Abstract
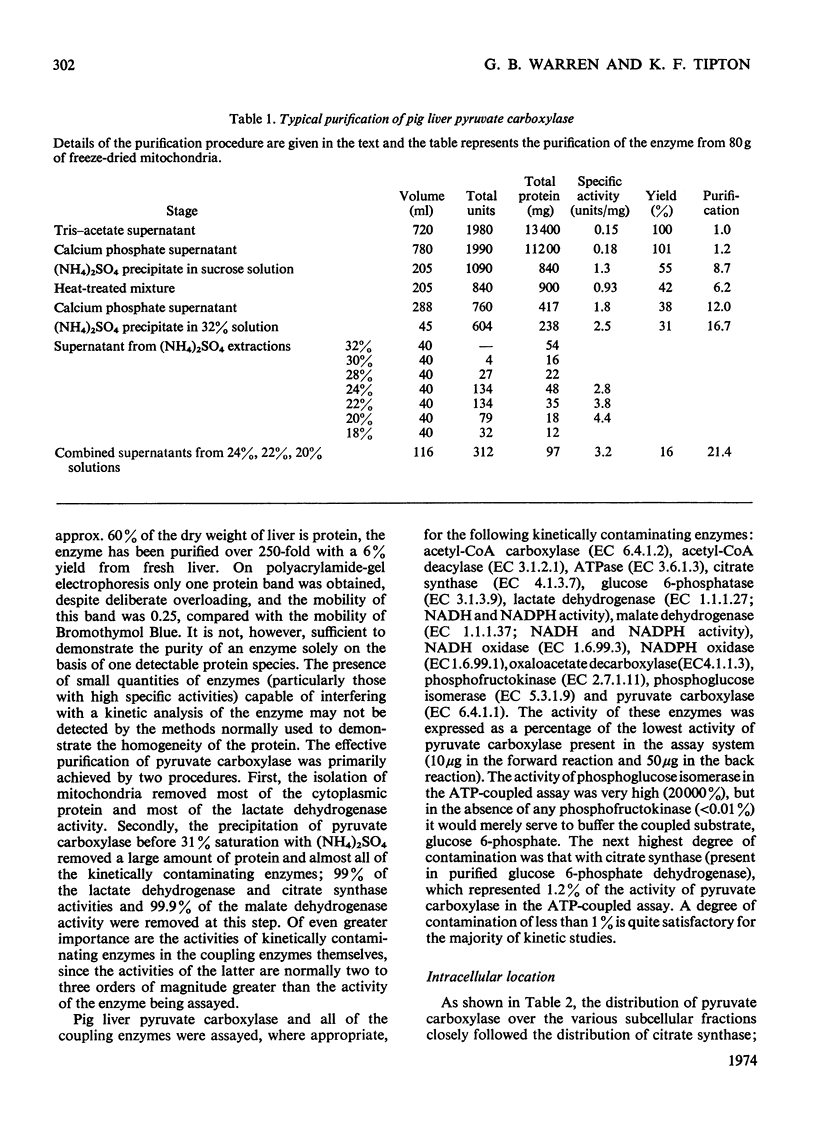
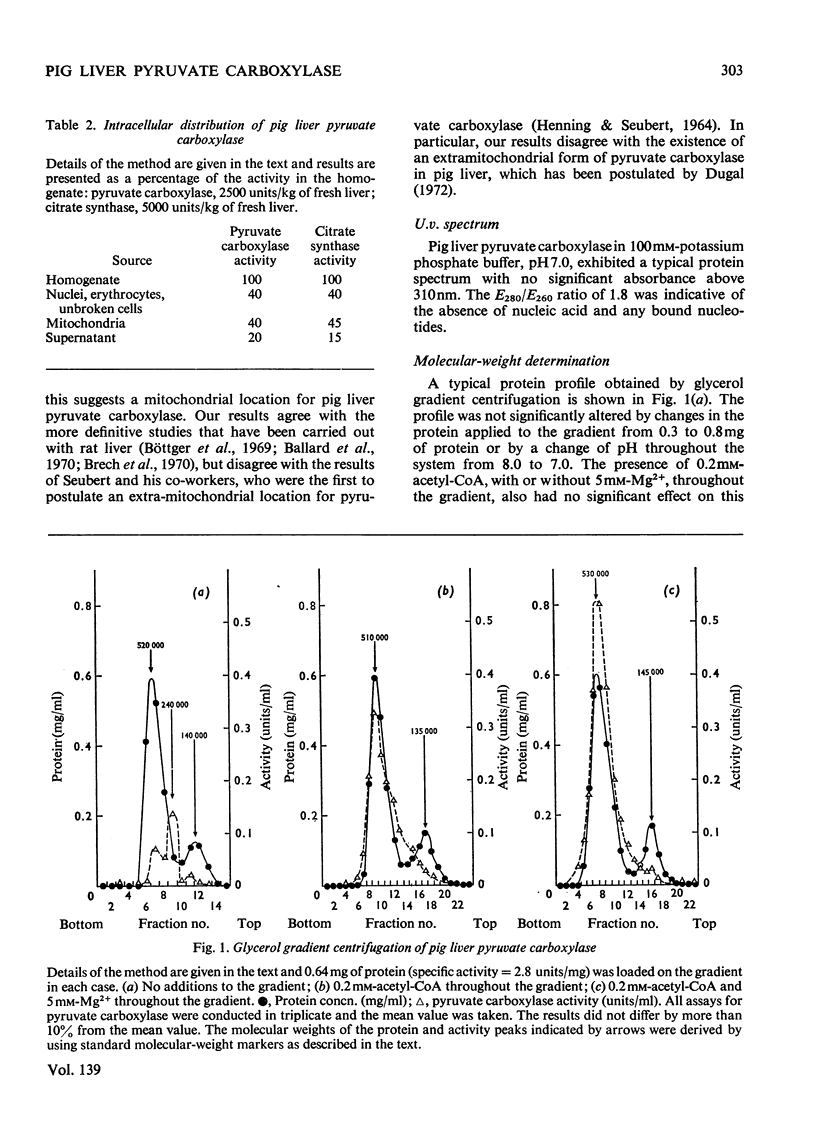
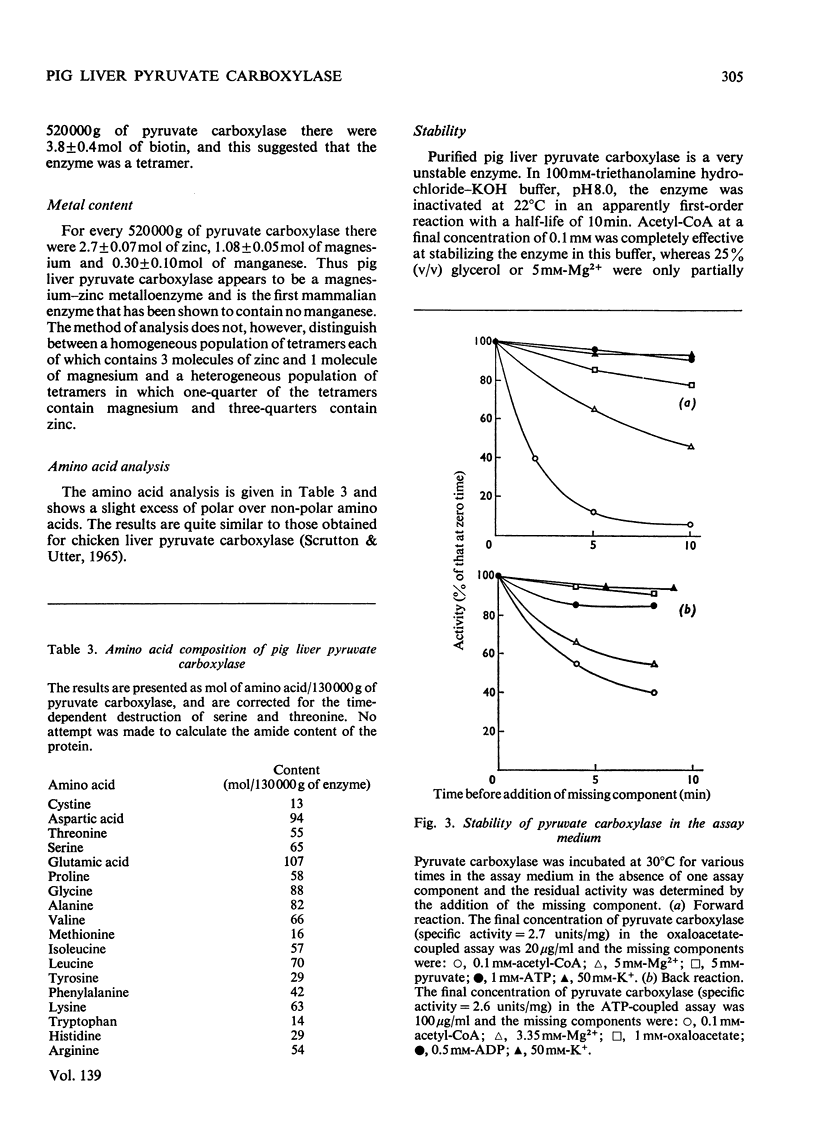
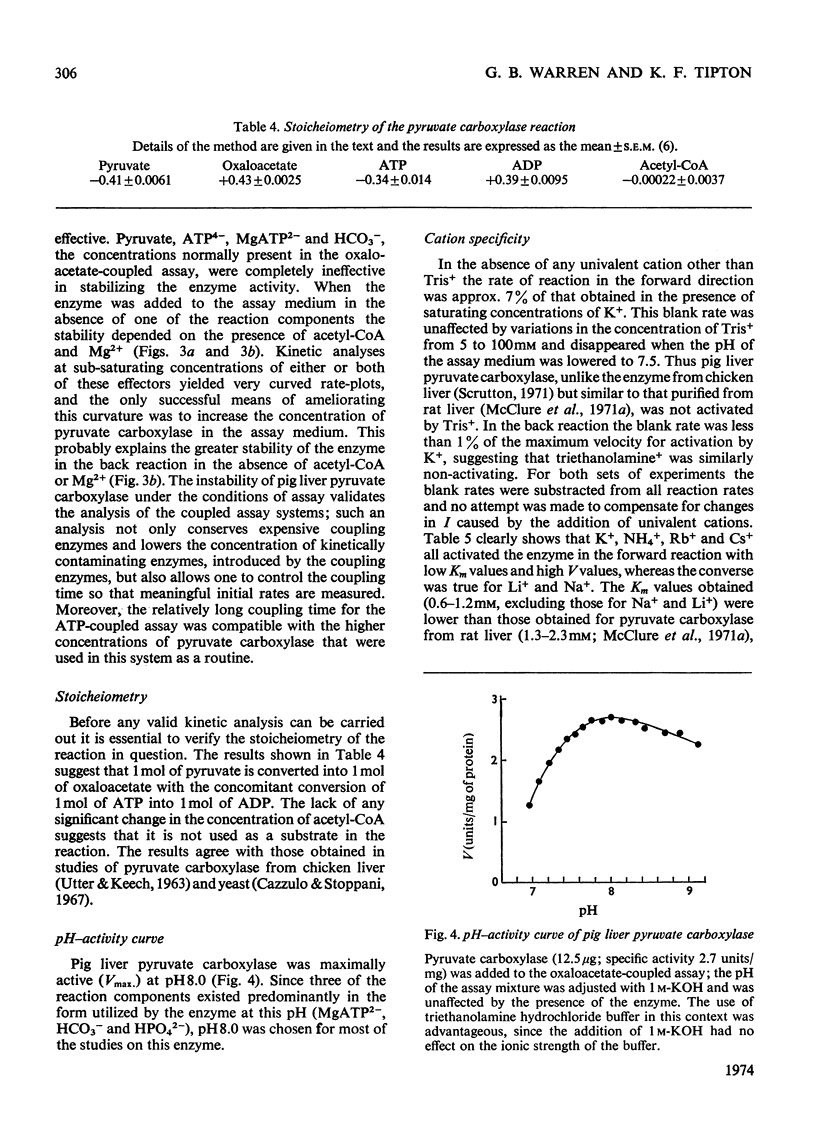
1. Pyruvate carboxylase was purified to apparent homogeneity from pig liver mitochondria and shown to be free of all kinetically contaminating enzymes. 2. The enzyme has a mol. wt. of 520000 and is composed of four subunits, each with a mol. wt. of 130000. 3. The enzyme can exist as the active tetramer, dimer and monomer, although the tetramer appears to be the form in which the enzyme is normally assayed. 4. For every 520000g of the enzyme there are 4mol of biotin, 3mol of zinc and 1mol of magnesium. No significant concentrations of manganese were detected. 5. Analysis by sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis indicates three polypeptide chains per monomer unit, each with a mol. wt. of 47000. 6. The amino acid analysis, stoicheiometry of the reaction and the activity of the enzyme as a function of pH are also presented. 7. The enzyme is activated by a variety of univalent cations but not by Tris+ or triethanolamine+. 8. The activity of the enzyme is dependent on the presence of acetyl-CoA; the low rate in the absence of added acetyl-CoA is not due to an enzyme-bound acyl-CoA. The dissociation constant for enzyme-bound acetyl-CoA is a marked function of pH.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of molecular size and molecular weights of biological compounds by gel filtration. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashman L. K., Keech D. B., Wallace J. C., Nielsen J. Sheep kidney pyruvate carboxylase. Studies on its activation by acetyl coenzyme A and characteristics of its acetyl coenzyme A independent reaction. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5818–5824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hanson R. W., Reshef L. Immunochemical studies with soluble and mitochondrial pyruvate carboxylase activities from rat tissues. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(4):735–742. doi: 10.1042/bj1190735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barden R. E., Fung C. H., Utter M. F., Scrutton M. C. Pyruvate carboxylase from chicken liver. Steady state kinetic studies indicate a "two-site" ping-pong mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1323–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brech W., Shrago E., Wilken D. Studies on pyruvate carboxylase in rat and human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 24;201(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90288-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger I., Wieland O., Brdiczka D., Pette D. Intracellular localization of pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(1):113–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAVEN G. R., STEERS E., Jr, ANFINSEN C. B. PURIFICATION, COMPOSITION, AND MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF THE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2468–2477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Stoppani A. O. Purification and properties of pyruvate carboxylase from baker's yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Sep;121(3):596–608. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. F. pH-dependence of carnitine acetyltransferase activity. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):503–509. doi: 10.1042/bj1040503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugal B. S. Determination of the distribution of pyruvate carboxylase in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 1;26(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80550-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Gluconeogenesis. Metabolism. 1972 Oct;21(10):945–990. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feir H. A., Suzuki I. Pyruvate carboxylase of Aspergillus niger: kinetic study of a biotin-containing carboxylase. Can J Biochem. 1969 Jul;47(7):697–710. doi: 10.1139/o69-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Toms E. J. Purification and crystallization of avidin. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):67–70. doi: 10.1042/bj1180067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNING H. V., SEUBERT W. ZUM MECHANISMUS DER GLUCONEOGENESE UND IHRER STEUERUNG. I. QUANTITATIVE BESTIMMUNG DER PYRUVATCARBOXYLASE IN ROHEXTRAKTEN DER RATTENLEBER. Biochem Z. 1964 Jul 29;340:160–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth J. A. Purification of yeast isocitrate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(5):1119–1124. doi: 10.1042/bj1291119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacker M. S., Ball E. G. Citrate cleavage in adipose tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):899–904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. A kinetic analysis of coupled enzyme assays. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2782–2786. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Lardy H. A., Kneifel H. P. Rat liver pyruvate carboxylase. I. Preparation, properties, and cation specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3569–3578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Lardy H. A., Wagner M., Cleland W. W. Rat liver pyruvate carboxylase. II. Kinetic studies of the forward reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3579–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Lane M. D. The biotin-dependent enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1971;35:321–442. doi: 10.1002/9780470122808.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOLTMANN E. A., GUBLER C. J., KUBY S. A. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (Zwischenferment). I. Isolation of the crystalline enzyme from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1225–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Gevers W. Control of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in liver and kidney cortex. Vitam Horm. 1967;25:1–87. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'SULLIVAN W. J., PERRIN D. D. THE STABILITY CONSTANTS OF METAL-ADENINE NUCLEOTIDE COMPLEXES. Biochemistry. 1964 Jan;3:18–26. doi: 10.1021/bi00889a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R. The molecular weight of the undegraded polypeptide chain of yeast hexokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 8;39(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90755-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognstad R., Katz J. The balance of pyridine nucleotides and ATP in adipose tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1148–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCRUTTON M. C., UTTER M. F. PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE. 3. SOME PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HIGHLY PURIFIED ENZYME. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton M. C., Griminger P., Wallace J. C. Pyruvate carboxylase. Bound metal content of the vertebrate liver enzyme as a function of diet and species. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3305–3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton M. C. Possible regulatory factors for pyruvate carboxylase with particular reference to enzyme from chicken liver. Metabolism. 1971 Feb;20(2):168–186. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton M. C., Utter M. F., Mildvan A. S. Pyruvate carboxylase. VI. The presence of tightly bound manganese. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3480–3487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton M. C., Utter M. F. Pyruvate carboxylase. IX. Some properties of the activation by certain acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1723–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton M. C., White M. D. Pyruvate carboxylase from rat liver: catalytic properties in the absence, and at low concentrations, of acetyl-CoA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90347-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton M. C., Young M. R., Utter M. F. Pyruvate carboxylase from baker's yeast. The presence of bound zinc. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):6220–6227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert D., Herlemann E. M., Albrecht E., Seubert W. On the mechanism of gluconeogenesis and its regulation. VII. Purification and properties of pyruvate carboxylase from rat liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Mar;352(3):459–478. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.1.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Barden R. E., Utter M. F. Identification of the reacting form of pyruvate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7383–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UTTER M. F., KEECH D. B. PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE. I. NATURE OF THE REACTION. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2603–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD W. A., GILFORD S. R. A system for automatic recording of absorbancy and its application to enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Anal Biochem. 1961 Dec;2:589–600. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(61)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Tipton K. F. Pig liver pyruvate carboxylase. The reaction pathway for the carboxylation of pyruvate. Biochem J. 1974 May;139(2):311–320. doi: 10.1042/bj1390311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


