Abstract
All-inside techniques are based on devices that use PEEK (polyether ether ketone) or biocomposite anchors placed at extracapsular locations such as anchorage points over which the sutures are tied. However, because of complications like irritability and intra-articular migration of these hard anchors, suture-based all-inside meniscal repair systems are now gaining popularity. Although these devices have advantages over conventional all-inside devices, they are costly, thus limiting their widespread use. The AJStitch meniscus repair system uses a specially designed spear to insert all-suture anchors, which can be made using a No. 5 Netbond and 2-0 Ultranet. This Technical Note describes the use of this system. It is an all-inside, all-suture meniscus repair system that provides a locally made, cost-effective option for posterior horn medial meniscus repair.
Technique Video
Arthroscopic meniscus repair can be achieved using the inside-out, outside-in, or all-inside techniques.1,2 Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages.3 All-inside techniques have gained popularity because of the possibility of repairing posterior horns, whereas outside-in and inside-out repair may be challenging. One of the major problems of these all-inside meniscus repair systems is implant-related complications like irritation and implant migration.4,5
All-suture meniscus repair systems are gaining popularity, as they eliminate these problems.6, 7, 8 They are claimed to have the same strength and fewer complications.7 However, these systems are costly, restricting their broader use. This Technical Note presents a technique for meniscus repair using the AJStitch Meniscal Repair System (Biotek, Ahmedabad, India) that provides a cost-effective and arthroscopic all-inside, all-suture meniscus repair (Video 1).
Surgical Technique (Medial Meniscus Repair)
An Institutional Review Committee approval waiver was obtained from the B&B Hospital Institutional Review Committee.
Positioning and Diagnostic Arthroscopy
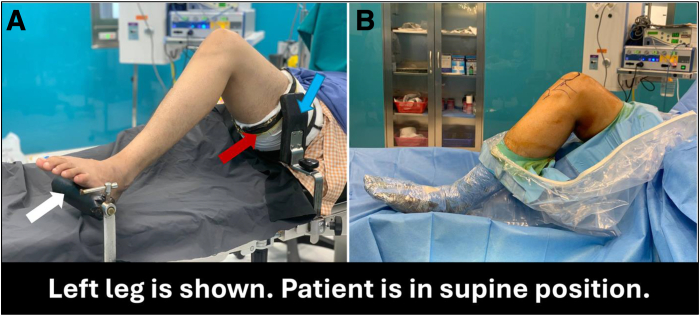
The patient is situated supine on a standard operating table with the hip flexed at 45° and the knee flexed at 90°. The thigh is supported by a lateral post, and the foot is supported by a foot roll (Fig 1). A pneumatic tourniquet is applied to the proximal thigh. Diagnostic arthroscopy is performed through standard anterolateral and anteromedial portals.
Fig 1.
Patient positioning with affected left knee. (A) The patient is positioned supine on the operating table with a tourniquet (red arrow) applied to the proximal thigh. The thigh is supported by a lateral post (blue arrow), and the foot rests in the foot holder (white arrow). (B) Position after painting and draping with a waterproof sterile drape.
Materials Required for Meniscus Repair
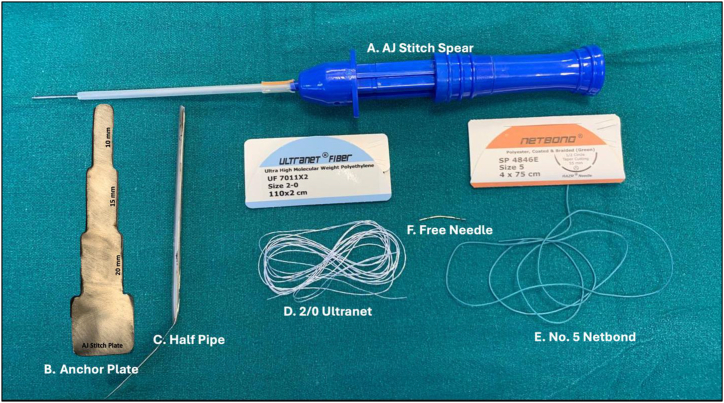
The implants and instruments required for this technique are as follows (Fig 2):
-
1.
AJStitch spear
-
2.
Anchor plate
-
3.
Half-pipe
-
4.
Ultranet No. 2-0 (ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene)
-
5.
Netbond No. 5 (braided polyester; Suture Planet, Bangalore, Karnataka)
-
6.
Free straight needle
Fig 2.
Materials required for this technique. (A) AJStitch pear. (B) Anchor plate. (C) Half-pipe. (D) 2/0 Ultranet Fiber (ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene) suture. (E) No. 5 Netbond (braided polyester). (F) Free needle.
In addition to these materials, a knot pusher and a small cord cutter are also required for this technique.
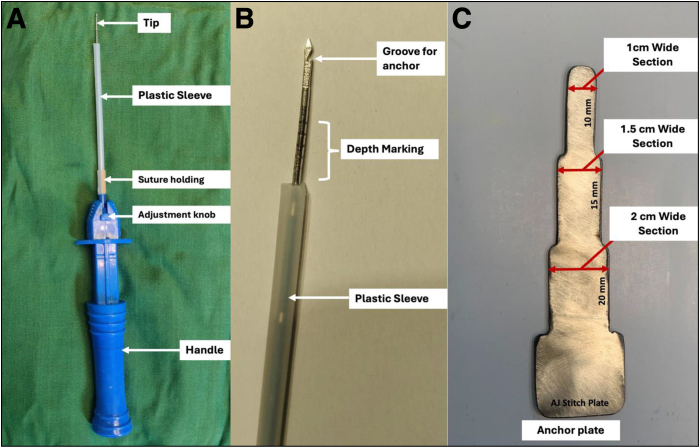
The spear is a specially designed instrument by Biotek (Fig 3). It is a solid metallic rod with a tip diameter of 1.5 mm. It is covered with a rigid plastic tube that is connected to the adjustment knob. This plastic tube works as a stopper, and the depth of the piercing portion of the spear can be adjusted by altering the length of the plastic tube by pushing or pulling the adjustment knob (Fig 3A). The tip has a groove for engaging the prepared all-suture anchor (Fig 3B). There is a graduated marking to guide the depth of the piercing.
Fig 3.
AJStitch spear (Biotek) and anchor plate. (A) Picture of the spear tip showing all the parts. (B) Inset view of the spear tip showing groove for anchor (nesting place for anchor), depth marking, and plastic sleeve which acts as a stopper. (C) Anchor plate with sections of various widths.
Anchor Plate
A specially designed stainless-steel plate with 3 sections of varying widths is used. These sections ensure the adequate size of the Netbond segment when a loop is tied and cut. Alternatively, a sterile scale can be used to cut segments of Netbond.
Creating an All-Suture All-Inside Meniscus Anchor
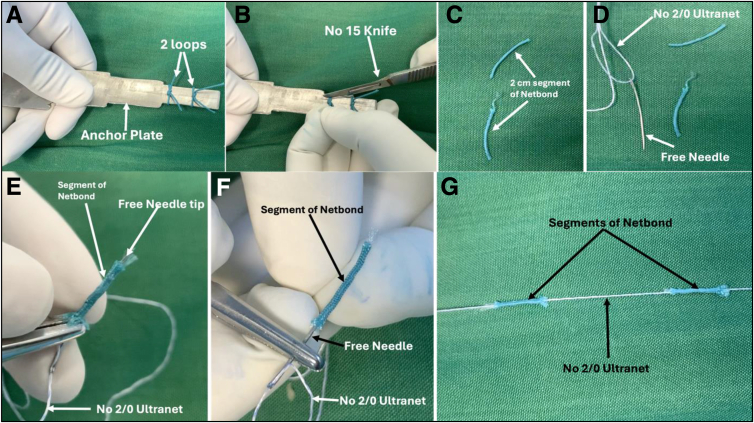
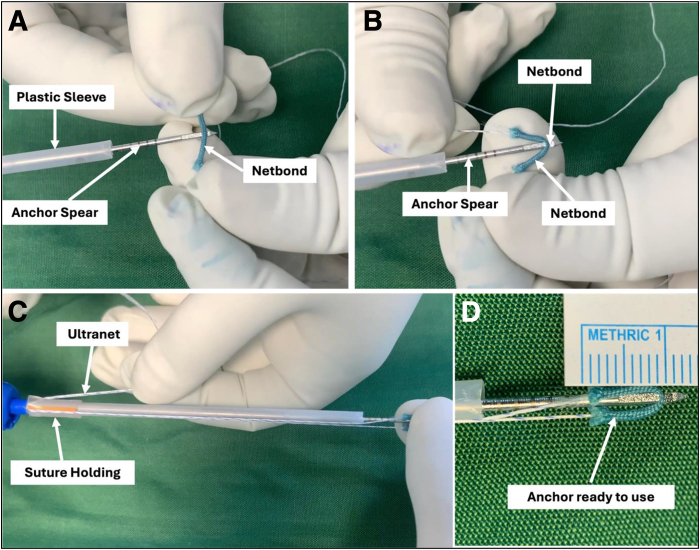
A No. 5 Netbond is taken, and 2 loops are made in the anchor plate’s 1-cm-wide section (Fig 4A). The loop is now cut next to the knot on either side of both loops (Fig 4B). This will leave 2 segments of Netbond that are 2 cm long (Fig 4C), and when they are doubled while making the anchor, the total length of the anchor will not be more than 1 cm. Take a straight free needle, and a 2-0 Ultranet fiber is passed through the eyelet (Fig 4D). Take the segment of Netbond prepared previously and pass the needle loaded with Ultranet from one end of the segment to the other through the core of the suture (Fig 4E). The exact process is repeated with another segment of Netbond to pass the Ultranet through the Netbond (Fig 4F). The final configuration is shown in Figure 4G. The segments of Netbond will act as an anchor and the Ultranet as a repairing suture.
Fig 4.
Steps for making all-suture anchors. (A) Two loops are tied with 2 simple surgical knots at the 1-cm-wide section of the anchor plate. (B) The loops are cut next to the knot to ensure a total length of less than 2 cm. (C) Two segments of 2-cm-long Netbond. (D) A 2/0 Ultranet is passed through the eyelet of the free needle. (E) The needle and suture are passed through the first segment of No. 5 Netbond. (F) The needle and suture are passed through the second segment of No. 5 Netbond. (G) A prepared all-suture anchor in which 2/0 Ultranet is passed through 2 segments of 2-cm-long No. 5 Netbond. The Netbond segments will work as all-suture anchors, and the Ultranet is used to repair the meniscal tear.
Loading the Anchor in the Spear
One segment of Netbond is engaged at the center into the anchor groove at the tip (Fig 5 A and B). Now, the Ultranet fiber tails are pulled and looped around the suture holding tube (Fig 5C) so the limbs are taught, and the anchor is securely placed into the groove. The anchor is ready to be deployed for repair (Fig 5D).
Fig 5.
Loading of the anchor into the spear. (A) The Netbond segment is loaded to the anchor groove at the tip of the spear. (B) The Netbond segment is loaded at the center, making both the limbs of the anchor equal (1 cm). (C) Both the limbs of Ultranet are brought to the suture holding post and engaged, keeping the suture tight. (D) Spear tip with a loaded anchor is shown. Note that the anchor length of about 1 cm.
Meniscal Lesion Preparation
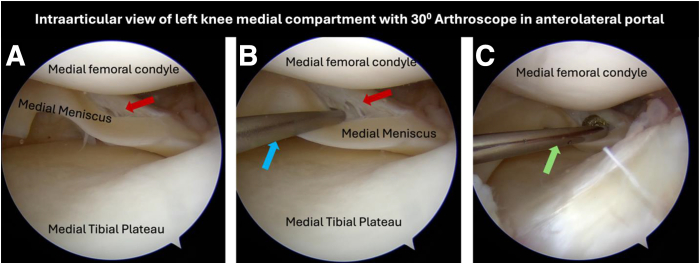
The meniscus is inspected after pie crusting of the medial collateral ligament (Fig 6A) and probed to ensure repairability of the meniscus (Fig 6B). The vascularity at the tear site is improved by abrading the torn edges with a diamond rasp (Fig 6C). The femoral tunnel is made before meniscal repair if there is an associated anterior cruciate ligament tear.
Fig 6.
The medial compartment of the left knee is visualized through a 30° arthroscope in the anterolateral portal after pie crusting of the deep medial collateral ligament. (A) Longitudinal tear (red arrow) of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus. (B) The tear (red arrow) is examined using an arthroscopy probe (blue arrow) to evaluate the repairability of the meniscus. (C) Abrading the tear edge using a diamond rasp (green arrow) to enhance healing.
Passage of the First Anchor of the First Stitch
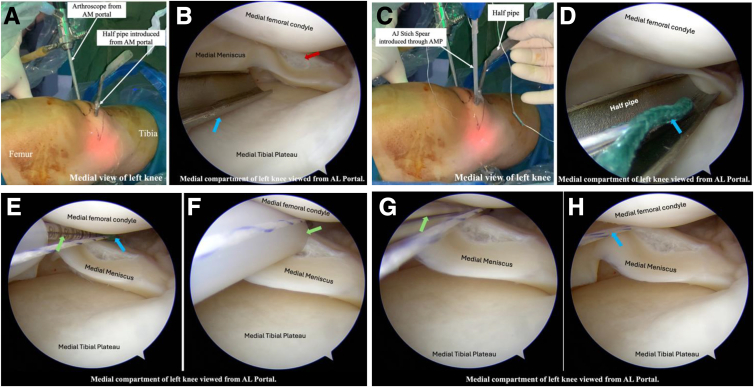
A 30° arthroscope is inserted through the anterolateral portal. The piercing depth of the spear is adjusted to 16 mm. A half-pipe is introduced from the anteromedial portal (Fig 7 A and B). The spear loaded with a single anchor is introduced by sliding along the half-pipe (Fig 7C). The half-pipe is removed once the anchor is intra-articular (Fig 7D). The spear’s tip is now directed toward the capsule above the meniscus (Fig 7E). With a gentle twisting movement, the capsule is pierced to the desired depth (Fig 7F). The suture tails are disengaged from the suture-holding sleeve, and the spear is removed (Fig 7G). Finally, both the suture limbs are pulled to deploy the anchor (Fig 7H).
Fig 7.
Passage of the first anchor of the first stitch. (A) Outside view of medial aspect of the left knee showing arthroscope in the anterolateral portal and a half-pipe is introduced through the anteromedial portal. (B) Arthroscopic view of medial compartment showing meniscal tear (red arrow) and half-pipe (blue arrow). (C) Outside view of the left knee; the spear is inserted along the half-pipe through the anteromedial portal. (D) Arthroscopy view of the medial compartment of the left knee showing the half-pipe and the spear with the anchor (blue arrow) coming along the half-pipe. (E) The spear (blue arrow) is directed toward the capsule above the meniscus. The green arrow indicates the graduation of depth. (F) The spear is inserted up to the desired depth, and the plastic tube (green arrow) acts as a stopper. (G) The spear (green arrow) is removed after deploying the first anchor. (H) Sutures (blue arrow) are pulled to deploy the anchor and confirm the pullout strength.
Passage of the Second Anchor of the First Stitch
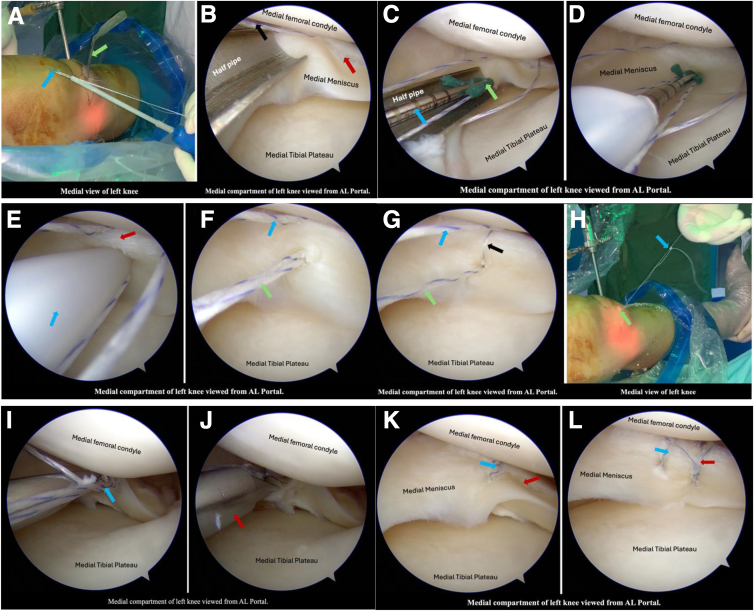
The piercing depth of the spear is adjusted to 20 mm by moving the adjustment knob of the spear. Another anchor from the same stitch is now loaded to the spear (Fig 8A). A half-pipe is introduced from the anteromedial portal (Fig 8B). The spear loaded with the second anchor is introduced by sliding along the half-pipe (Fig 8C). Once the anchor is intra-articular, the half-pipe is removed. The spear’s tip is directed toward the meniscus across the tear (Fig 8D). With a gentle twisting movement, the meniscus is pierced to the desired depth (Fig 8E).
Fig 8.
Passage of the second anchor of the first stitch. (A) The second anchor (blue arrow) is loaded into the spear. The half-pipe (green arrow) is in the anteromedial portal. (B) Arthroscopic view of medial compartment of left knee with half-pipe. The tear (red arrow) and sutures from the first anchor (black arrow) can also be seen. (C) The spear (blue arrow) with the second anchor (green arrow) is inserted along the half-pipe into the medial compartment of the knee joint. (D) The second anchor is inserted through the meniscus. (E) The spear is inserted up to the desired depth (20 mm), and the plastic tube (blue arrow) acts as a stopper. Red arrow depicts the tear. (F) The sutures from the first anchor (blue arrow) and second anchor (green arrow). (G) The first loop of the suture (black arrow) across the tear repairs the meniscus. (H) Outside picture of the left knee; both the suture limbs are in the anteromedial portal (green arrow). A Samsung Medical Center knot (blue arrow) is made. (I) The knot (blue arrow) is delivered inside the joint and secured by pass-pointing with a knot pusher. (J) The sutures are cut using a cord cutter (red arrow). (K) Arthroscopic view of medial compartment of left knee depicting the tear (red arrow) and suture (blue arrow) of the first stitch. (L) The final picture of the medial meniscus shows 2 stitches (blue arrow and red arrow) applied across the tear.
The suture tails are disengaged from the suture-holding tube, and the spear is withdrawn (Fig 8F). One limb of the suture is pulled to deliver the loop of the Ultranet inside the joint to repair the meniscus tear (Fig 8G). The suture limbs are pulled alternatively to confirm the smooth gliding. If both the limbs are gliding, a Samsung Medical Center knot is applied, making the capsular suture a post (Fig 8H). The sliding knot is delivered on the capsular side, and pass pointing is done using a knot pusher to secure the knot (Fig 8I). A single half hitch can be applied to secure the knot. Four alternating half hitches must be applied if the suture limbs do not glide. Once the knot is secured, it is cut using a cord cutter (Fig 8J). This provides a secure repair of the tear (Fig 8K). Depending on the length of the tear, multiple stitches can be applied similarly (Fig 8L).
Discussion
There are several techniques to repair meniscal tears, including inside-out, outside-in, and all-inside techniques. Although various types of all-inside meniscal repair devices are available, their hard anchors are considered one of the components causing several complications. Migration of these solid anchors may lead to migration into the intra-articular locations, leading to a loose body within the joint.1,3
Because of these disadvantages of hard anchors, all-suture anchor meniscus repair devices are becoming popular.6, 7, 8 Avila et al.6 described a Superball meniscus repair device that allows all-inside repair without intra-articular knots or extracapsular implants. FiberStich is also an all-suture meniscal repair device developed by Arthrex (Naples, FL). Bachmaier et al.7 found that FiberStich had the greatest stiffness and resistance against gap formation and failure to load among the all-inside repairs. Likes et al.8 described a MaxFire device very similar to AJStitch. MaxFire is an all-suture implant with two No. 5 pieces of suture woven into a 2-0 MaxBraid suture. In a cadaver study, they found this device to have fewer complications.
Although all-suture and all-inside repairs have advantages over their counterpart, they are costly, limiting their widespread use. The AJStitch meniscus repair device is designed to deploy all-suture anchors in the extracapsular space, which allows for a secure reduction without the need for hard anchors, which are known to cause irritation. AJStitch System is cost-effective and has all the advantages of an all-inside, all-suture repair system. The spear is disposable but can be used multiple times in the same patient. The anchor is made on the back table by the surgeon or the trained assistant during surgery (Video 1). There are several advantages and disadvantages of this technique (Table 1). The pearls and pitfalls are elaborated in Table 2.
Table 1.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Technique
| Advantages |
| Cost-effective. |
| Stitches can be made using locally available suture material. |
| It can be performed with both absorbable and nonabsorbable materials. |
| Disadvantages |
| It is time-consuming, as the anchors and stitches need to be prepared on the table each time during the procedure. |
| Need of extra suture materials. |
| Biomechanical testing has not been performed. |
Table 2.
Pearls and Pitfalls of the Technique
| Pearls |
| Shave off excess fat pad than usual using an aggressive shaver from and around both the portals to avoid suture entanglement. |
| Remove the fat at the position of repair (valgus for medial and figure of 4 for lateral) for unobstructed passage of instruments. |
| Suture entanglement is possible, as it requires the insertion of the spear 2 times through the same portal. The use of a small-sized cannula may be helpful in this scenario. |
| After both the anchors are deployed, both the limbs are pulled to check the smooth glide through the anchor. A Samsung Medical Center knot may be applied if there is a smooth glide; 4 alternating half hitches must be applied if the limbs do not glide. |
| The synovial side suture limb should be made post to place the knot away from the joint. |
| A smaller-sized knot pusher is used. |
| A small cord cutter is ideal to use. |
| Pitfalls |
| An assistant is needed to prepare the anchors on the back table. |
| Loading the second anchor on the spear is tedious and cumbersome. |
| The length of the anchor may not be the same all the time. |
Disclosures
All authors (A.J., B.B., R.B., R.S., N.S., and I.P.) declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Supplementary Data
This Technical Note describes an all-inside medial meniscal repair using the AJStitch System. This system requires specially designed instruments. The assistant holds the anchor preparation plate, and the surgeon ties 2 secured loops around the 1-cm blade using the No 5 Netbond. Using a No. 15 blade, the loop is cut next to the knot. This will ensure a Netbond length of less than 2 cm, which will act as all-suture anchors of less than 1 cm when doubled. A straight needle loaded with 2/0 Ultranet is passed through the previously cut Netbond. The same thing is done for the second strand of Netbond. This creates one stitch with 2 anchors. Now, the Netbond part is loaded onto the spear, and the tails are secured. The system is now ready to use. Medial meniscus of left knee is prepared in standard fashion using a diamond rasp. The half-pipe is passed through the anteromedial portal, and the spear is introduced inside the joint through the half-pipe. The half-pipe is removed, and the spear is directed toward the capsule superior to the meniscus. The spear is pierced to the preset desired length (1.6 mm). The tail of the anchor is disengaged, and the spear is removed. Sutures are now pulled to deploy the anchor. The second anchor is loaded into the spear, and the half-pipe is again introduced. The spear is inserted along the half pipe. Now, the meniscus is pierced to the premeasured desired depth (20 mm). The tails are disengaged, and the spear is removed. The second suture also is applied in the same manner.
References
- 1.Bansal S., Floyd E.R., A Kowalski M., et al. Meniscal repair: The current state and recent advances in augmentation. J Orthop Res. 2021;39:1368–1382. doi: 10.1002/jor.25021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Marigi E.M., Till S.E., Wasserburger J.N., Reinholz A.K., Krych A.J., Stuart M.J. Inside-out approach to meniscus repair: Still the gold standard? Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2022;15:244–251. doi: 10.1007/s12178-022-09764-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lipson S.E., Morris A., Chan F.J. The “under, over” technique for repair of a peripheral bucket-handle meniscus tear with circumferential compression stitches. Arthrosc Tech. 2023;12:e1139–e1143. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2023.03.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tanaka A., Tsujii A., Shimomura K., Yonetani Y., Hamada M. Two uncommon complications related to suture knots after meniscal all-inside suture repair: A case report. JBJS Case Connect. 2022;12:1–8. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.CC.22.00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wright R.W., Huston L.J., Haas A.K. Ten-year outcomes of second-generation, all-inside meniscal repair in the setting of ACL reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2023 21;105:908–914. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.22.01196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Avila A., Rao N., Buzin S., Shankar D.S., Davidson P., Strauss E.J. Arthroscopic meniscus repair using an all-inside, all-suture, knotless device. Arthrosc Tech. 2023 2;12:e615–e619. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2022.12.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bachmaier S., Krych A.J., Smith P.A., et al. Primary fixation and cyclic performance of single-stitch all-inside and inside-out meniscal devices for repairing vertical longitudinal meniscal tears. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50:2705–2713. doi: 10.1177/03635465221107086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Likes R.L., Julka A., Aros B.C., et al. Meniscal repair with the MaxFire device: A cadaveric study. Orthop Surg. 2011;3:259–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1757-7861.2011.00151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
This Technical Note describes an all-inside medial meniscal repair using the AJStitch System. This system requires specially designed instruments. The assistant holds the anchor preparation plate, and the surgeon ties 2 secured loops around the 1-cm blade using the No 5 Netbond. Using a No. 15 blade, the loop is cut next to the knot. This will ensure a Netbond length of less than 2 cm, which will act as all-suture anchors of less than 1 cm when doubled. A straight needle loaded with 2/0 Ultranet is passed through the previously cut Netbond. The same thing is done for the second strand of Netbond. This creates one stitch with 2 anchors. Now, the Netbond part is loaded onto the spear, and the tails are secured. The system is now ready to use. Medial meniscus of left knee is prepared in standard fashion using a diamond rasp. The half-pipe is passed through the anteromedial portal, and the spear is introduced inside the joint through the half-pipe. The half-pipe is removed, and the spear is directed toward the capsule superior to the meniscus. The spear is pierced to the preset desired length (1.6 mm). The tail of the anchor is disengaged, and the spear is removed. Sutures are now pulled to deploy the anchor. The second anchor is loaded into the spear, and the half-pipe is again introduced. The spear is inserted along the half pipe. Now, the meniscus is pierced to the premeasured desired depth (20 mm). The tails are disengaged, and the spear is removed. The second suture also is applied in the same manner.