degradation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Nov;128(2):312–318. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh C. A., Gourlay G. C. Evidence for a non-lysosomal alpha-mannosidase in rat liver homogenates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 14;235(1):142–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors A., Harwalkar V. R. Glycosidases in bovine milk: alpha-mannosidase and its inhibition by zwitterions. Can J Biochem. 1968 Nov;46(11):1351–1356. doi: 10.1139/o68-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordén N. E., Lundblad A., Ockerman P. A., Jolly R. D. Mannosidosis in Angus cattle: partial characterization of two mannose containing oligosaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 15;35(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordén N. E., Lundblad A., Svensson S., Ockerman P. A., Autio S. A mannose-containing trisaccharide isolated from urines of three patients with mannosidosis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6210–6215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockerman P. A. Fluorimetric estimation of 4-methyl-umbelliferyl-alpha-mannosidase activity in blood plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Mar;23(3):479–482. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockerman P. A. Mannosidosis: isolation of oligosaccharide storage material from brain. J Pediatr. 1969 Sep;75(3):360–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenaru L., Dreyfus J. C. Electrophoretic heterogeneity of human -mannosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 23;303(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Price R. G., Dance N. Separation and properties of beta-galactosidase, beta-glucosidase, beta-glucuronidase and N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase from rat kidney. Biochem J. 1967 Feb;102(2):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1020525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaith S. M., Levvy G. A. Purification and properties of alpha-D-mannosidase from rat epididymis. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):25–33. doi: 10.1042/bj1140025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki I., Kushida H., Shida H. [Mammalian glycosidases. IV. Characterization of alpha-D-mannosidase, alpha-D-glucosidase and beta-D-galactosidase and other various glycosidase activities in organs of rabbits and cats]. Seikagaku. 1970 Jul;42(7):361–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


