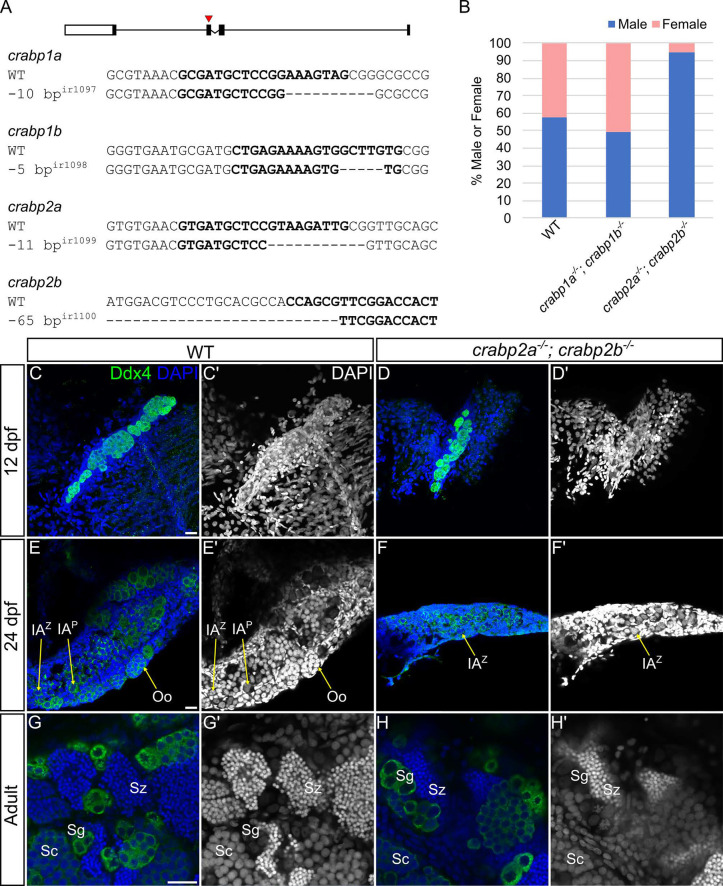
Fig. 1.
Crabp2 mutants are disproportionately male and have smaller gonads. (A) Schematic of the four Crabp1 and Crabp2 genes. Red arrowhead indicates the exon 2 gRNA target site. Selected sequences depict Crabp1 and Crabp2 wild-type gRNA target sites in bold and corresponding mutant alleles for crabp1a, crabp1b, crabp2a and crabp2b. (B) Histogram displaying sex ratios in wild types (male, n=77; female, n=57), crabp1a−/−; crabp1b−/− double mutants (male, n=51; female, n=52) and crabp2a−/−; crabp2b−/− double mutants (male, n=88; female, n=5). (C-H′) Representative images of 12 dpf (C-D′), 24 dpf (E-F′) and adult (G-H′) gonads in wild types and crabp2a−/−; crabp2b−/− double mutants. (C-H) Anti-Ddx4 antibody-labeled germ cells (GCs) are green; DAPI-labeled nuclei are blue. (C′-H′) Grayscale DAPI. (C-D′) Z-projections; (E-H′) single slices. Oo, oogonia; IAZ, zygotene stage IA oocyte; IAP, pachytene stage IA oocyte; Sg, spermatogonia; Sc, spermatocytes; Sz, spermatozoa. GC staging according to Draper (2012) and Selman et al. (1993). Scale bars: 20 μm. Wild type: 12 dpf, n=4 larvae; 24 dpf, n=4 fish; adult, n=8 fish. crabp2a−/−; crabp2b−/−mutants: 12 dpf, n=4 larvae; 24 dpf, n=5 fish; adult, n=6 fish.