Abstract
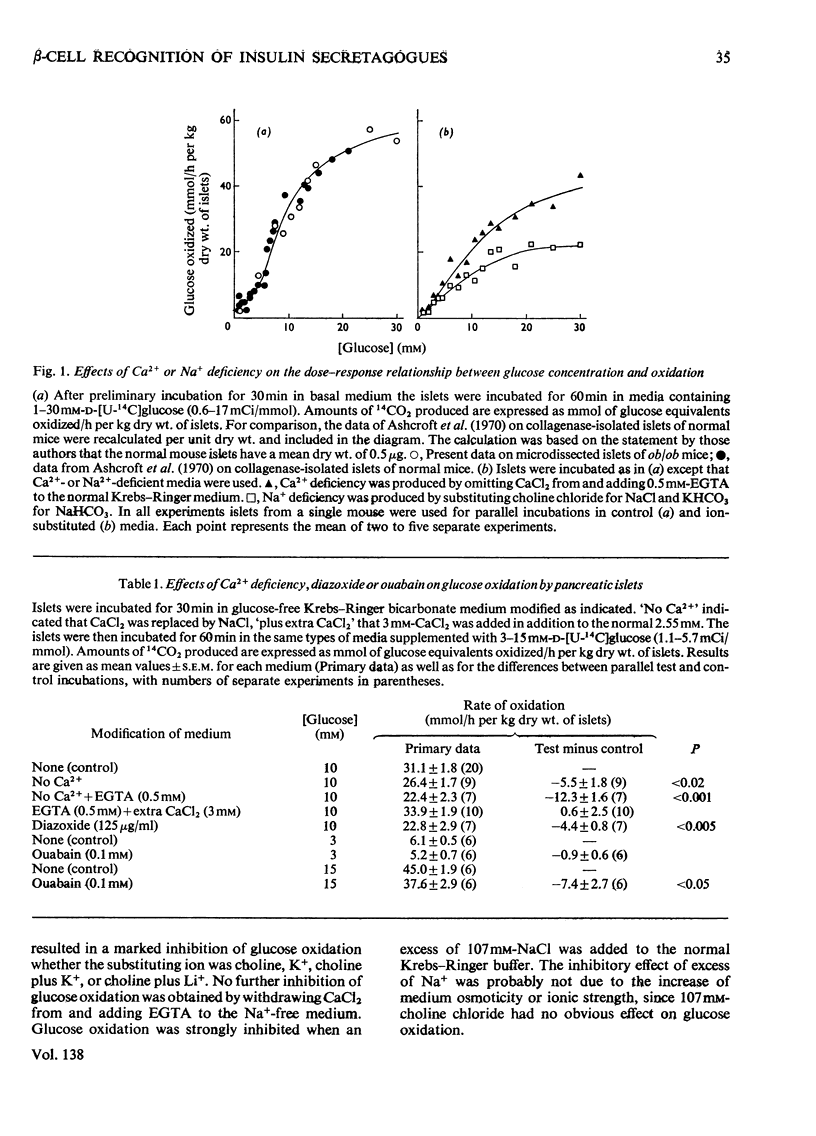
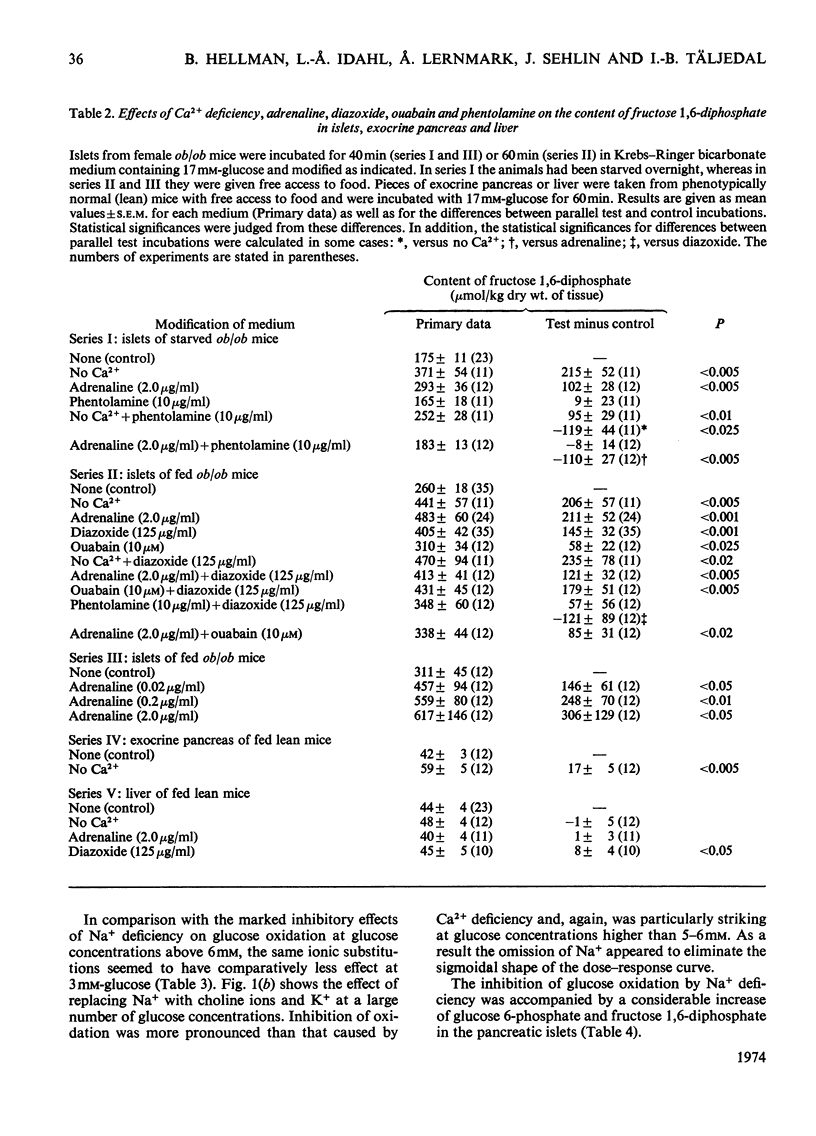
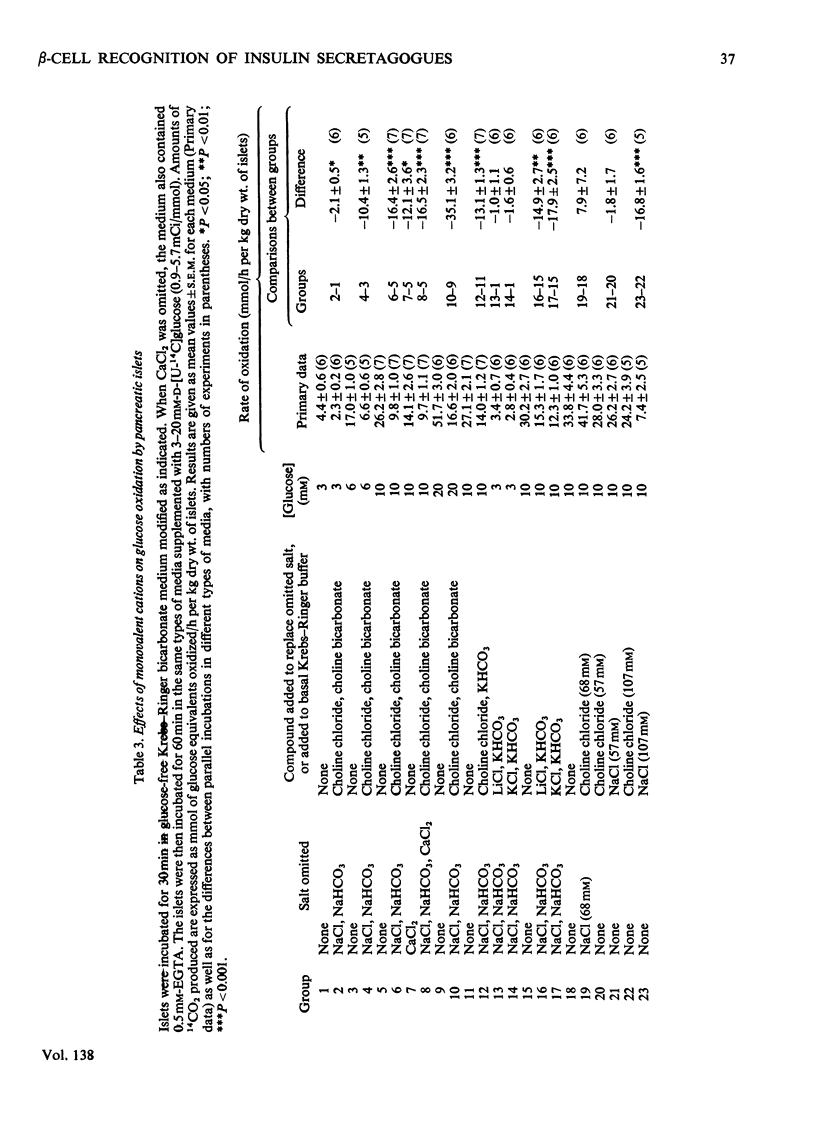
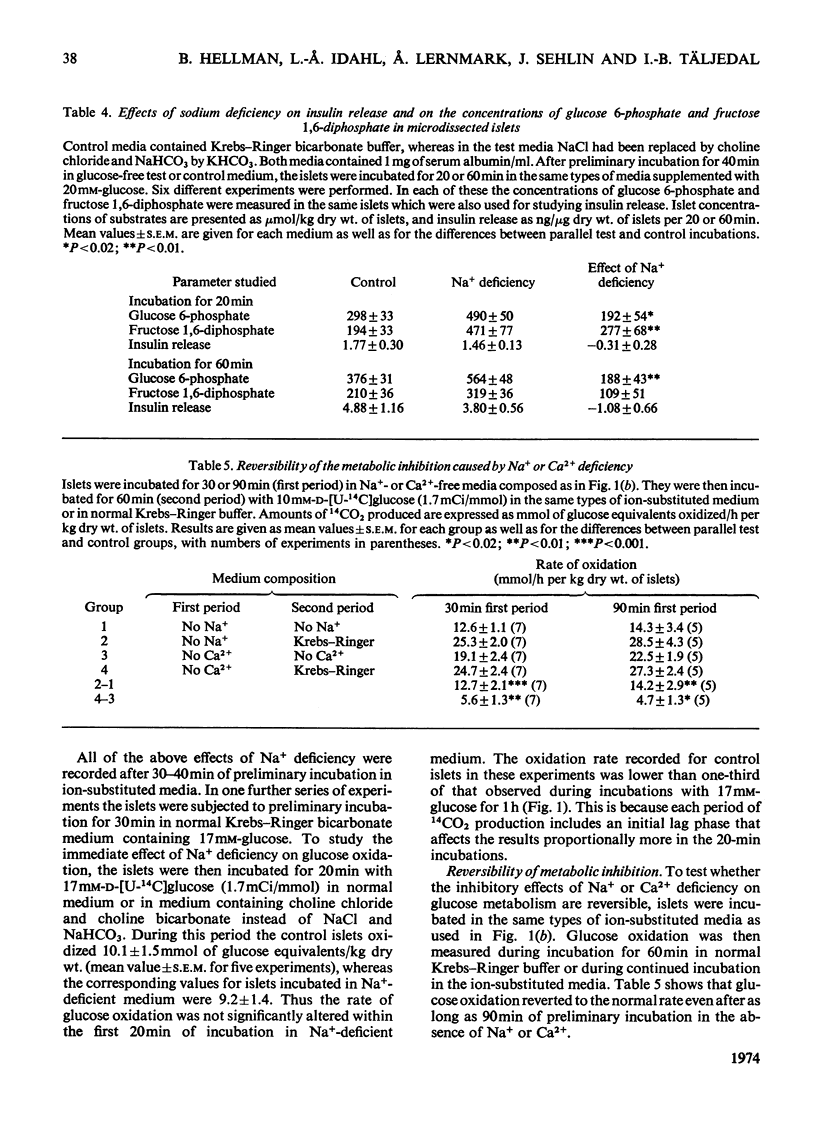
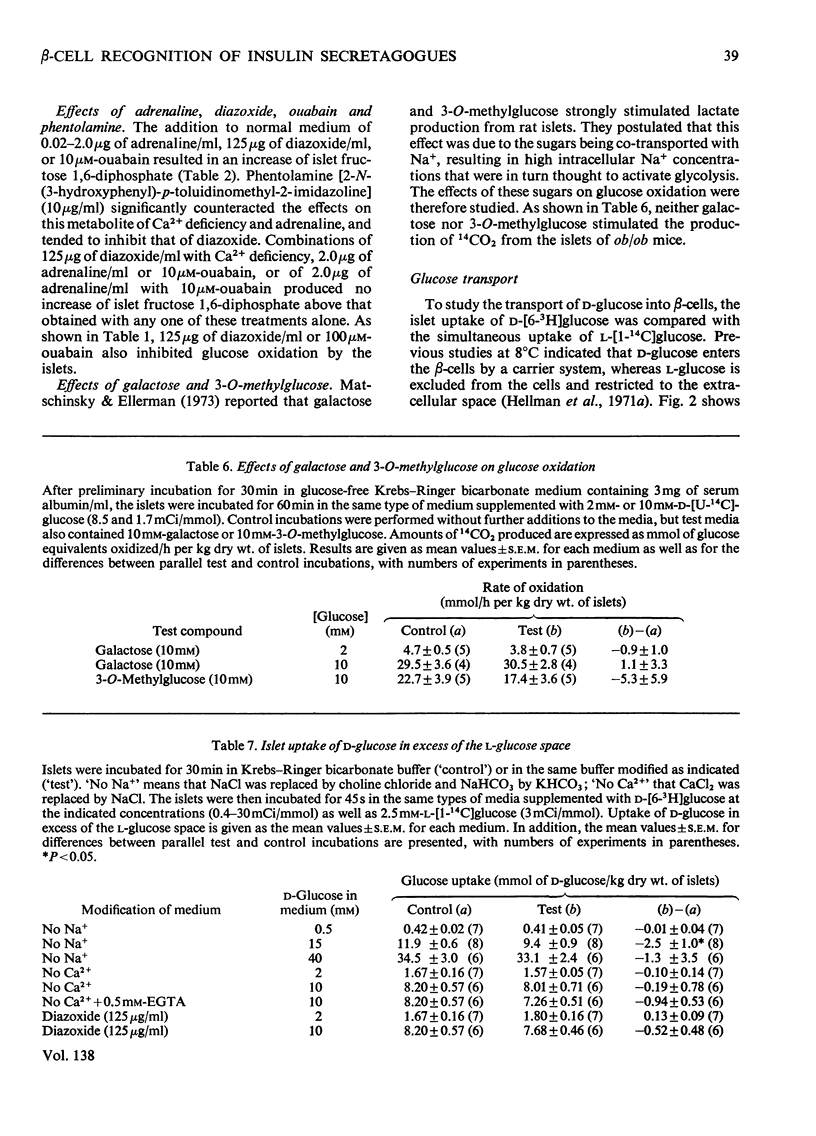
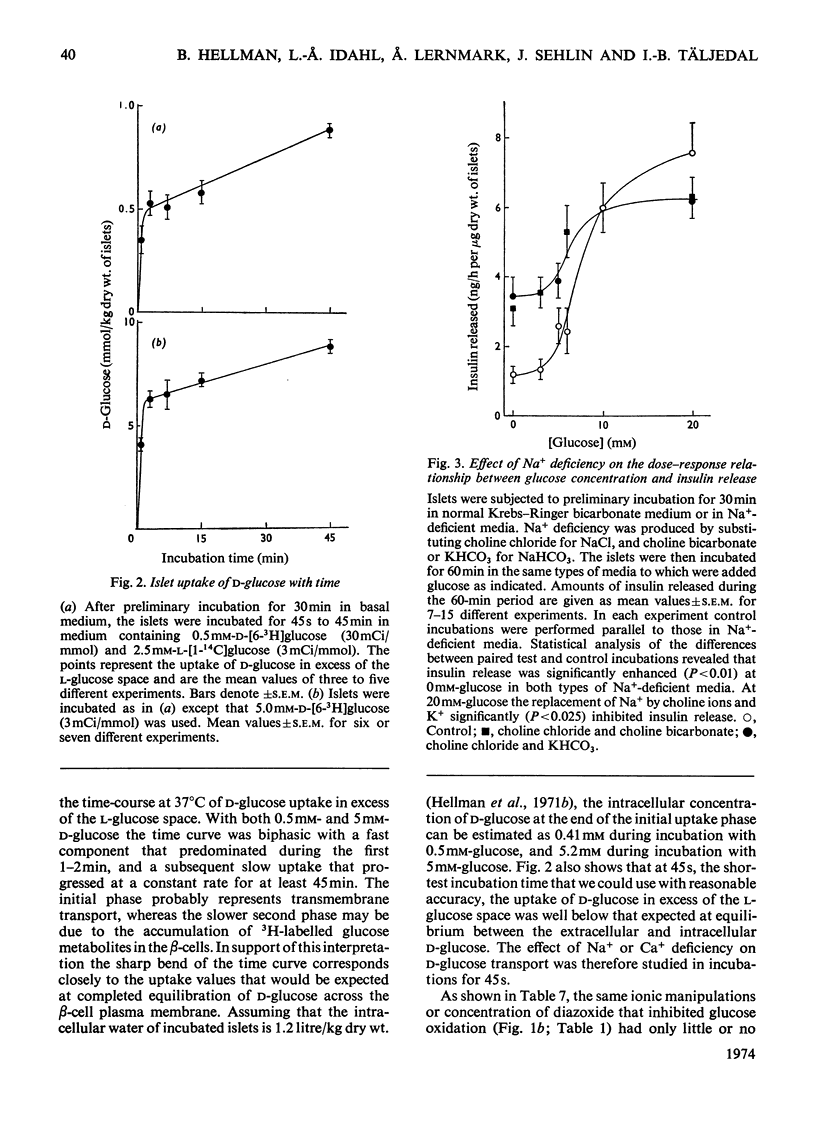
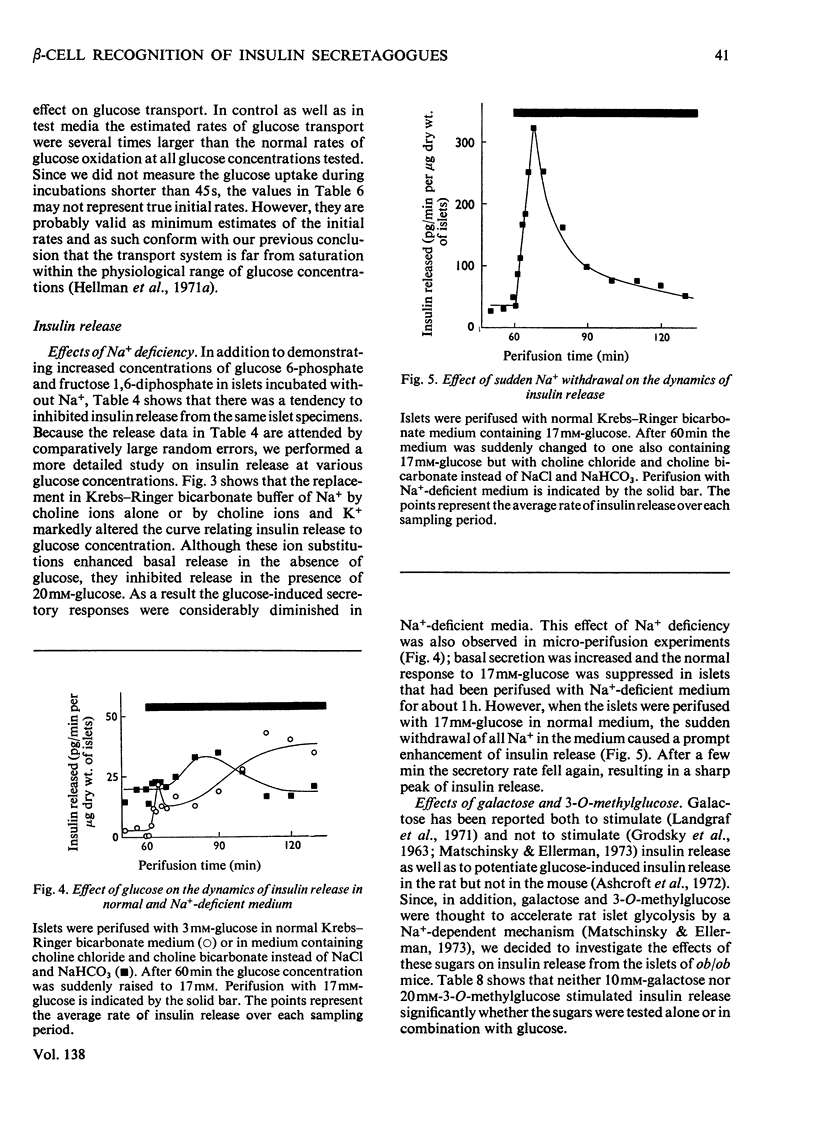
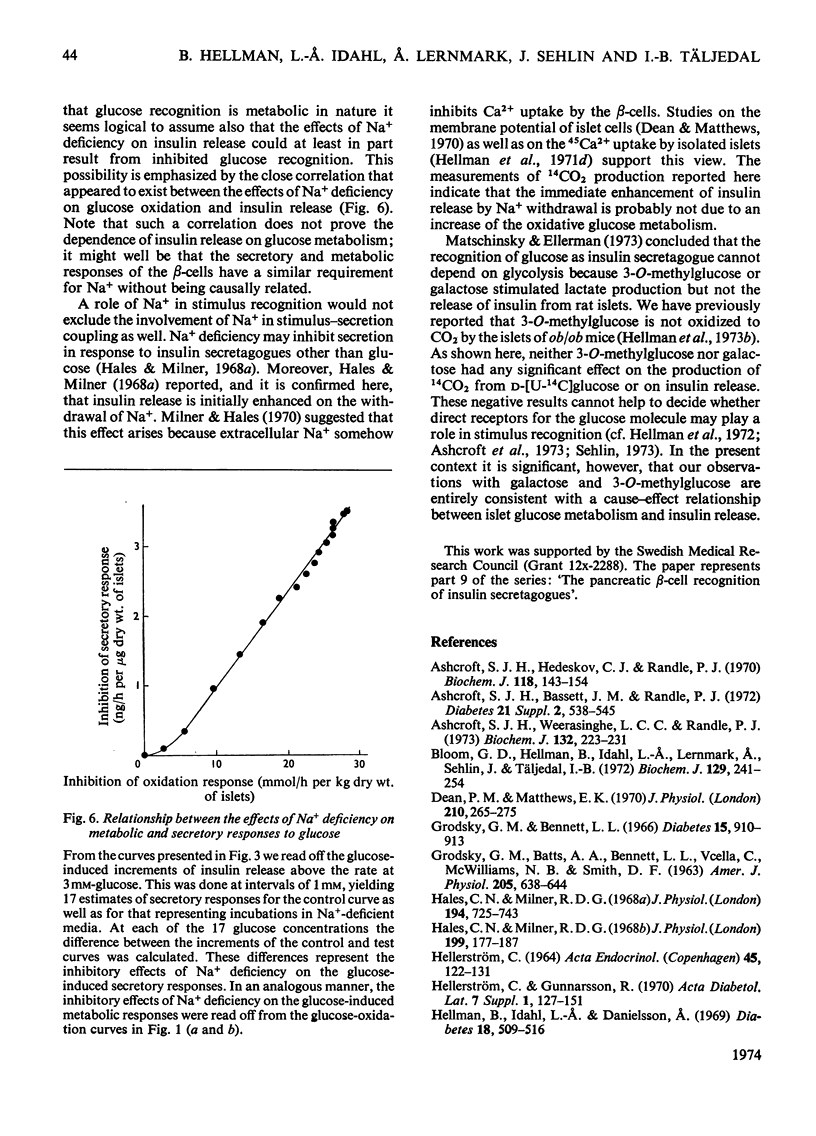
The transport and oxidation of glucose, the content of fructose 1,6-diphosphate, and the release of insulin were studied in microdissected pancreatic islets of ob/ob mice incubated in Krebs–Ringer bicarbonate medium. Under control conditions glucose oxidation and insulin release showed a similar dependence on glucose concentration with the steepest slope in the range 5–12mm. The omission of Ca2+, or the substitution of choline ions for Na+, or the addition of diazoxide had little if any effect on glucose transport. However, Ca2+ or Na+ deficiency as well as diazoxide (7-chloro-3-methyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide) or ouabain partially inhibited glucose oxidation. These alterations of medium composition also increased the islet content of fructose 1,6-diphosphate, as did the addition of adrenaline. Phentolamine [2-N-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-p-toluidinomethyl-2-imidazoline] counteracted the effects of adrenaline and Ca2+ deficiency on islet fructose 1,6-diphosphate. After equilibration in Na+-deficient medium, the islets exhibited an increase in basal insulin release whereas the secretory response to glucose was inhibited. The inhibitory effects of Na+ deficiency on the secretory responses to different concentrations of glucose correlated with those on 14CO2 production. When islets were incubated with 17mm-glucose, the sudden replacement of Na+ by choline ions resulted in a marked but transient stimulation of insulin release that was not accompanied by a demonstrable increase of glucose oxidation. Galactose and 3-O-methylglucose had no effect on glucose oxidation or on insulin release. The results are consistent with a metabolic model of the β-cell recognition of glucose as insulin secretagogue and with the assumption that Ca2+ or Na+ deficiency, or the addition of adrenaline or diazoxide, inhibit insulin release at some step distal to stimulus recognition. In addition the results suggest that these conditions create a partial metabolic block of glycolysis in the β-cells. Hence the interrelationship between the processes of stimulus recognition and insulin discharge may involve a positive feedback of secretion on glucose metabolism.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft S. J., Bassett J. M., Randle P. J. Insulin secretion mechanisms and glucose metabolism in isolated islets. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):538–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Hedeskov C. J., Randle P. J. Glucose metabolism in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):143–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1180143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Weerasinghe L. C., Randle P. J. Interrelationship of islet metabolism, adenosine triphosphate content and insulin release. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):223–231. doi: 10.1042/bj1320223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. D., Hellman B., Idahl L. A., Lernmark A., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effects of organic mercurials on mammalian pancreatic -cells. Insulin release, glucose transport, glucose oxidation, membrane permeability and ultrastructure. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(2):241–254. doi: 10.1042/bj1290241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells: effect of ions. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):265–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRODSKY G. M., BATTS A. A., BENNETT L. L., VCELLA C., MCWILLIAMS N. B., SMITH D. F. EFFECTS OF CARBOHYDRATES ON SECRETION OF INSULIN FROM ISOLATED RAT PANCREAS. Am J Physiol. 1963 Oct;205:638–644. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.4.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Bennett L. L. Cation requirements for insulin secretion in the isolated perfused pancreas. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):910–913. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Milner R. D. Cations and the secretion of insulin from rabbit pancreas in vitro. J Physiol. 1968 Nov;199(1):177–187. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Milner R. D. The role of sodium and potassium in insulin secretion from rabbit pancreas. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):725–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerström C., Gunnarsson R. [Bioenergetics of islet function: oxygen utilization and oxidative metabolism in the beta-cells]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1970 Sep;7 (Suppl 1):127–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Idahl L. A., Danielsson A. Adenosine triphosphate levels of mammalian pancreatic B cells after stimulation with glucose and hypoglycemic sulfonylureas. Diabetes. 1969 Aug;18(8):509–516. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.8.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Idahl L. A., Lernmark A., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Iodoacetamide-induced sensitization of the pancreatic beta-cells to glucose stimulation. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;132(4):775–789. doi: 10.1042/bj1320775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Lernmark A., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. The pancreatic -cell recognition of insulin secretagogues. V. Binding and stimulatory action of phlorizin. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Nov;8(6):759–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Calcium uptake by pancreatic -cells as measured with the aid of 45 Ca and mannitol- 3 H. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1795–1801. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effect of adrenaline on glucose oxidation by pancreatic beta-cells. Med Exp Int J Exp Med. 1969;19(6):351–356. doi: 10.1159/000137220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Evidence for mediated transport of glucose in mammalian pancreatic -cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 6;241(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Stereospecific glucose uptake by pancreatic -cells. Horm Metab Res. 1971 May;3(3):219–220. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1096775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Transport of -aminoisobutyric acid in mammalian pancretic -cells. Diabetologia. 1971 Aug;7(4):256–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01211878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Transport of 3-O-methyl-D-glucose into mammalian pancreatic -cells. Pflugers Arch. 1973;340(1):51–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00592196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idahl L. A. A micro perifusion device for pancreatic islets allowing concomitant recordings of intermediate metabolites and insulin release. Anal Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(2):386–398. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idahl L. A. Dynamics of pancreatic beta-cell responses to glucose. Diabetologia. 1973 Oct;9(5):403–412. doi: 10.1007/BF01239437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idahl L. A. Glucose-6-phosphate content in mammalian pancreatic beta-cells. Effects of various stimulators and inhibitors of insulin release. Hormones. 1971;2(6):371–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf R., Kotler-Brajtburg J., Matschinsky F. M. Kinetics of insulin release from the perfused rat pancreas caused by glucose, glucosamine, and galactose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):536–540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Hellman B. Effect of epinephrine and mannoheptulose on early and late phases of glucose-stimulated insulin release. Metabolism. 1970 Aug;19(8):614–618. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A. [Isolated mouse islets as a model for studying insulin release]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1971 Jul-Aug;8(4):649–679. doi: 10.1007/BF01550894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. 3. Uptake of 45 calcium by isolated islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1971 Jan;88(1):72–80. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Brisson G. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. II. Interaction of alkali and alkaline earth cations. Horm Metab Res. 1971 Mar;3(2):65–70. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Pipeleers D. G., Mahy M. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XII. Effects of diazoxide and gliclazide upon 45 calcium efflux from perifused islets. Diabetologia. 1973 Feb;9(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF01225992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M., Ellerman J. Dissociation of the insulin releasing and the metabolic functions of hexoses in islets of Langerhans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90826-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M., Passonneau J. V., Lowry O. H. Quantitative histochemical analysis of glycolytic intermediates and cofactors with an oil well technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Jan;16(1):29–39. doi: 10.1177/16.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. D., Hales C. N. The interaction of various inhibitors and stimuli of insulin release studied with rabbit pancreas in vitro. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):473–479. doi: 10.1042/bj1130473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin Janove. Effect of mannoheptulose on the dynamics of glucose oxidation in the pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 1973 Feb 15;30(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80615-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


