Abstract
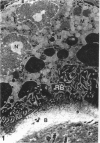
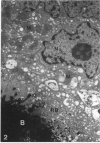
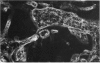
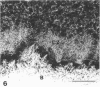
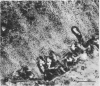
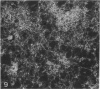
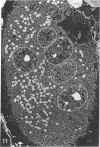
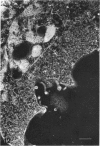
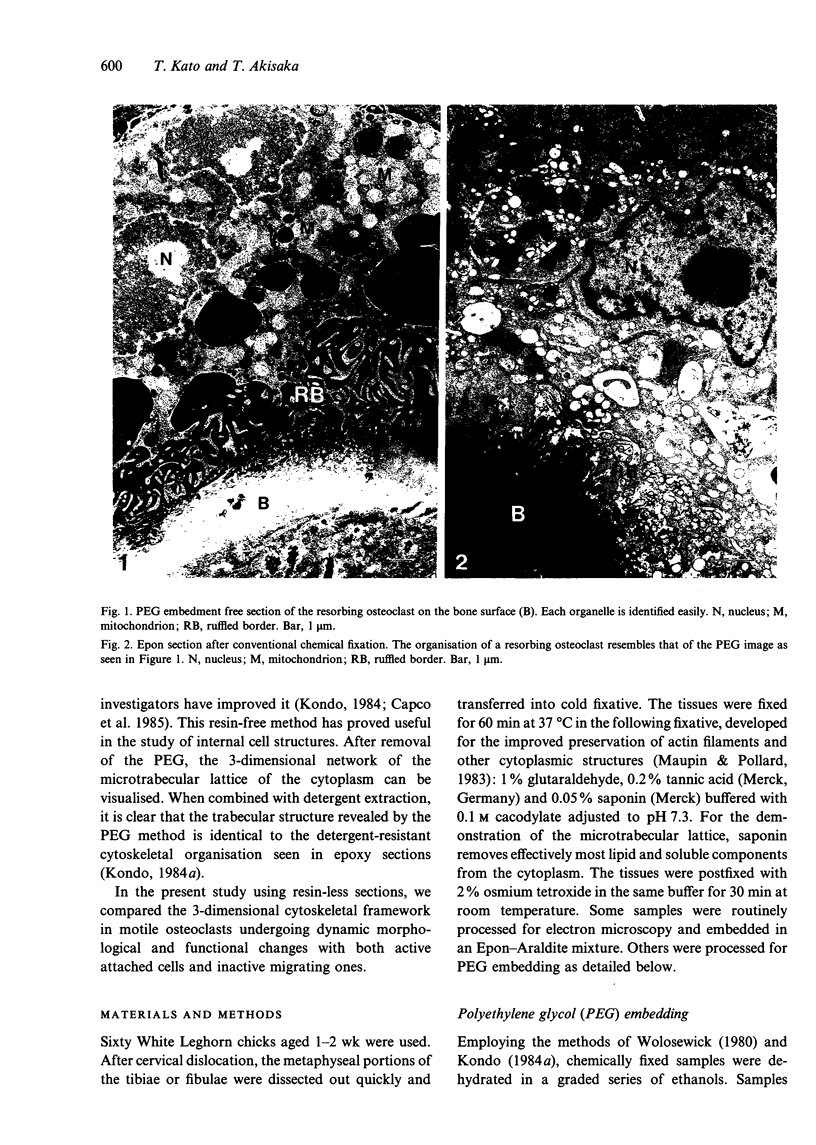
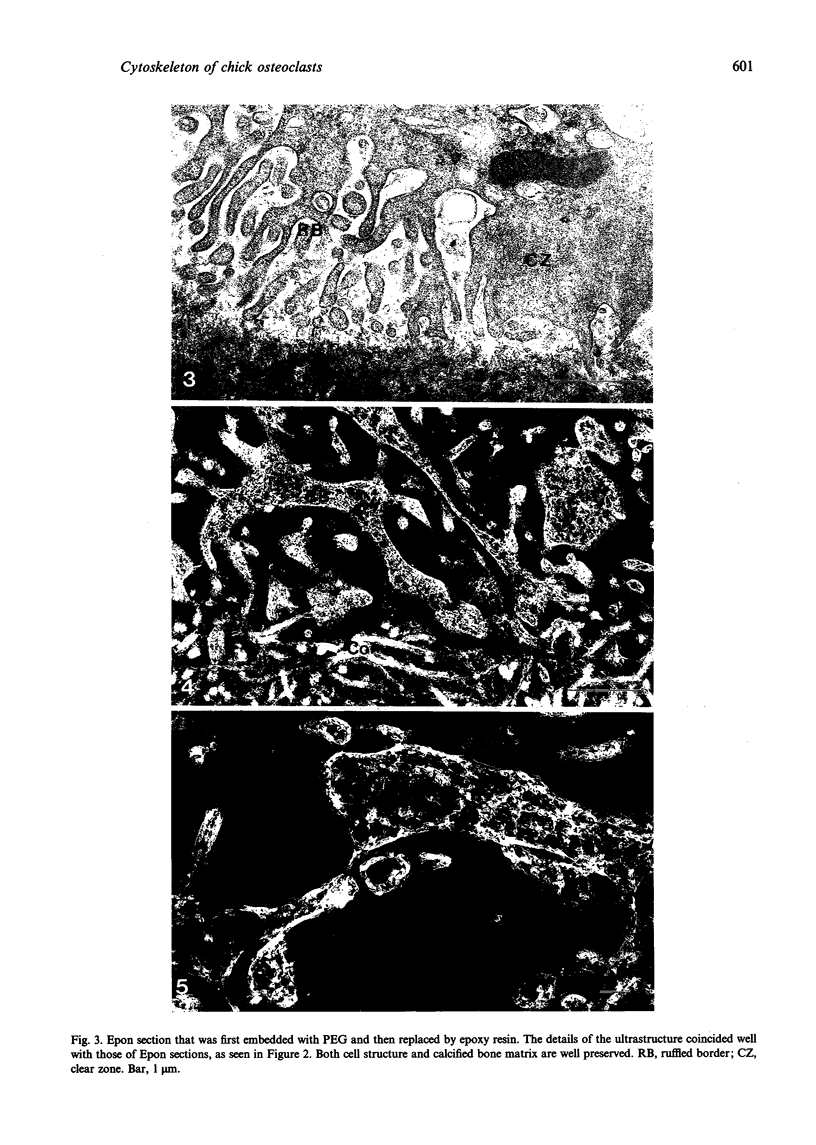
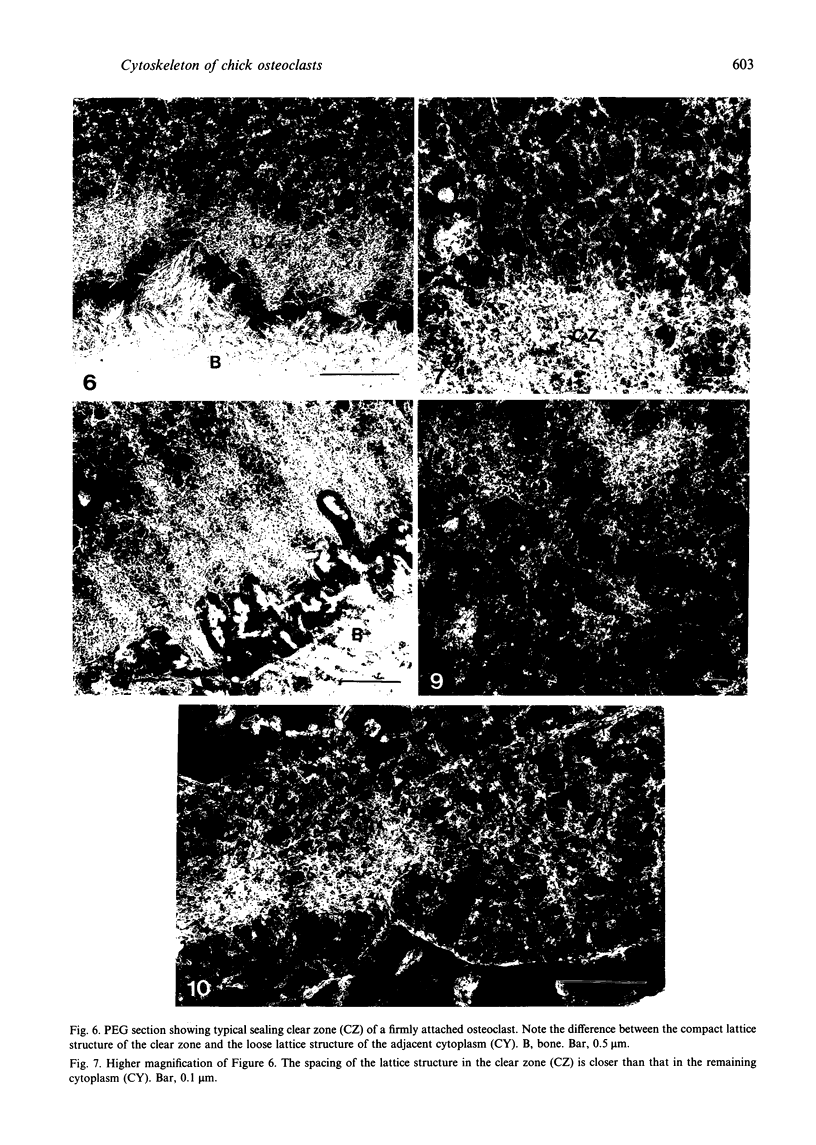
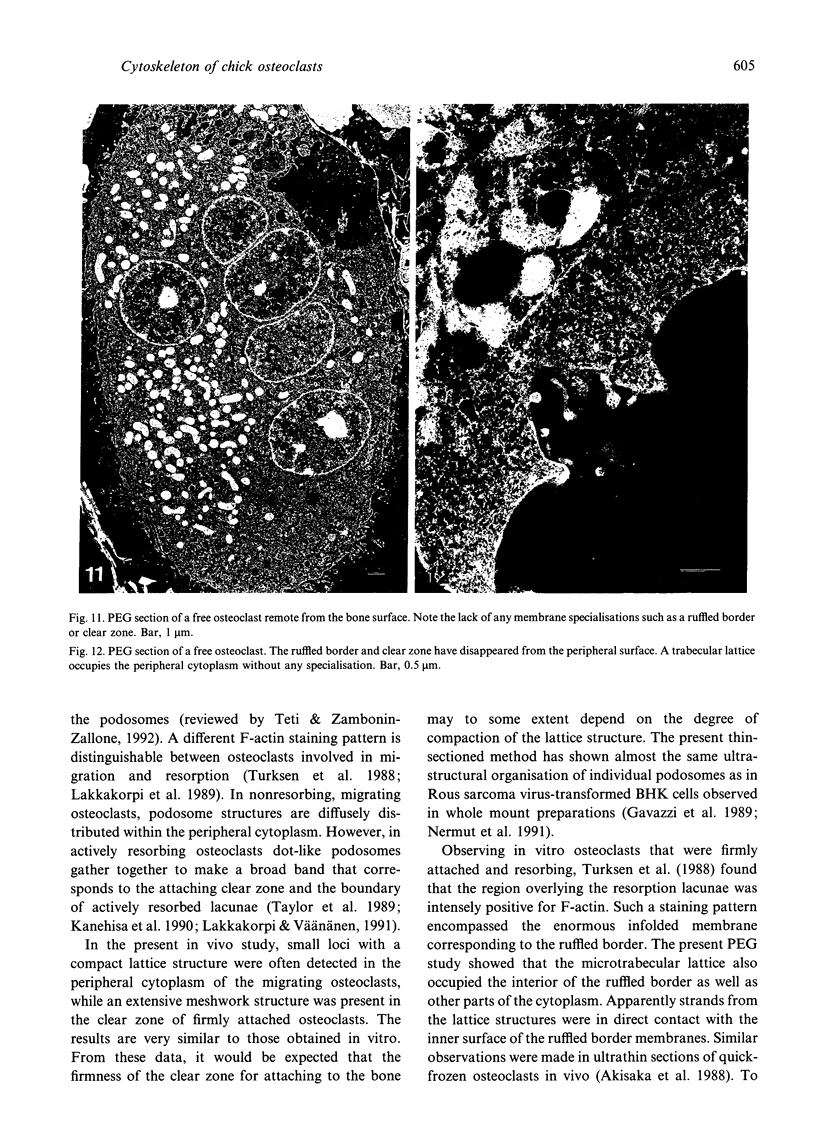
The cytoskeletal framework of chick osteoclasts was examined by the resin-less polyethylene glycol (PEG) method. Resin-less thin sections revealed changes in the 3-dimensional organisation of a microtrabecular lattice during different phases of osteoclast activity. This lattice, composed of interconnecting strands, occupied part of the osteoclast cytoplasm including the ruffled border and clear zone areas. In firmly attached, active osteoclasts, the clear zone exhibited a compact and orderly array with a meshwork appearance. This organelle-free area could be clearly distinguished from other cytoplasmic regions by the compactness of its lattice structure. Well developed membrane infoldings of the ruffled border next to the resorption lacunae were composed of interconnected strands, some of which were in direct contact with the ruffled border membrane. Migrating osteoclasts remote from the bone surface lacked these membrane modifications. Their peripheral cytoplasm exhibited a disorganised meshwork of strands without the clear zone. While migrating, osteoclasts which still adhered to the bone surface, appeared to form loci within the compact lattice structure referred to as podosomes. These results demonstrate the dynamic morphological changes in the organisation of the trabecular lattice that occur within attached and migrating osteoclasts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akisaka T., Subita G. P., Shigenaga Y. Surface modifications at the periosseous region of chick osteoclast as revealed by freeze-substitution. Anat Rec. 1988 Dec;222(4):323–332. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092220404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubin J. E. Osteoclast adhesion and resorption: the role of podosomes. J Bone Miner Res. 1992 Apr;7(4):365–368. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650070402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgman P. C., Reese T. S. The structure of cytoplasm in directly frozen cultured cells. I. Filamentous meshworks and the cytoplasmic ground substance. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1655–1668. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capco D. G., Krochmalnic G., Penman S. A new method of preparing embeddment-free sections for transmission electron microscopy: applications to the cytoskeletal framework and other three-dimensional networks. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1878–1885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Revell P. A., Fuller K., Athanasou N. A. Resorption of bone by isolated rabbit osteoclasts. J Cell Sci. 1984 Mar;66:383–399. doi: 10.1242/jcs.66.1.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavazzi I., Nermut M. V., Marchisio P. C. Ultrastructure and gold-immunolabelling of cell-substratum adhesions (podosomes) in RSV-transformed BHK cells. J Cell Sci. 1989 Sep;94(Pt 1):85–99. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Kirschner M. W. Filament organization revealed in platinum replicas of freeze-dried cytoskeletons. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):212–234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. J., Taylor M. L. Confocal fluorescence microscopy: some applications in bone cell biology. J Microsc. 1990 May;158(Pt 2):249–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1990.tb02998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa J., Yamanaka T., Doi S., Turksen K., Heersche J. N., Aubin J. E., Takeuchi H. A band of F-actin containing podosomes is involved in bone resorption by osteoclasts. Bone. 1990;11(4):287–293. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(90)90082-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H. Ultrastructural localization of actin in the intermediate lobe of rat hypophysis. Biol Cell. 1987;60(1):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1987.tb00546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H., Wolosewick J. J., Pappas G. D. The microtrabecular lattice of the adrenal medulla revealed by polyethylene glycol embedding and stereo electron microscopy. J Neurosci. 1982 Jan;2(1):57–65. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-01-00057.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakkakorpi P. T., Vänänen H. K. Kinetics of the osteoclast cytoskeleton during the resorption cycle in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 1991 Aug;6(8):817–826. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650060806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakkakorpi P., Tuukkanen J., Hentunen T., Järvelin K., Vänänen K. Organization of osteoclast microfilaments during the attachment to bone surface in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 1989 Dec;4(6):817–825. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650040605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchisio P. C., Cirillo D., Naldini L., Primavera M. V., Teti A., Zambonin-Zallone A. Cell-substratum interaction of cultured avian osteoclasts is mediated by specific adhesion structures. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1696–1705. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maupin P., Pollard T. D. Improved preservation and staining of HeLa cell actin filaments, clathrin-coated membranes, and other cytoplasmic structures by tannic acid-glutaraldehyde-saponin fixation. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):51–62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V., Eason P., Hirst E. M., Kellie S. Cell/substratum adhesions in RSV-transformed rat fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Apr;193(2):382–397. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson J. A., Krockmalnic G., He D. C., Penman S. Immunolocalization in three dimensions: immunogold staining of cytoskeletal and nuclear matrix proteins in resinless electron microscopy sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2259–2263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K. R., Anderson K. L. The structure of the cytoplasmic matrix preserved by freeze-drying and freeze-substitution. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;29(1):83–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross-Canada J., Becker R. P., Pappas G. D. Synaptic vesicles and the nerve-muscle preparation in resinless sections. J Neurocytol. 1983 Oct;12(5):817–830. doi: 10.1007/BF01258153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M., van Blerkom J., Porter K. R. Stabilization and the cytoplasmic ground substance in detergent-opened cells and a structural and biochemical analysis of its composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4329–4333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. L., Boyde A., Jones S. J. The effect of fluoride on the patterns of adherence of osteoclasts cultured on and resorbing dentine: a 3-D assessment of vinculin-labelled cells using confocal optical microscopy. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1989;180(5):427–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00305117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teti A., Marchisio P. C., Zallone A. Z. Clear zone in osteoclast function: role of podosomes in regulation of bone-resorbing activity. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 1):C1–C7. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turksen K., Kanehisa J., Opas M., Heersche J. N., Aubin J. E. Adhesion patterns and cytoskeleton of rabbit osteoclasts on bone slices and glass. J Bone Miner Res. 1988 Aug;3(4):389–400. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650030405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G. Cellular biology and biochemical mechanism of bone resorption. A review of recent developments on the formation, activation, and mode of action of osteoclasts. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988 Jun;(231):239–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J., Porter K. R. Microtrabecular lattice of the cytoplasmic ground substance. Artifact or reality. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):114–139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J. The application of polyethylene glycol (PEG) to electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):675–661. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zallone A. Z., Teti A., Primavera M. V., Naldini L., Marchisio P. C. Osteoclasts and monocytes have similar cytoskeletal structures and adhesion property in vitro. J Anat. 1983 Aug;137(Pt 1):57–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambonin-Zallone A., Teti A., Carano A., Marchisio P. C. The distribution of podosomes in osteoclasts cultured on bone laminae: effect of retinol. J Bone Miner Res. 1988 Oct;3(5):517–523. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650030507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]