Abstract
Two operators are known to bind Escherichia coli galactose repressor with roughly equal affinity. A study of the control these two operators exert on the two overlapping gal promoters is reported. The experiments rest on a set of mutations specifically constructed to inactivate individual control units of the gal operon and on quantitation of gal promoter activities. Messenger RNAs initiated at one or other of the promoters in a cell-free transcription-translation system were determined by a primer extension assay with synthetic deoxyoligonucleotide primers. The main conclusions are: (i) the classical galactose operator O1, located upstream with respect to the two overlapping promoters is sufficient for negative control of the cAMP activated promoter P1; (ii) complete repression of the second promoter P2, on the other hand, needs the presence of both intact operators O1 and O2. Thus, the two overlapping gal promoters (with only 5 bp separating their respective transcriptional start sites) are both subject to negative control by the galactose repressor. This regulation, however, is exerted by two different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Miller W. Modulation of the two promoters of the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):492–494. doi: 10.1038/279492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Aiba H., de Crombrugghe B. Mutations in the Escherichia coli operon that define two promoters and the binding site of the cyclic AMP receptor protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):211–227. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLauro R., Taniguchi T., Musso R., de Crombrugghe B. Unusual location and function of the operator in the Escherichia coli galactose operon. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):494–500. doi: 10.1038/279494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehring R., Beyreuther K., Wright J. K., Overath P. In vitro and in vivo products of E. coli lactose permease gene are identical. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):537–540. doi: 10.1038/283537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron L., Morse D., Reznikoff W., Beckwith J. Fusions of the lac and trp regions of escherichia coli: covalently fused messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90458-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiethen L., Starlinger P. Mutations in the galactose-operator. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(4):322–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00267769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H. J., Bicknäse H., Gleumes B., Heibach C., Rosahl S., Ehring R. Characterization of two mutations in the Escherichia coli galE gene inactivating the second galactose operator and comparative studies of repressor binding. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2129–2135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M. H., Orosz L., Adhya S. A control element within a structural gene: the gal operon of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer B., Kramer W., Fritz H. J. Different base/base mismatches are corrected with different efficiencies by the methyl-directed DNA mismatch-repair system of E. coli. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A., Adhya S. Demonstration of two operator elements in gal: in vitro repressor binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6100–6104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., McClure W. R. Dual promoter control of the Escherichia coli lactose operon. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
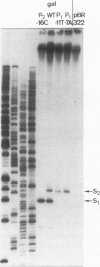
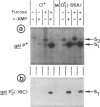
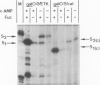
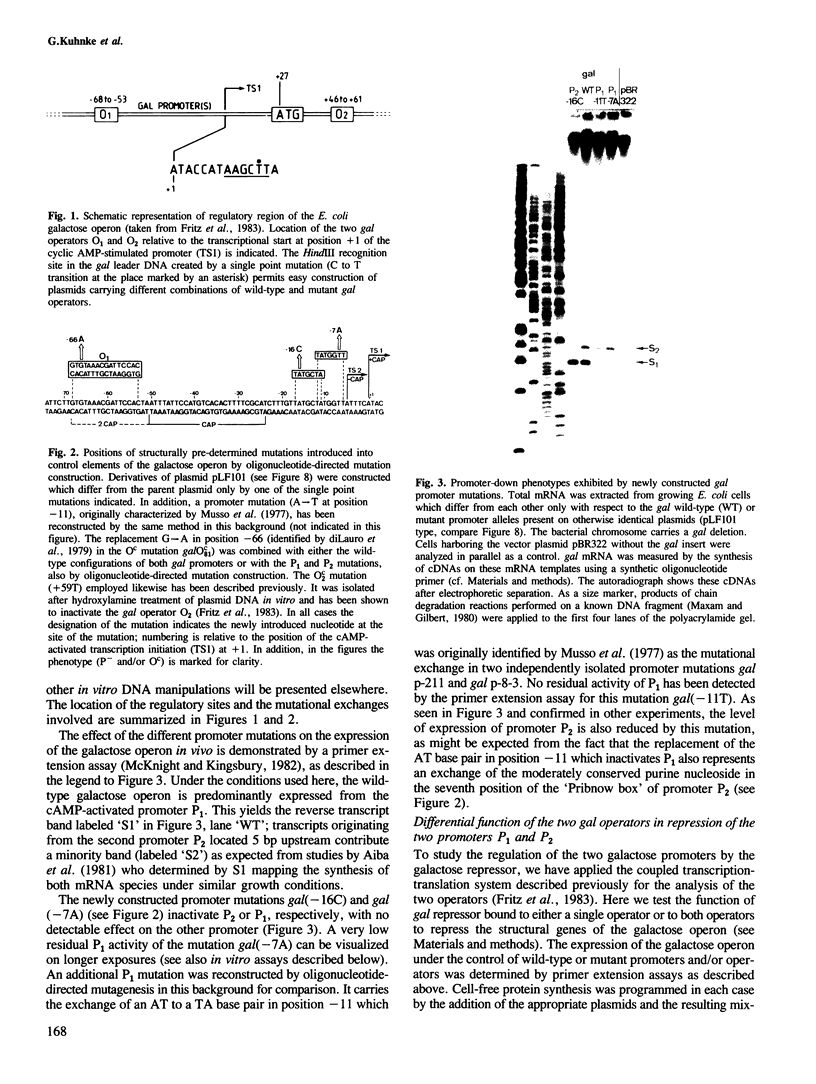
- Musso R. E., Di Lauro R., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Dual control for transcription of the galactose operon by cyclic AMP and its receptor protein at two interspersed promoters. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. J., Belagaje R., Brown E. L., Fritz H. J., Khorana H. G. A synthetic tyrosine suppressor tRNA gene with an altered promoter sequence. Its cloning and relative expression in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10803–10810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanblatt S. H., Revzin A. Two catabolite activator protein molecules bind to the galactose promoter region of Escherichia coli in the presence of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1594–1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., de Crombrugghe B. Interactions of RNA polymerase and the cyclic AMP receptor protein on DNA of the E. coli galactose operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5165–5180. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetekam W., Staack K., Ehring R. DNA-dependent in vitro synthesis of enzymes of the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;112(1):14–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00266928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetekam W., Staack K., Ehring R. Relief of polarity in DNA-dependent cell-free synthesis of enzymes of the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(3):258–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00269770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 3. The Escherichia coli lac repressor--operator interaction: kinetic measurements and conclusions. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6961–6977. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Koenen M., Griesser H. W., Müller-Hill B. 72 residues of gal repressor fused to beta-galactosidase repress the gal operon of E. coli. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1271–1274. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of galR gene indicates a common evolutionary origin of lac and gal repressor in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]