Abstract
1. Experiments were performed to determine whether the specific collagenases and other metal proteinases are bound and inhibited by α2-macroglobulin, as are endopeptidases of other classes. 2. A specific collagenase from rabbit synovial cells was inhibited by human serum. The inhibition could be attributed entirely to α2-macroglobulin; α1-trypsin inhibitor was not inhibitory. α2-Macroglobulin presaturated with trypsin or cathepsin B1 did not inhibit collagenase, and pretreatment of α2-macroglobulin with collagenase prevented subsequent reaction with trypsin. The binding of collagenase by α2-macroglobulin was not reversible in gel chromatography. 3. The collagenolytic activity of several rheumatoid synovial fluids was completely inhibited by incubation of the fluids with α2-macroglobulin. 4. The collagenase of human polymorphonuclear-leucocyte granules showed time-dependent inhibition by α2-macroglobulin. 5. The collagenolytic metal proteinase of Crotalus atrox venom was inhibited by α2-macroglobulin. 6. The collagenase of Clostridium histolyticum was bound by α2-macroglobulin, and inhibited more strongly with respect to collagen than with respect to a peptide substrate. 7. Thermolysin, the metal proteinase of Bacillus thermoproteolyticus, was bound and inhibited by α2-macroglobulin. 8. It was shown by polyacrylamidegel electrophoresis of reduced α2-macroglobulin in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate that synovial-cell collagenase, clostridial collagenase and thermolysin cleave the quarter subunit of α2-macroglobulin near its mid-point, as do serine proteinases. 9. The results are discussed in relation to previous work, and it is concluded that the characteristics of interaction of the metal proteinases with α2-macroglobulin are the same as those of other proteinases.
Full text
PDF

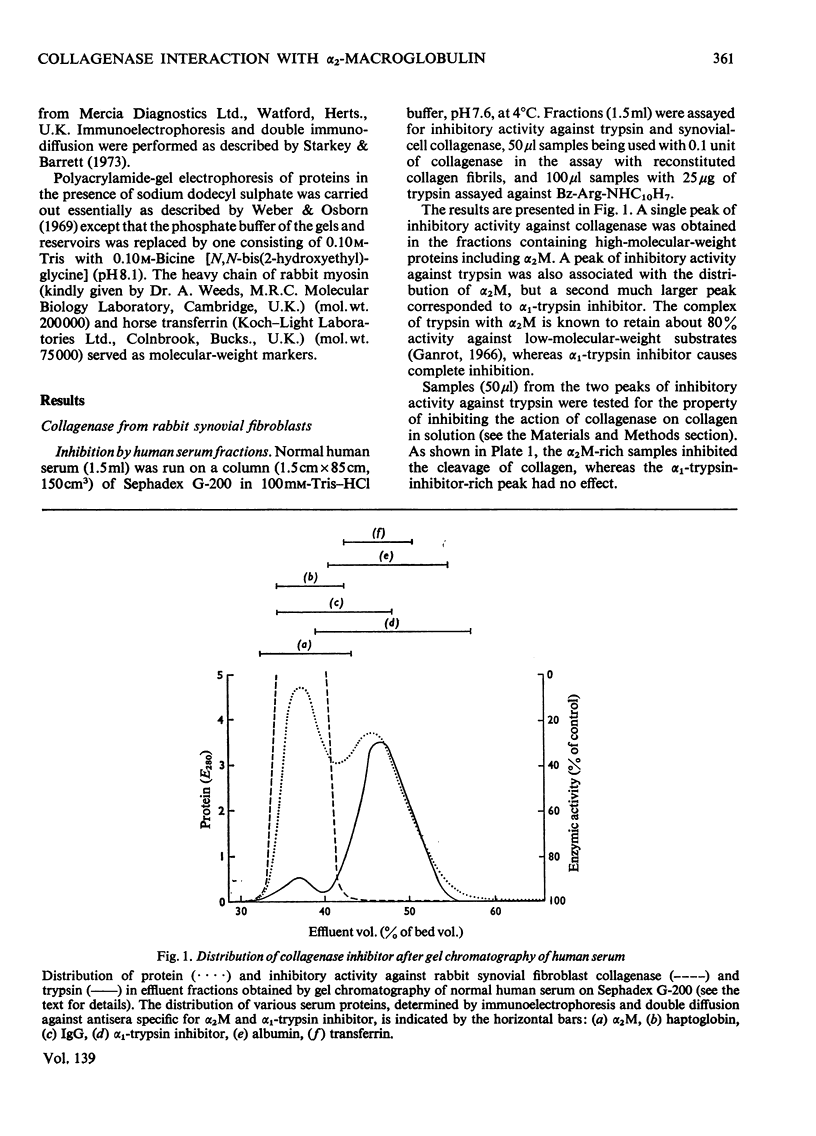
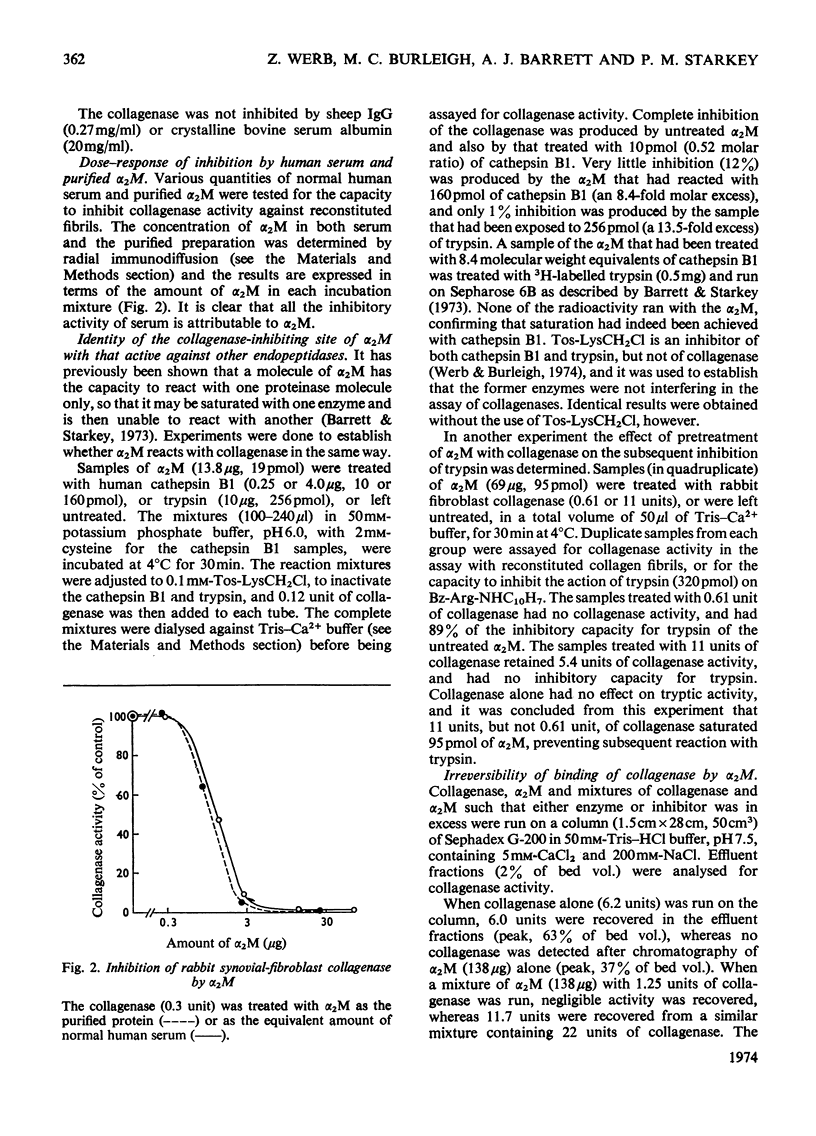
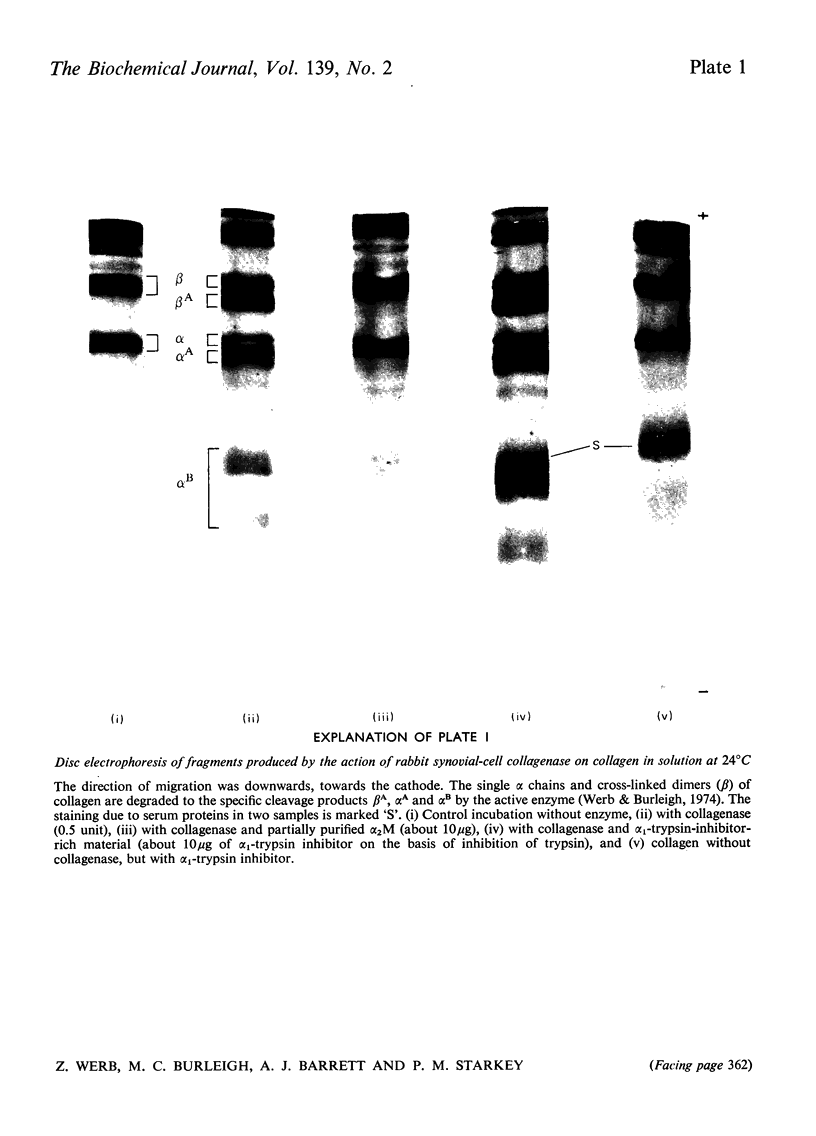
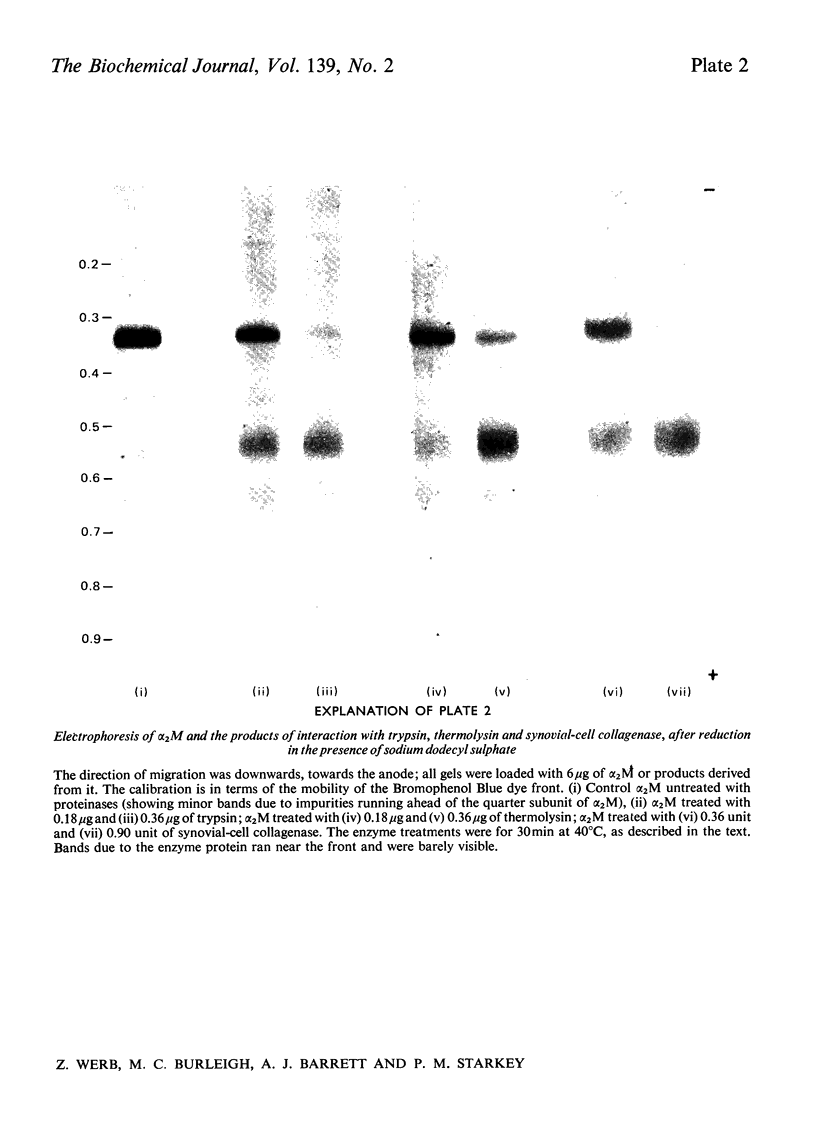
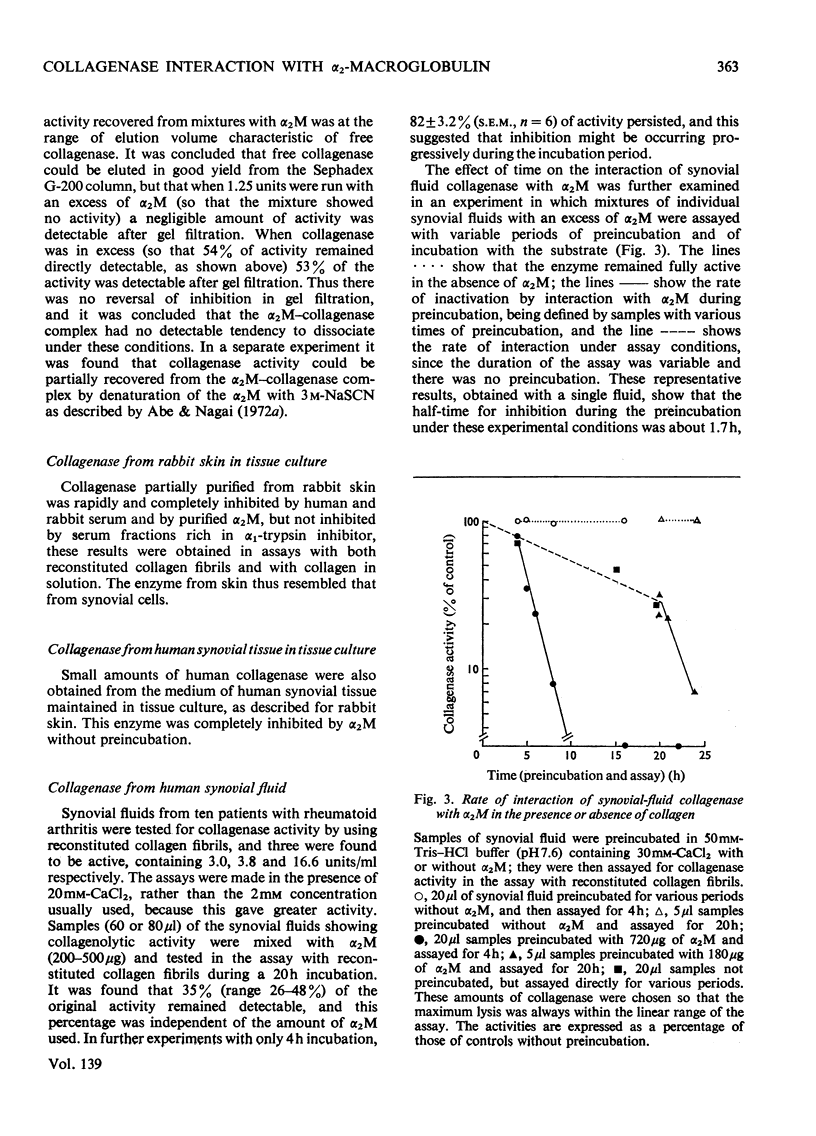

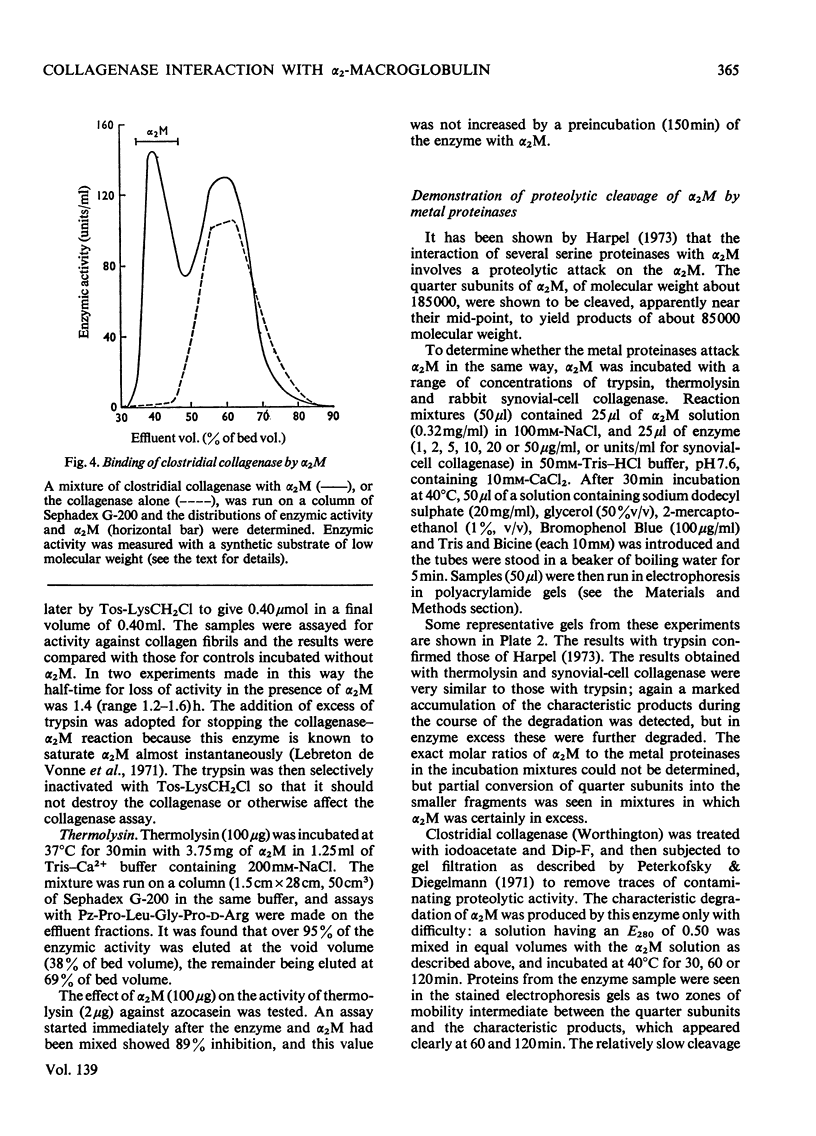



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe S., Nagai Y. Evidence for the presence of a complex of collagenase with alpha2-macroglobulin in human rheumatoid synovial fluid: a possible regulatory mechanism of collagenase activity in vivo. J Biochem. 1973 Apr;73(4):897–900. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe S., Nagai Y. Evidence for the presence of a latent form of collagenase in human rheumatoid synovial fluid. J Biochem. 1972 May;71(5):919–922. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe S., Nagai Y. Interaction between tadpole collagenase and human 2 -macroglobulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 31;278(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. A new assay for cathepsin B1 and other thiol proteinases. Anal Biochem. 1972 May;47(1):280–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90302-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Human cathepsin B1. Purification and some properties of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):809–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1310809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer E. A., Eisen A. Z., Jeffrey J. J. Studies on purified rheumatoid synovial collagenase in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2056–2064. doi: 10.1172/JCI106699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T., Jr, Shaw E. p-Nitrophenyl-p'-guanidinobenzoate HCl: a new active site titrant for trypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):508–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Jansonius J. N., Matthews B. W. The structure of thermolysin: an electron density map at 2-3 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):701–724. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90569-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoff R. B., McLennan J. E., Grillo H. C. Preparation and properties of collagenases from epithelium and mesenchyme of healing mammalian wounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 10;227(3):639–653. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresden M. H., Heilman S. A., Schmidt J. D. Collagenolytic enzymes in human neoplasms. Cancer Res. 1972 May;32(5):993–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A. Z., Bauer E. A., Jeffrey J. J. Animal and human collagenases. J Invest Dermatol. 1970 Dec;55(6):359–373. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12260483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A. Z., Bauer E. A., Jeffrey J. J. Human skin collagenase. The role of serum alpha-globulins in the control of activity in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):248–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A. Z., Bloch K. J., Sakai T. Inhibition of human skin collagenase by human serum. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Feb;75(2):258–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evanson J. M., Jeffrey J. J., Krane S. M. Studies on collagenase from rheumatoid synovium in tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2639–2651. doi: 10.1172/JCI105947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer H. M., Taylor R. E., Guthrie R. W. Human gingival collagenase: purification, molecular weight, and inhibitor studies. J Dent Res. 1972 Mar-Apr;51(2):349–355. doi: 10.1177/00220345720510022101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. The combining ratio between trypsin and serum alpha-2-macroglobulin. Acta Chem Scand. 1966;20(8):2299–2300. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-2299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY B. S. Proteolytic enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1960;29:45–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.29.070160.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Studies on human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin-enzyme interactions. Evidence for proteolytic modification of the subunit chain structure. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):508–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, DiBona D. R., Krane S. M. Collagenases in human synovial fluid. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2104–2113. doi: 10.1172/JCI106177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. An endopeptidase from rheumatoid synovial tissue culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):566–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M., Creeth J. M., Kekwick R. A. Thio reduction of human 2 -macroglobulin. The subunit structure. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):187–197. doi: 10.1042/bj1270187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanchantin G. F., Plesset M. L., Friedmann J. A., Hart D. W. Dissociation of esterolytic and clotting activities of thrombin by trypsin-binding macroglobulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):444–449. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus G. S., Daniels J. R., Brown R. S., Bladen H. A., Fullmer H. M. Degradation of collagen by a human granulocyte collagenolytic system. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2622–2629. doi: 10.1172/JCI105945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus G. S., Daniels J. R., Lian J., Burleigh M. C. Role of granulocyte collagenase in collagen degradation. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):565–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mella K., Volz M., Pfleiderer G. Application of Crotalus atrox venom alpha-protease for amino acid sequence determination. Anal Biochem. 1967 Nov;21(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN P. S. Studies of the plasmin system. II. Inhibition of plasmin by serum or plasma. J Exp Med. 1958 Jul 1;108(1):53–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Lapiere C. M., Gross J. Tadpole collagenase. Preparation and purification. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3123–3130. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. M. Motivating office personnel for increased efficiency. Trans Eur Orthod Soc. 1973:379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto S., Goldhaber P., Glimcher M. J. Further studies on the nature of the components in serum which inhibit mouse bone collagenase. Calcif Tissue Res. 1972;10(4):280–288. doi: 10.1007/BF02012559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto S., Goldhaber P., Glimcher M. J. Maintenance of mouse bone collagenase activity in the presence of serum protein by addition of trypsin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Mar;139(3):1038–1041. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey P. M., Barrett A. J. Inhibition by alpha-macroglobulin and other serum proteins. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):823–831. doi: 10.1042/bj1310823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Burleigh M. C. A specific collagenase from rabbit fibroblasts in monolayer culture. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):373–385. doi: 10.1042/bj1370373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vonne T. L., Mouray H., Berthillier G., Got R. Influence de l'alpha 2-macroglobuline du lapin sur l'activate enzymatique de la trypsine et de la chymotrypsine. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1971 Oct;40(2):439–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]