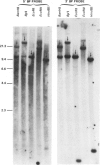
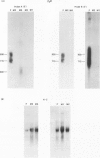
Abstract
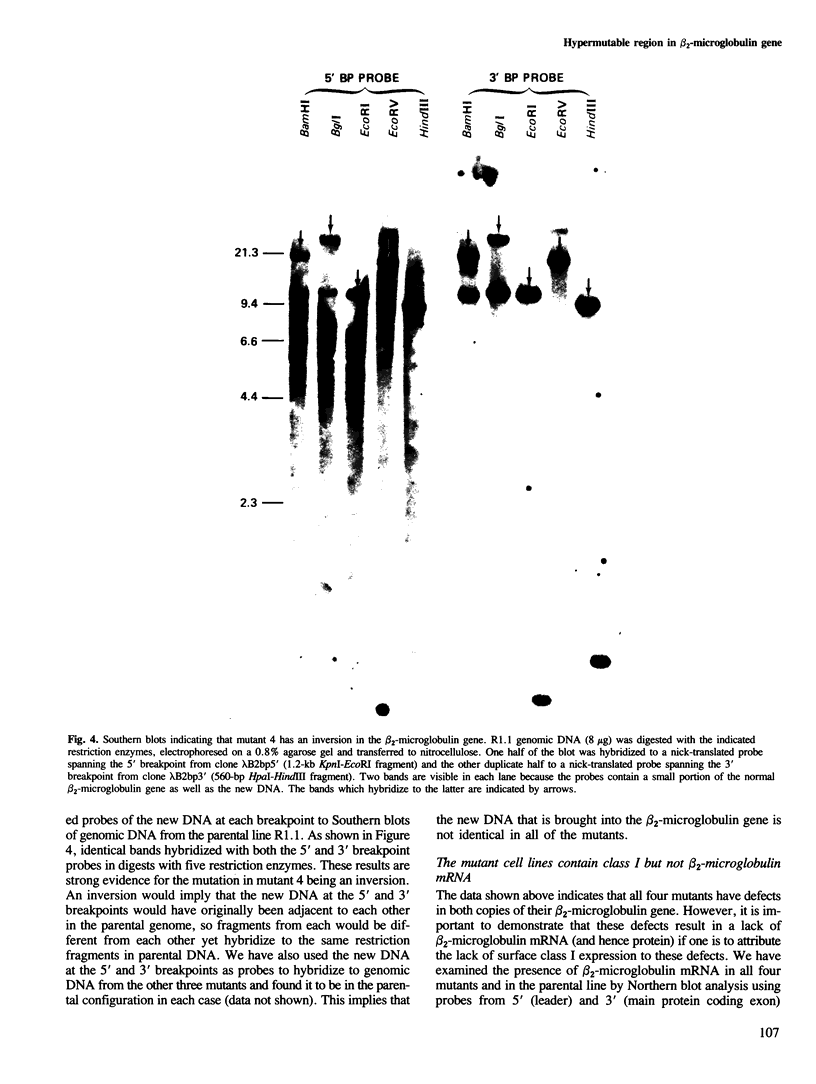
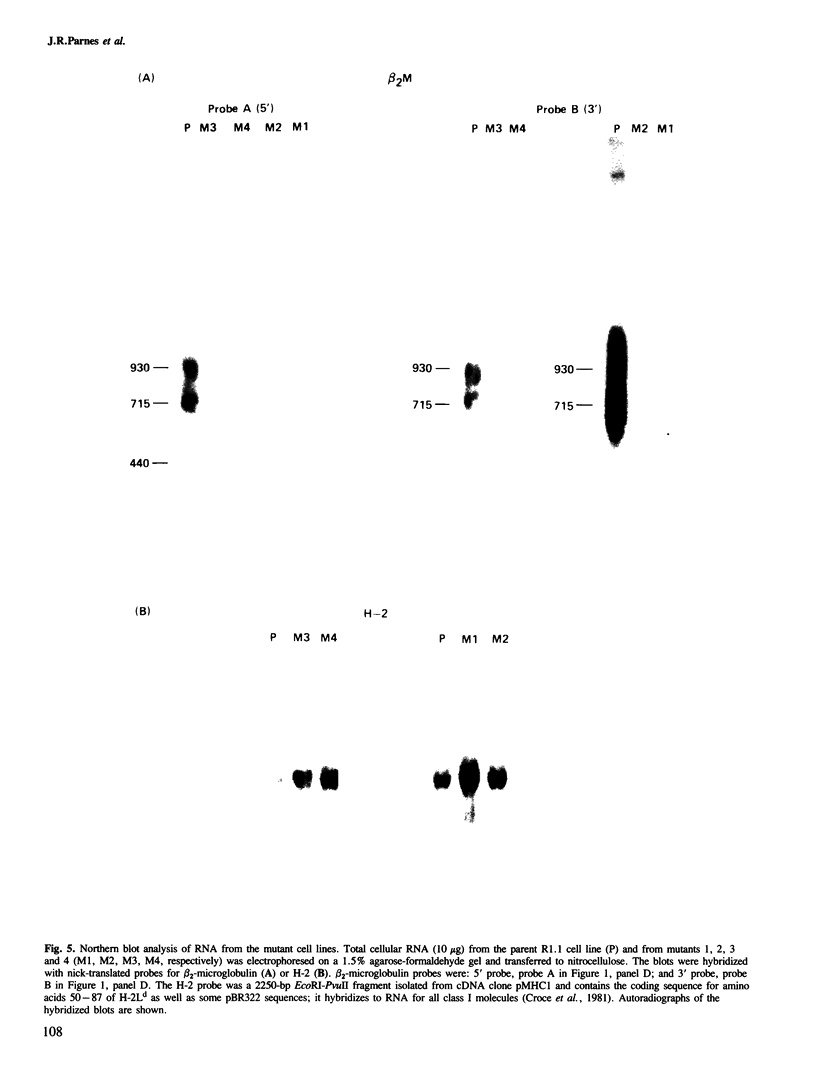
beta 2-Microglobulin is the smaller, relatively non-polymorphic chain of class I major histocompatibility complex proteins. We have previously described a mutant mouse cell line which had been selected for loss of the class I thymus leukemia (TL) antigen and had concomitantly lost surface expression of H-2k antigens. Expression of class I antigens on the cell surface was restored by fusion to an antigenically distinct mouse lymphoma line, and the defect in the mutant was shown to be the loss of a functional beta 2-microglobulin gene. We now describe three additional mutants with the same phenotype, all selected for loss of TL but after different types of mutagenesis. All of these mutants have genomic rearrangements resulting in the absence of a functional beta 2-microglobulin gene. These data provide strong evidence for the requirement of beta 2-microglobulin for cell surface expression of the heavy chain of class I major histocompatibility complex proteins. We further show that the defects in at least one beta 2-microglobulin gene in each mutant cell line map to the same small DNA segment within the first intron. The breakpoints of these mutations define a hypermutable site within the mouse beta 2-microglobulin gene.
Full text
PDF
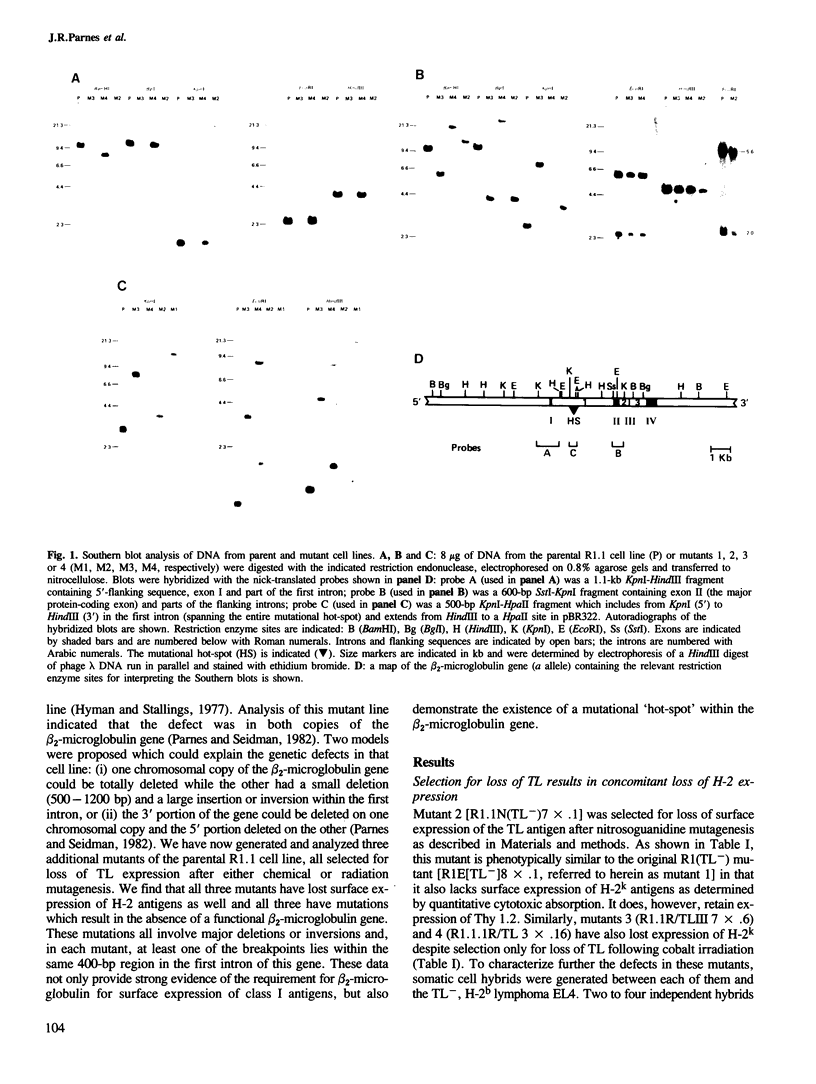





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arce-Gomez B., Jones E. A., Barnstable C. J., Solomon E., Bodmer W. F. The genetic control of HLA-A and B antigens in somatic cell hybrids: requirement for beta2 microglobulin. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Feb;11(2):96–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Linnenbach A., Huebner K., Parnes J. R., Margulies D. H., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Control of expression of histocompatibility antigens (H-2) and beta 2-microglobulin in F9 teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5754–5758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B., Garoff H., Warren G., Robinson P. J. Cell-free synthesis and membrane insertion of mouse H-2Dd histocompatibility antigen and beta 2-microglobulin. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):759–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Clustered arrangement of immunoglobulin lambda constant region genes in man. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):536–540. doi: 10.1038/294536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R., Stallings V. Complementation patterns of Thy-1 variants and evidence that antigen loss variants "pre-exist" in the parental population. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Feb;52(2):429–436. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Tuan D., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. A gene deletion ending at the midpoint of a repetitive DNA sequence in one form of hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):469–470. doi: 10.1038/296469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. The major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):516–521. doi: 10.1126/science.104386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancet D., Parham P., Strominger J. L. Heavy chain of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens is conformationally labile: a possible role for beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3844–3848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):140–146. doi: 10.1126/science.3155573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Michelson A. Partial deletion of the alpha-globin structural gene in human alpha-thalassaemia. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):538–540. doi: 10.1038/286538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi S., Giglioni B. The deletion in a type of delta 0-beta 0-thalassaemia begins in an inverted AluI repeat. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):770–771. doi: 10.1038/300770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Seidman J. G. Structure of wild-type and mutant mouse beta 2-microglobulin genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Cannon L. E., Strominger J. L. Cell-free translation of the mRNAs for the heavy and light chains of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2273–2277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter T. A., Boyer C., Verhulst A. M., Golstein P., Rajan T. V. Expression of H-2Db on the cell surface in the absence of detectable beta 2 microglobulin. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):317–322. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter T. A., Zeff R. A., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Rajan T. V. Molecular analysis of an EL4 cell line that expresses H-2Db but not H-2Kb or beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2950–2954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Berissi H., Weissenbach J., Maroteaux L., Fellous M., Revel M. The beta2-microglobulin mRNA in human Daudi cells has a mutated initiation codon but is still inducible by interferon. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):239–243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinsson L., Peterson P. A. Beta 2-microglobulin induces intracellular transport of human class I transplantation antigen heavy chains in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):226–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P., Sizer K. C., Vollmer A. C., Hunkapiller T., Parnes J. R. The T cell differentiation antigen Leu-2/T8 is homologous to immunoglobulin and T cell receptor variable regions. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):591–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Henthorn P. S., Kioussis D., Grosveld F., Smithies O. Unexpected relationships between four large deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Henthorn P. S., Kioussis D., Grosveld F., Smithies O. Unexpected relationships between four large deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Capra J. D. The protein products of the murine 17th chromosome: genetics and structure. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:147–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]