Abstract
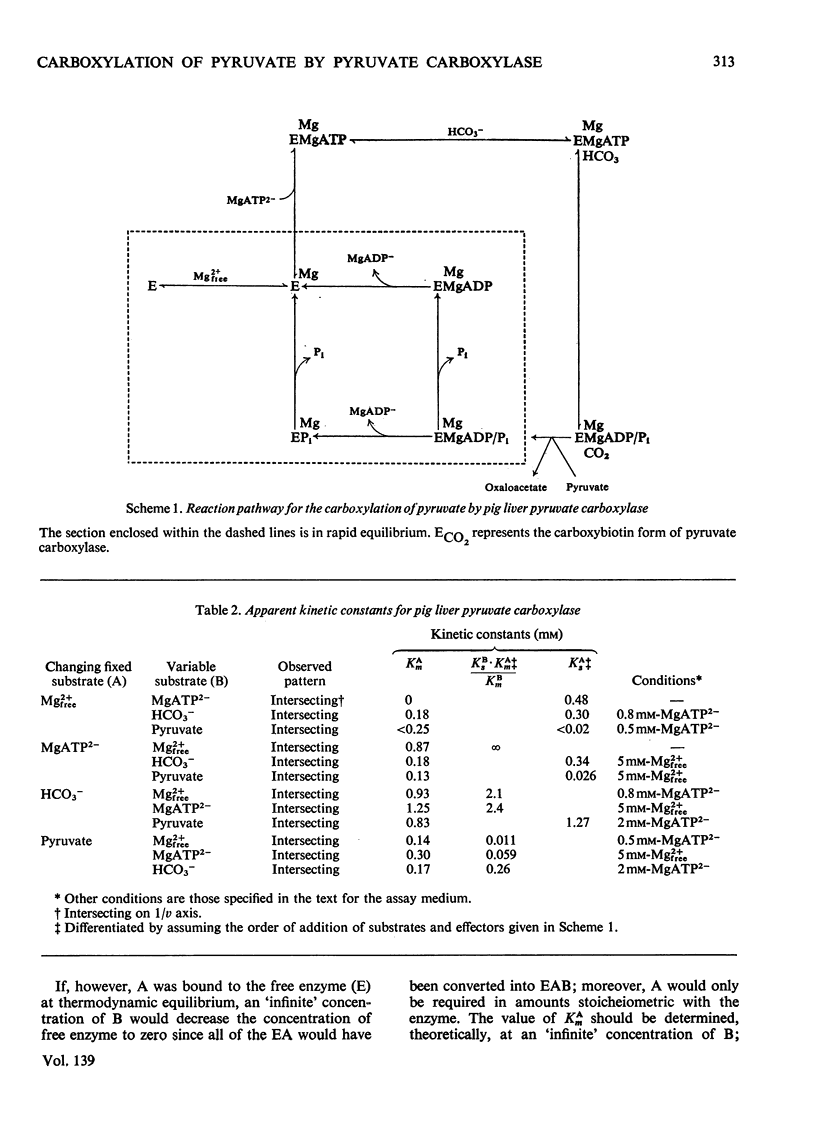
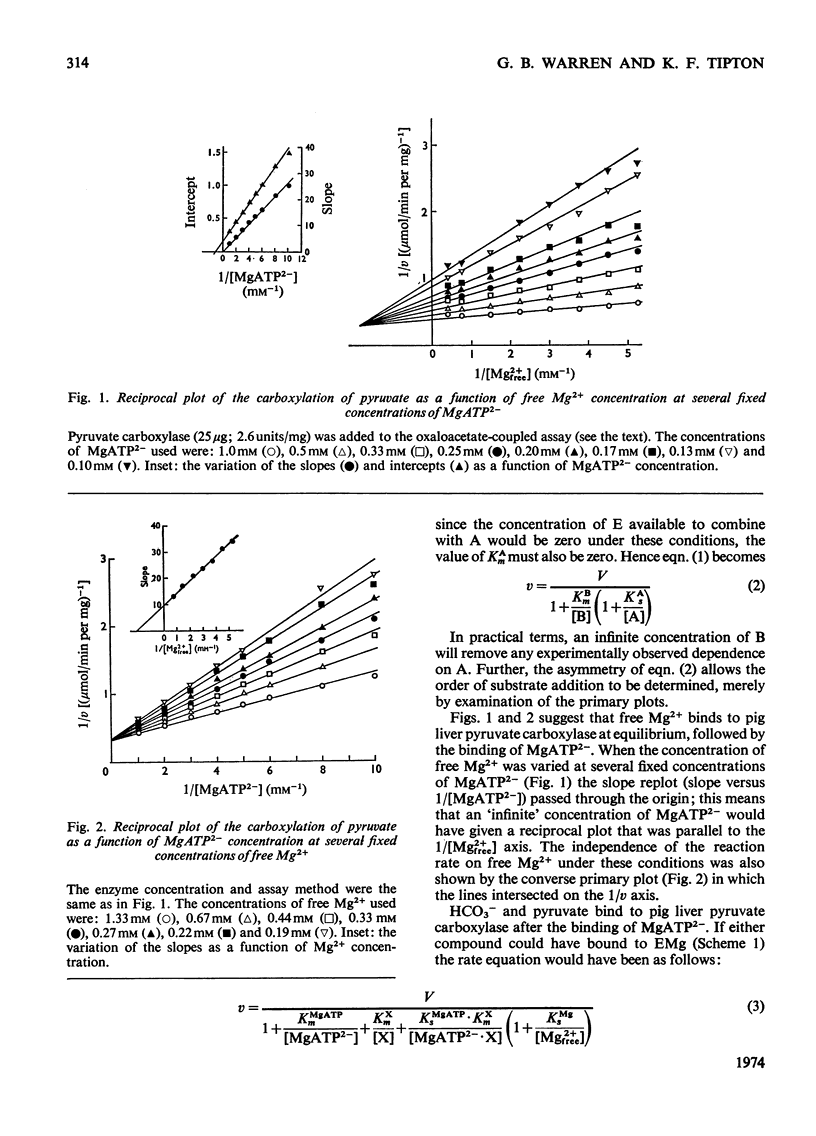
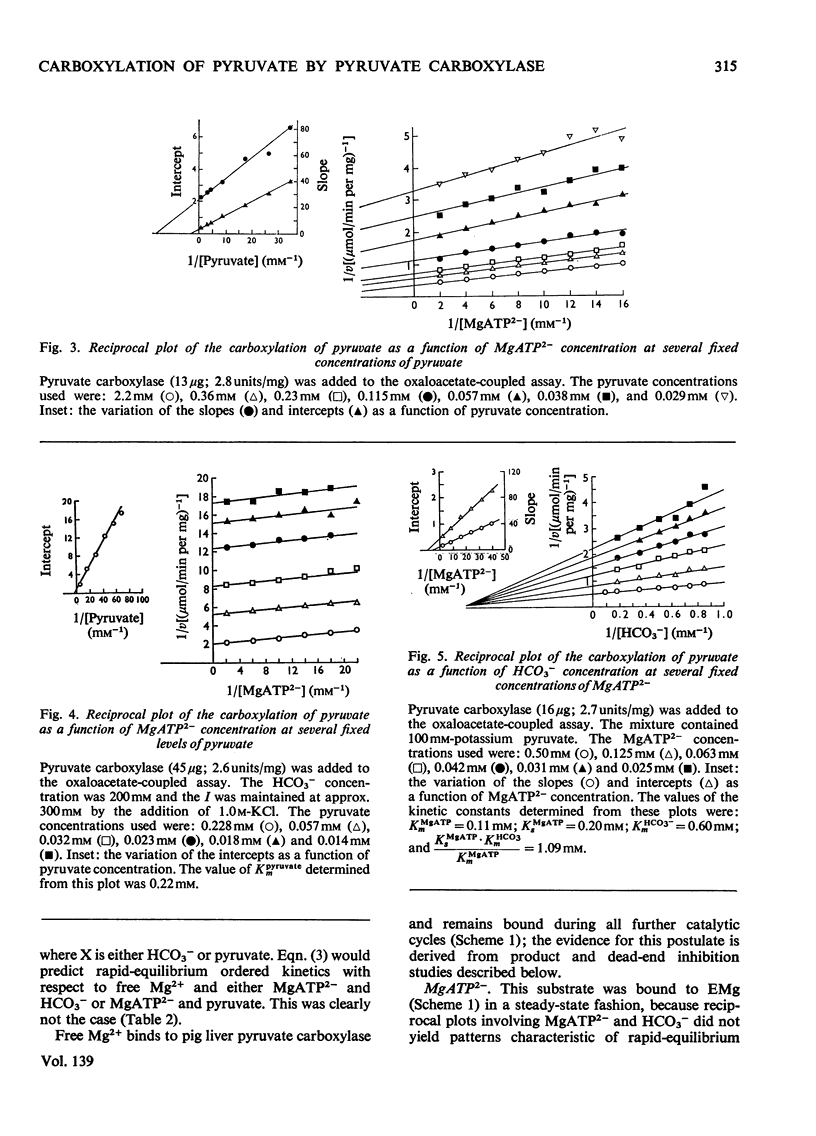
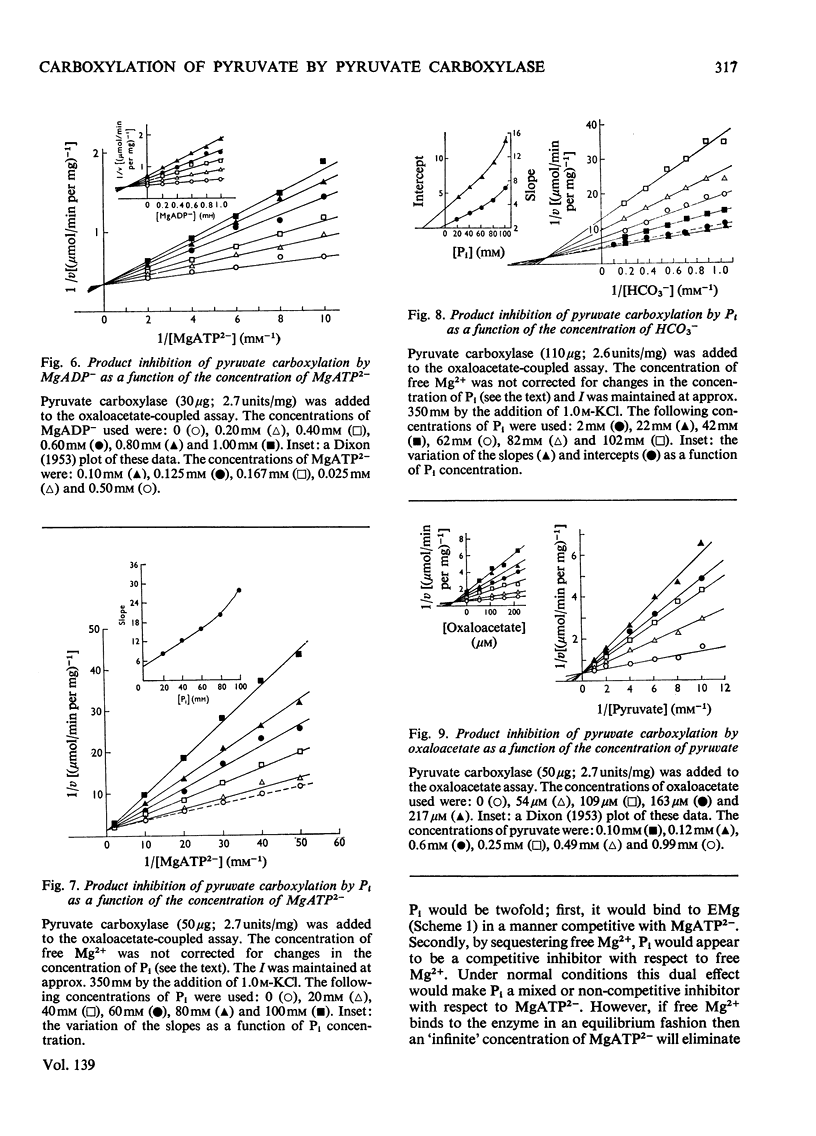
1. The reaction pathway for the carboxylation of pyruvate, catalysed by pig liver pyruvate carboxylase, was studied in the presence of saturating concentrations of K+ and acetyl-CoA. 2. Free Mg2+ binds to the enzyme in an equilibrium fashion and remains bound during all further catalytic cycles. MgATP2− binds next, followed by HCO3− and then pyruvate. Oxaloacetate is released before the random release, at equilibrium, of Pi and MgADP−. 3. This reaction pathway is compared with the double displacement (Ping Pong) mechanisms that have previously been described for pyruvate carboxylases from other sources. The reaction pathway proposed for the pig liver enzyme is superior in that it shows no kinetic inconsistencies and satisfactorily explains the low rate of the ATP[unk][32P]Pi equilibrium exchange reaction. 4. Values are presented for the stability constants of the magnesium complexes of ATP, ADP, acetyl-CoA, Pi, pyruvate and oxaloacetate.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. Formation constants for the complexes of adenosine di- or tri-phosphate with magnesium or calcium ions. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):388–395. doi: 10.1042/bj0710388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bais R., Keech B. The magnesium ion (Mg 2+ ) activation of sheep kidney pyruvate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3255–3261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barden R. E., Fung C. H., Utter M. F., Scrutton M. C. Pyruvate carboxylase from chicken liver. Steady state kinetic studies indicate a "two-site" ping-pong mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1323–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair J. M. A reinterpretation of the kinetics of pyruvate carboxylase. FEBS Lett. 1969 Feb;2(4):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Stoppani A. O. Effects of adenosine phosphates and nicotinamide nucleotides on pyruvate carboxylase from baker's yeast. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):755–762. doi: 10.1042/bj1120755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Stoppani A. O. Purification and properties of pyruvate carboxylase from baker's yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Sep;121(3):596–608. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Sundaram T. K., Kornberg H. L. Properties and regulation of pyruvate carboxylase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Oct 13;176(1042):1–19. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1970.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby R. G., Dennis D. T. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase from a higher plant. The requirement for free and metal-complexed isocitrate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3745–3750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLORINI J. R., VESTLING C. S. Graphical determination of the dissociation constants for two-substrate enzyme systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):575–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90529-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDEN C. Glutamic dehydrogenase. III. The order of substrate addition in the enzymatic reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2891–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feir H. A., Suzuki I. Pyruvate carboxylase of Aspergillus niger: kinetic study of a biotin-containing carboxylase. Can J Biochem. 1969 Jul;47(7):697–710. doi: 10.1139/o69-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEECH D. B., UTTER M. F. PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE. II. PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2609–2614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keech B., Barritt G. J. Allosteric activation of sheep kidney pyruvate carboxylase by the magnesium ion (Mg2+) and the magnesium adenosine triphosphate ion (MgATP2-). J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):1983–1987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELCHIOR N. C., MELCHIOR J. B. The role of complex metal ions in the yeast hexokinase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):609–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. A kinetic analysis of coupled enzyme assays. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2782–2786. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Lardy H. A., Cleland W. W. Rat liver pyruvate carboxylase. 3. Isotopic exchange studies of the first partial reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3584–3590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Lardy H. A., Kneifel H. P. Rat liver pyruvate carboxylase. I. Preparation, properties, and cation specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3569–3578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Lardy H. A., Wagner M., Cleland W. W. Rat liver pyruvate carboxylase. II. Kinetic studies of the forward reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3579–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mildvan A. S., Scrutton M. C. Pyruvate carboxylase. X. The demonstration of direct coordination of pyruvate and alpha-ketobutyrate by the bound manganese and the formation of enzyme-metal-substrate bridge complexes. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):2978–2994. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mildvan A. S., Scrutton M. C., Utter M. F. Pyruvate carboxylase. VII. A possible role for tightly bound manganese. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3488–3498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrop D. B. Transcarboxylase. VI. Kinetic analysis of the reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5808–5819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'SULLIVAN W. J., PERRIN D. D. THE STABILITY CONSTANTS OF METAL-ADENINE NUCLEOTIDE COMPLEXES. Biochemistry. 1964 Jan;3:18–26. doi: 10.1021/bi00889a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roger Phillips S. J. Adenosine and the adenine nucleotides. Ionization, metal complex formation, and conformation in solution. Chem Rev. 1966 Oct;66(5):501–527. doi: 10.1021/cr60243a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCRUTTON M. C., KEECH D. B., UTTER M. F. PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE. IV. PARTIAL REACTIONS AND THE LOCUS OF ACTIVATION BY ACETYL COENZYME A. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:574–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton M. C., Mildvan A. S. Pyruvate carboxylase: nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the enzyme-manganese-oxalacetate and enzyme-manganese-pyruvate bridge complexes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Sep;140(1):131–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert D., Herlemann E. M., Albrecht E., Seubert W. On the mechanism of gluconeogenesis and its regulation. VII. Purification and properties of pyruvate carboxylase from rat liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Mar;352(3):459–478. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.1.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H., Nielsen J., Keech D. B. Substrate activation of pyruvate carboxylase by pyruvate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Nov 20;37(5):723–728. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90951-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE S., TROSPER T., LYNN M., EVENSON L. THE MAGNESIUM BINDING CONSTANTS OF ADENOSINETRIPHOSPHATE AND SOME OTHER COMPOUNDS ESTIMATED BY THE USE OF FLUORESCENCE OF MAGNESIUM-8-HYDROXYQUINOLINE. J Biochem. 1963 Jul;54:17–24. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Tipton K. F. Pig liver pyruvate carboxylase. Purification, properties and cation specificity. Biochem J. 1974 May;139(2):297–310. doi: 10.1042/bj1390297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Tipton K. F. Pig liver pyruvate carboxylase. The reaction pathway for the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate. Biochem J. 1974 May;139(2):321–329. doi: 10.1042/bj1390321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


