Abstract
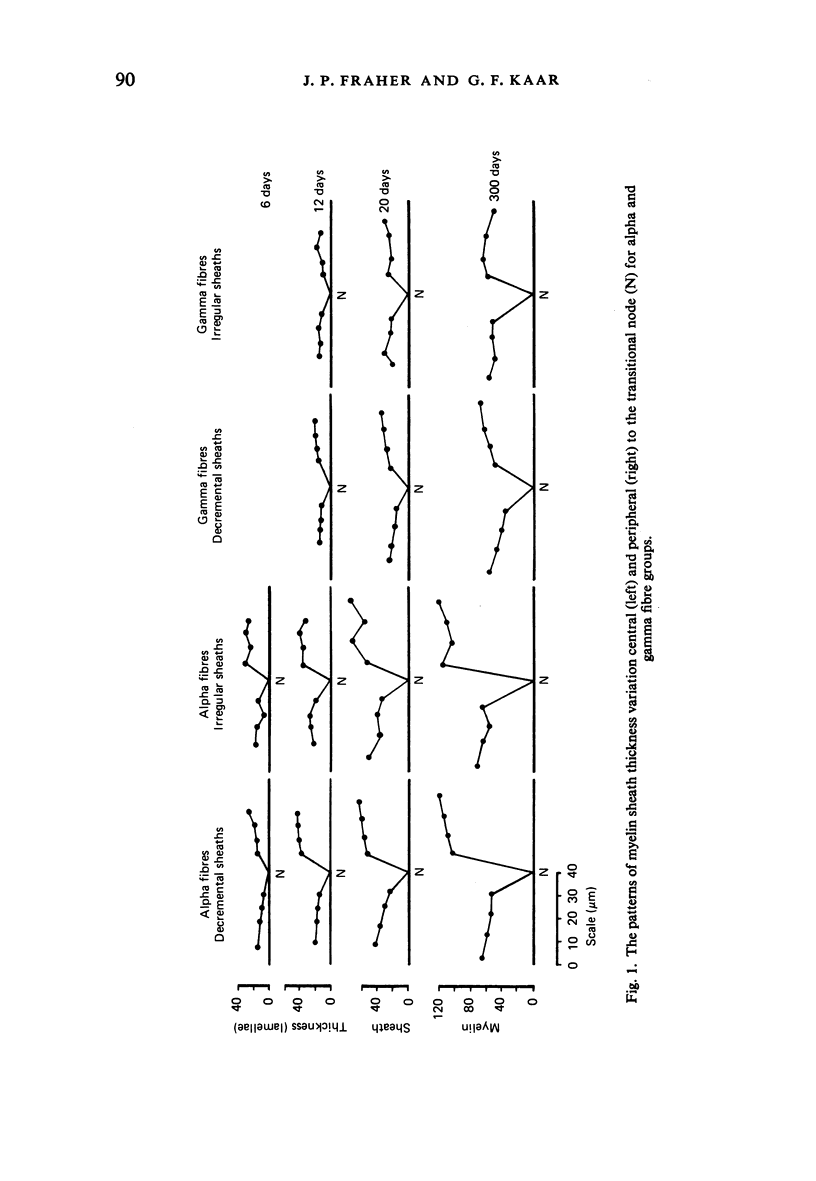
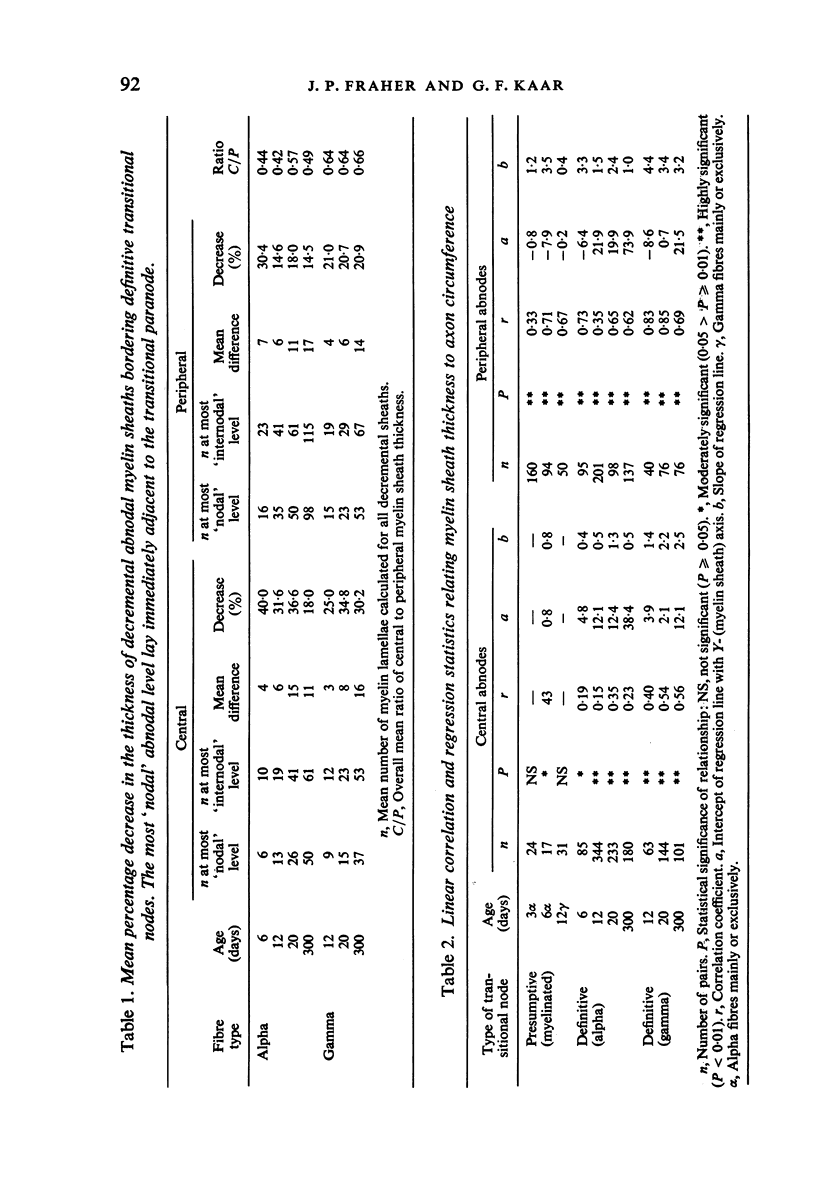
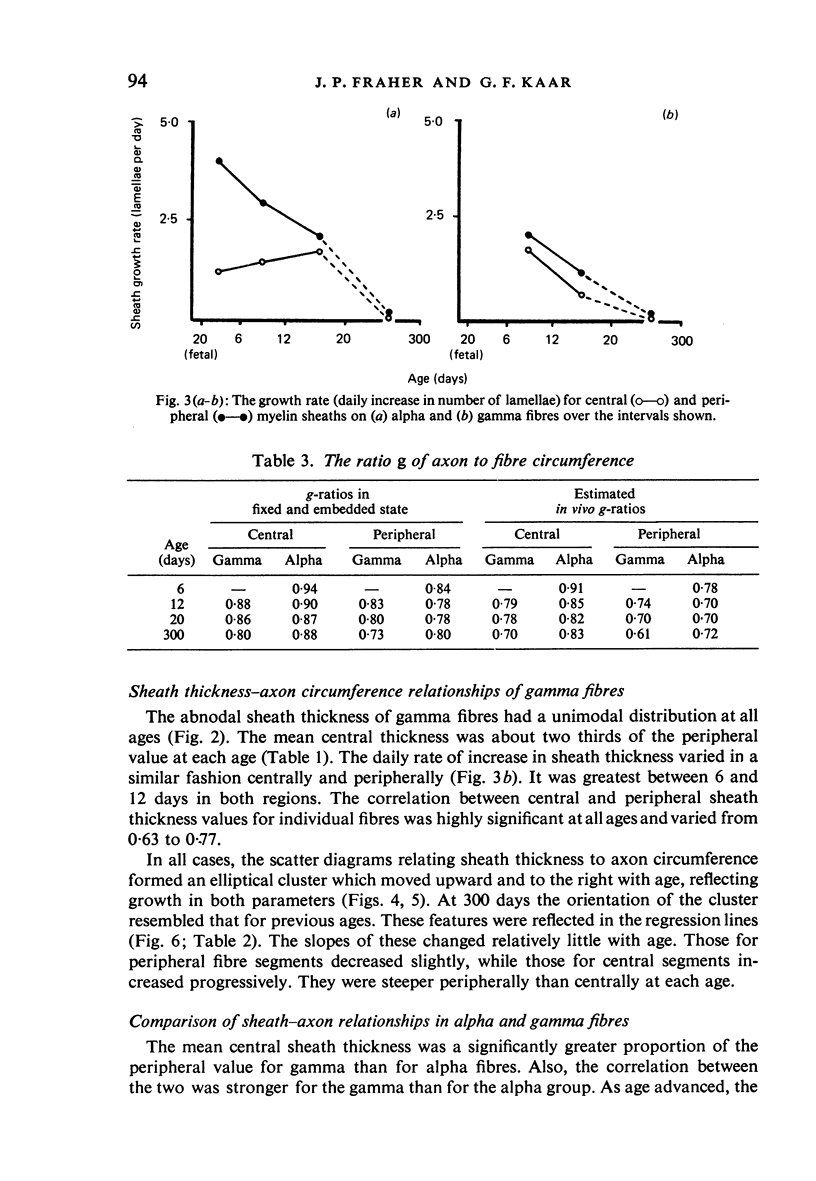
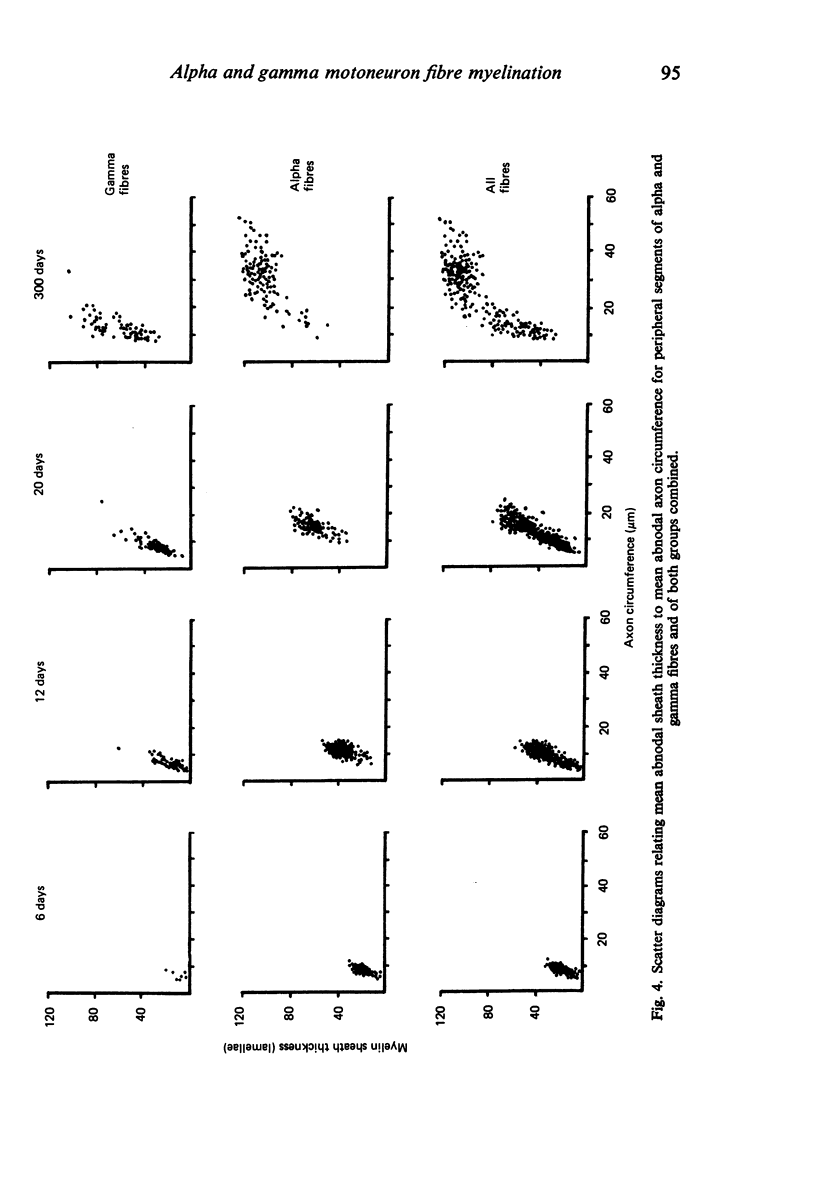
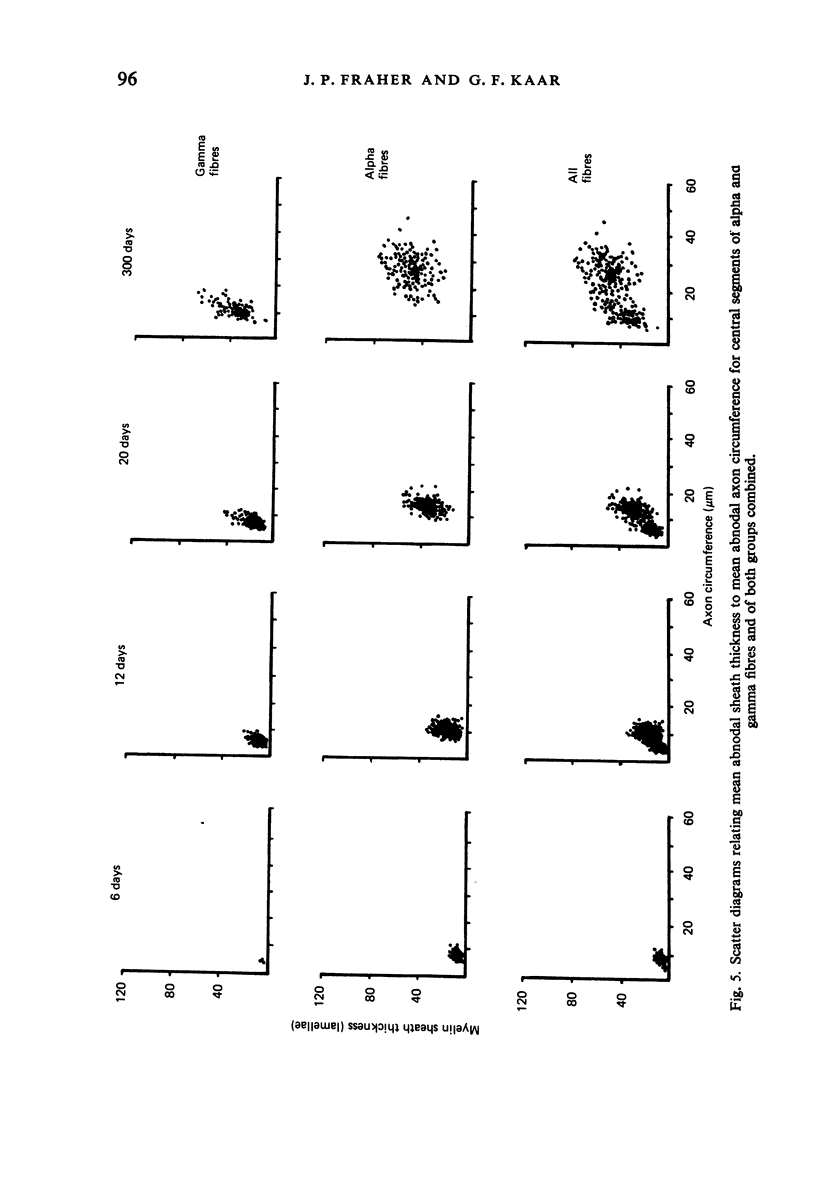
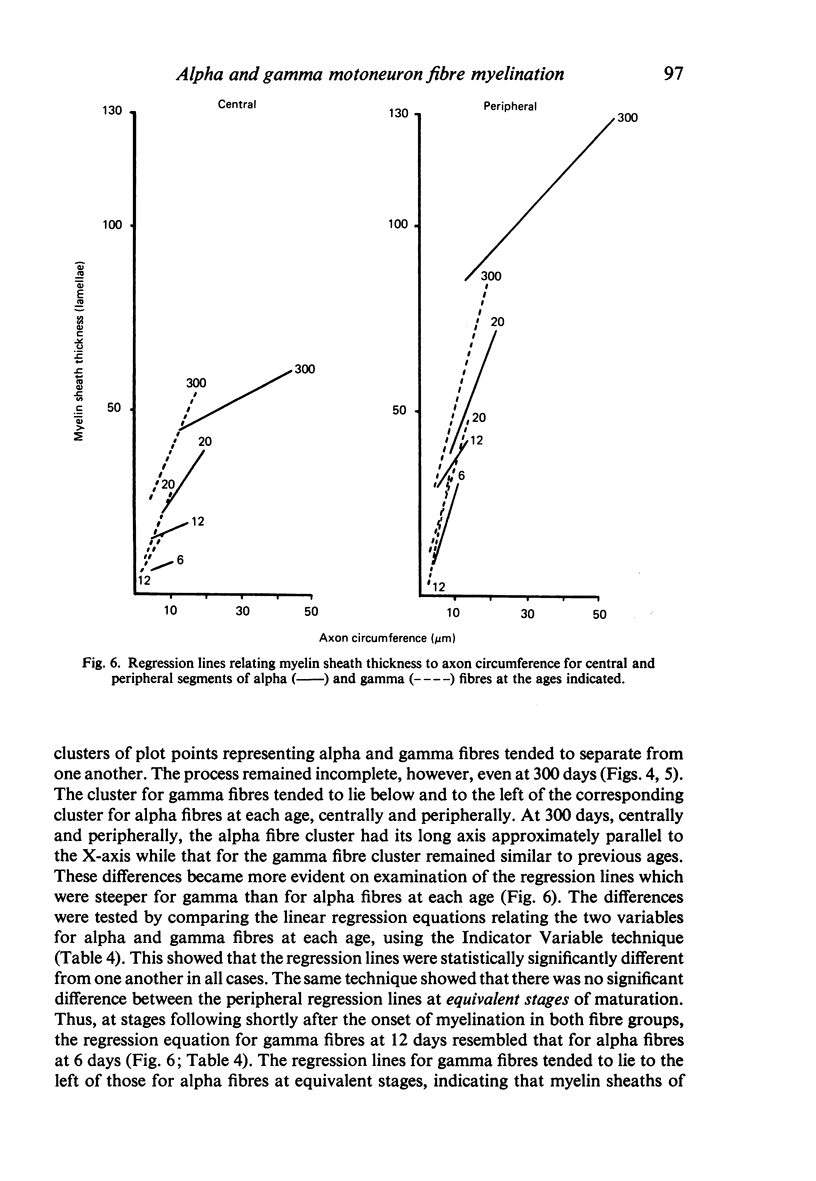
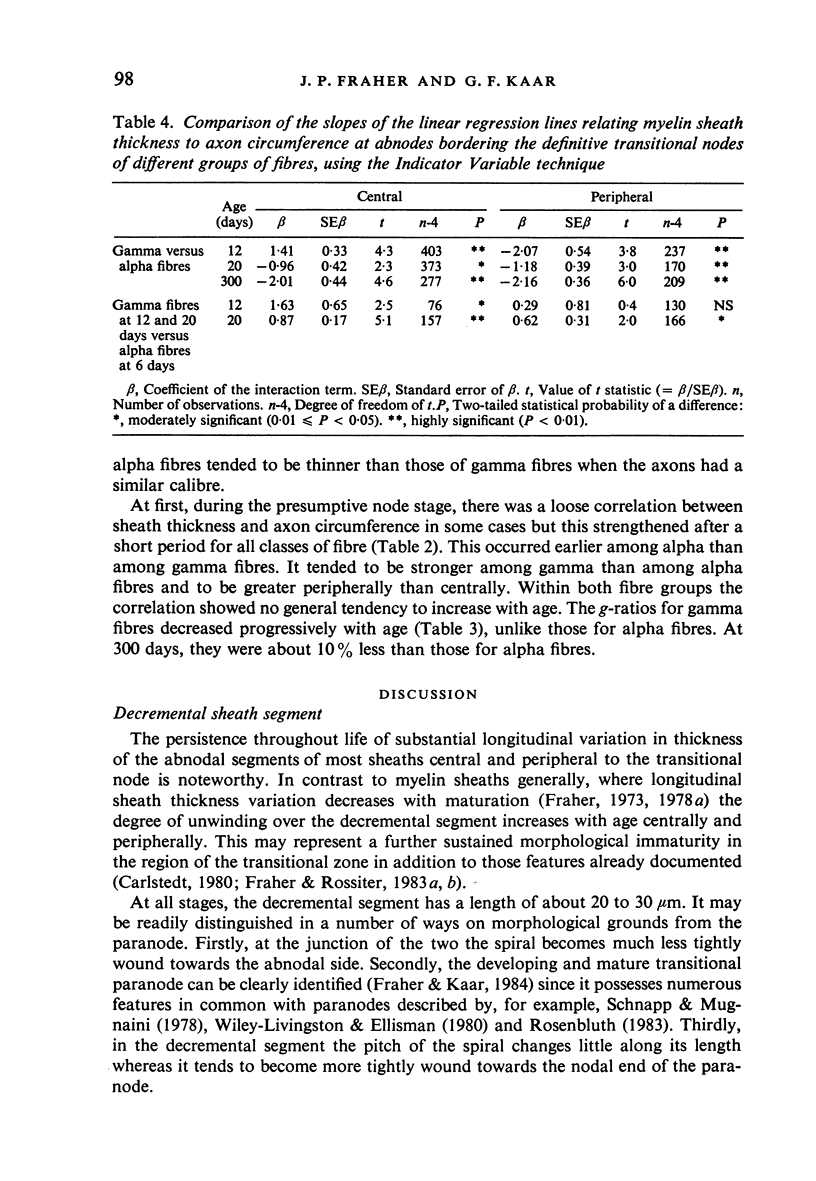
The abnodal myelin sheaths of the internodes immediately central and peripheral to the transitional node possess a decremental segment over which sheath thickness gradually decreases in the direction of the paranode. This may represent a sustained morphological immaturity of the sheath. Alpha and gamma fibre groups have different sheath thickness to axon circumference relationships at each age during development and at maturity. Gamma fibres have relatively thicker sheaths than alpha fibres. In both groups the relationship is different for central and peripheral fibre segments and also changes during maturation. It is therefore not permissible to make inferences from the adult relationship regarding the relationship during development. Changes in the relationship follow similar patterns for central and peripheral fibre segments, suggesting that the control mechanisms are closely linked in both locations. Sheath thickness growth both peripherally and centrally lags behind axon calibre growth for alpha fibres. The two keep pace for gamma fibres. The strength of the correlation between sheath thickness and axon circumference changes little with maturation in either group. The morphological differences between central and peripheral segments of ventral motoneuron fibres suggest that conduction velocity increases when the impulse enters the peripheral nervous system.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott E. R., Boyd I. A., Kalu K. U. Ultrastructural dimensions of myelinated peripheral nerve fibres in the cat and their relation to conduction velocity. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:125–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold C. H., Carlstedt T. Myelination of S1 dorsal root axons in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Aug 10;209(3):225–232. doi: 10.1002/cne.902090302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold C. H., Carlstedt T. Observations on the morphology at the transition between the peripheral and the central nervous system in the cat. III. Myelinated fibres in S1 dorsal rootlets. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1977;446:43–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold C. H., Corneliuson O., Rydmark M. Changes in shape and size of cat spinal root myelinated nerve fibers during fixation and Vestopal-w embedding for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1982 Jul;80(1):23–41. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(82)80029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold C. H., Nilsson I., Rydmark M. Axon diameter and myelin sheath thickness in nerve fibres of the ventral spinal root of the seventh lumbar nerve of the adult and developing cat. J Anat. 1983 May;136(Pt 3):483–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Nickels S. M., Stirling C. A. Numbers and sizes of nerve fibres in mouse spinal roots. Q J Exp Physiol. 1982 Jul;67(3):473–494. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1982.sp002663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronson R. T., Bishop Y., Hedley-Whyte E. T. A contribution to the electron microscopic morphometric analysis of peripheral nerve. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 1;178(1):177–186. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt T. Internodal length of nerve fibres in dorsal roots of cat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Oct 2;19(3):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINEAN J. B. The nature and stability of nerve myelin. Int Rev Cytol. 1961;12:303–336. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60543-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. A quantitative study of anterior root fibres during early myelination. II. Longitudinal variation in sheath thickness and axon circumference. J Anat. 1973 Sep;115(Pt 3):421–444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. A quantitative study of anterior root fibres during early myelination. J Anat. 1972 May;112(Pt 1):99–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P., Kaar G. F. The transitional node of Ranvier at the junction of the central and peripheral nervous systems: an ultrastructural study of its development and mature form. J Anat. 1984 Sep;139(Pt 2):215–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. Quantitative studies on the maturation of central and peripheral parts of individual ventral motoneuron axons. I. Myelin sheath and axon calibre. J Anat. 1978 Aug;126(Pt 3):509–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. Quantitative studies on the maturation of central and peripheral parts of individual ventral motoneuron axons. II. Internodal length. J Anat. 1978 Sep;127(Pt 1):1–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P., Rossiter J. P. Cell clusters on fetal rat ventral roots: prenatal development. J Anat. 1983 Jan;136(Pt 1):111–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P., Rossiter J. P. Cell clusters on rat ventral roots: postnatal development. J Anat. 1983 Oct;137(Pt 3):555–571. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. The growth and myelination of central and peripheral segments of ventral motoneurone axons. A quantitative ultrastructural study. Brain Res. 1976 Mar 26;105(2):193–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90421-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. The maturation of the ventral root-spinal cord transitional zone. An ultrastructural study. J Neurol Sci. 1978 May;36(3):427–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friede R. L., Bischhausen R. The precise geometry of large internodes. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Dec;48(3):367–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friede R. L., Samorajski T. Myelin formation in the sciatic nerve of the rat. A quantitative electron microscopic, histochemical and radioautographic study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Oct;27(4):546–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friede R. L., Samorajski T. Relation between the number of myelin lamellae and axon circumference in fibers of vagus and sciatic nerves of mice. J Comp Neurol. 1967 Jul;130(3):223–231. doi: 10.1002/cne.901300304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton P. M., Barnes J. M. Peripheral neuropathy in rats produced by acrylamide. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Jul;23(3):210–221. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A., YOUNG J. Z. The nodes of Ranvier. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1952 Nov 20;140(900):301–320. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1952.0063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand C., Hahn R. Relation between myelin sheath thickness and axon size in spinal cord white matter of some vertebrate species. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Oct;38(3):421–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand C., Müller H. Low-angle x-ray diffraction studies on the period of central myelin sheaths during preparation for electron microscopy. A comparison between different anatomical areas. Neurobiology. 1974;4(2):71–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson U. Comparison of the myelin period of peripheral and central origin by electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Jun;15(3):451–468. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A. Hereditary hypertrophic neuropathy in the trembler mouse. Part 2. Histopathological studies: electron microscopy. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Dec;30(2-3):343–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald W. I., Ohlrich G. D. Quantitative anatomical measurements on single isolated fibres from the cat spinal cord. J Anat. 1971 Nov;110(Pt 2):191–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHTON W. A. H. A theory of the effects of fibre size in medullated nerve. J Physiol. 1951 Sep;115(1):101–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluth J. Electrophysiology and morphology of myelinated nerve fibers. V. Intramembranous particle distribution in nerve fiber membranes. Experientia. 1983 Sep 15;39(9):953–963. doi: 10.1007/BF01989760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. Relation between the number of myelin lamellae and axon circumference in fibres of ventral and dorsal roots and optic nerve in normal, undernourished, and rehabilitated rats. An ultrastructural morphometric study. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1974;410:1–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Koles Z. J. Myelinated nerve fibers: computed effect of myelin thickness on conduction velocity. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1256–1258. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizoso A. D., Young J. Z. Internode length and fibre diameter in developing and regenerating nerves. J Anat. 1948 Apr;82(Pt 1-2):110–134.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S. G. Determinants of conduction velocity in myelinated nerve fibers. Muscle Nerve. 1980 Mar-Apr;3(2):141–150. doi: 10.1002/mus.880030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley-Livingston C., Ellisman M. H. Development of axonal membrane specializations defines nodes of Ranvier and precedes Schwann cell myelin elaboration. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):334–355. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. L., Wendell-Smith C. P. Some additional parametric variations between peripheral nerve fibre populations. J Anat. 1971 Sep;109(Pt 3):505–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


