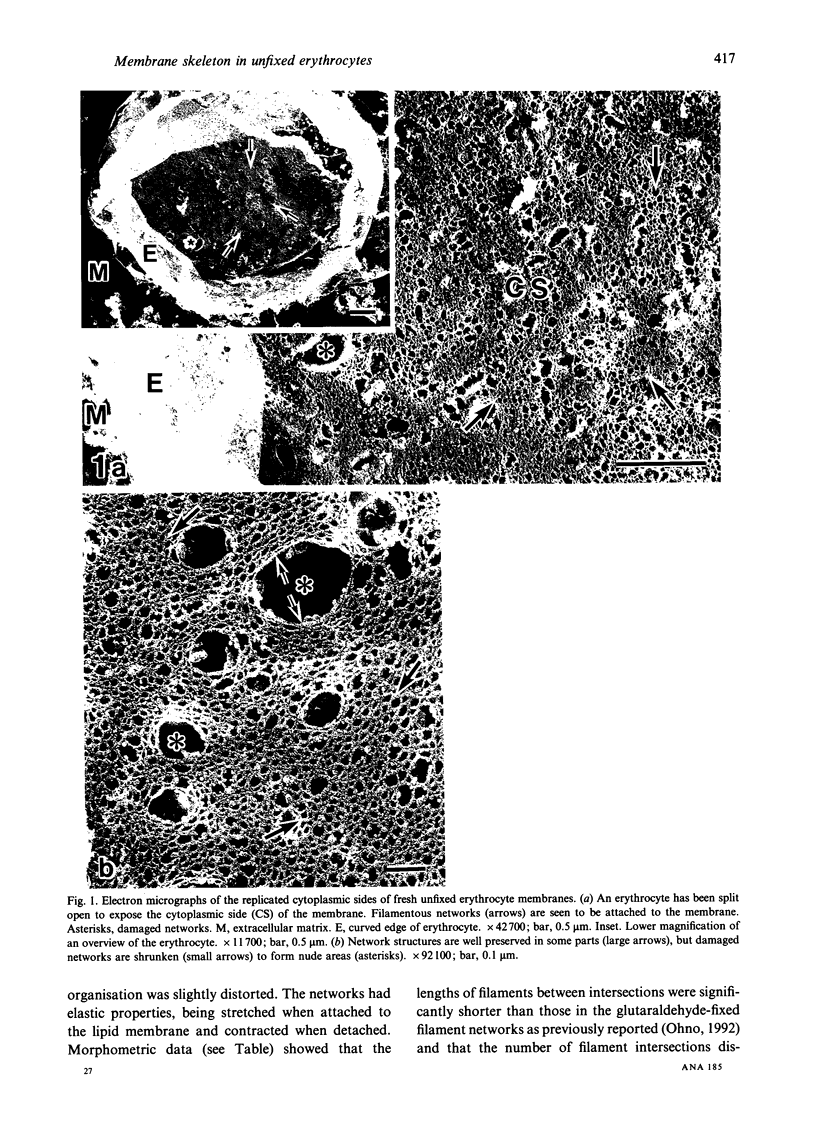
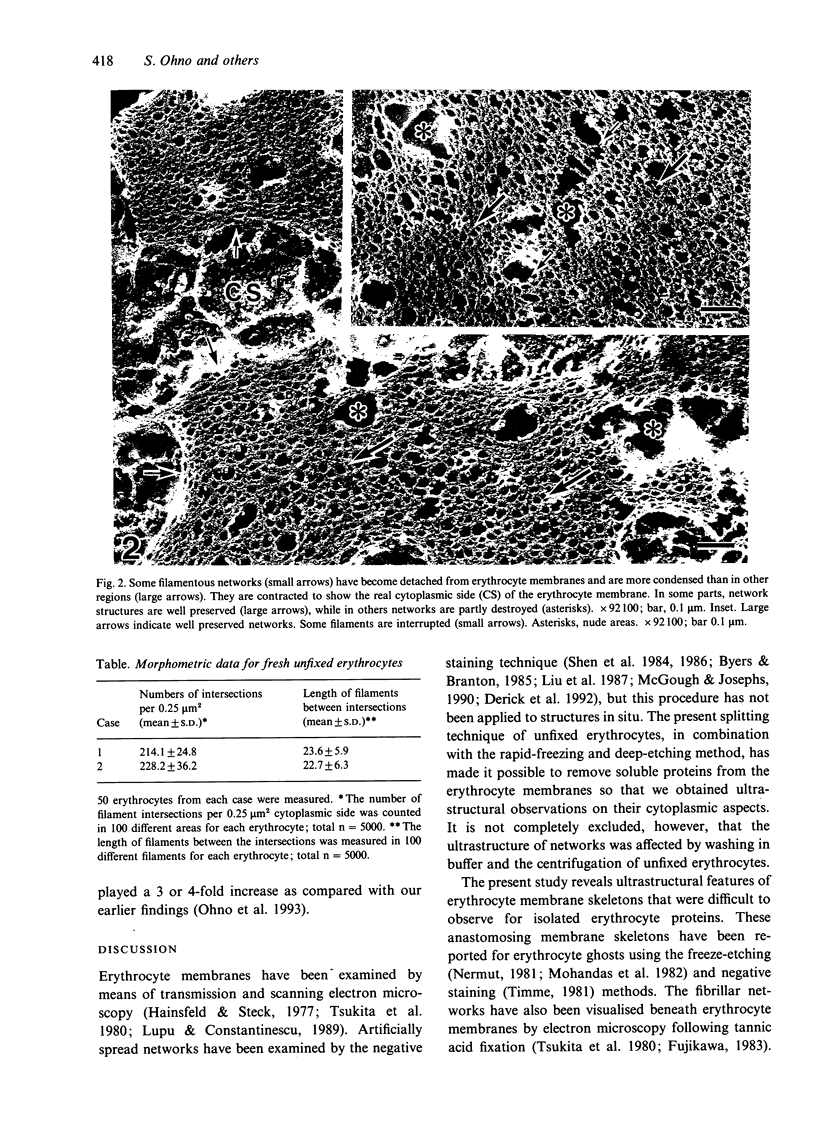
Abstract
A rapid-freezing and deep-etching method for examining en face the cytoplasmic aspects of unfixed erythrocyte membranes is described, which provides improved resolution. Normal human erythrocytes were centrifuged, washed in a phosphate buffer solution and pelleted. Glass coverslips were coated with 3-aminopropyl triethoxy silane and glutaraldehyde to make erythrocytes stick to them. A drop containing the erythrocyte pellet was sandwiched between 2 coverslips. The attached erythrocytes were slowly split open in the cytosol buffer solution. The specimens on coverslips were rapidly frozen in an isopentane-propane mixture (-193 degrees C), deeply etched and rotary shadowed with platinum and carbon. Filamentous structures were observed to form fine networks on the cytoplasmic side of erythrocyte membranes. The length of the filaments was shorter than that previously reported for glutaraldehyde-fixed filaments. The number of intersections between filaments was increased as compared with the previous data. It is concluded that dense in situ networks of short filaments beneath erythrocyte membranes can be viewed in a relatively intact state by splitting fresh unfixed specimens followed by the rapid-freezing and deep-etching method.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. The membrane skeleton of human erythrocytes and its implications for more complex cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:273–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The spectrin-actin junction of erythrocyte membrane skeletons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers T. J., Branton D. Visualization of the protein associations in the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6153–6157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M., Tyler J. M., Branton D. Spectrin-actin associations studied by electron microscopy of shadowed preparations. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):875–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90451-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derick L. H., Liu S. C., Chishti A. H., Palek J. Protein immunolocalization in the spread erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;57(2):317–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa S. Tannic acid improves the visualization of the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton by freeze-etching. J Ultrastruct Res. 1983 Sep;84(3):289–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(83)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Weidner S. A. Binding of spectrin alpha 2-beta 2 tetramers to human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8082–8086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainfeld J. F., Steck T. L. The sub-membrane reticulum of the human erythrocyte: a scanning electron microscope study. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(3):301–311. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Derick L. H., Palek J. Visualization of the hexagonal lattice in the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):527–536. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Windisch P., Kim S., Palek J. Oligomeric states of spectrin in normal erythrocyte membranes: biochemical and electron microscopic studies. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):587–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupu F., Constantinescu E. A new freeze-drying device for platinum replica studies of cell surface and cytoskeleton: an example using immunogold-labeled human erythrocytes. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1989 Jan;11(1):76–82. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060110110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T. The red cell membrane skeleton: recent progress. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGough A. M., Josephs R. On the structure of erythrocyte spectrin in partially expanded membrane skeletons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5208–5212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Wyatt J., Mel S. F., Rossi M. E., Shohet S. B. Lipid translocation across the human erythrocyte membrane. Regulatory factors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6537–6543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V. Visualization of the "membrane skeleton" in human erythrocytes by freeze-etching. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;25(2):265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S. An ultrastructural study of the cytoplasmic aspects of erythrocyte membranes by a quick-freezing and deep-etching method. J Anat. 1992 Apr;180(Pt 2):315–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Terada N., Fujii Y., Ueda H., Kuramoto H., Kamisawa N. Immunocytochemical study of membrane skeletons in abnormally shaped erythrocytes as revealed by a quick-freezing and deep-etching method. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1993;422(1):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01605136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Sawyer D. Triton shells of intact erythrocytes. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(4):399–412. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B. W., Josephs R., Steck T. L. Ultrastructure of the intact skeleton of the human erythrocyte membrane. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):997–1006. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B. W., Josephs R., Steck T. L. Ultrastructure of unit fragments of the skeleton of the human erythrocyte membrane. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):810–821. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D., Burke B., Branton D. The shape of spectrin molecules from human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 26;536(1):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timme A. H. The ultrastructure of the erythrocyte cytoskeleton at neutral and reduced pH. J Ultrastruct Res. 1981 Nov;77(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(81)80041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Tsukita S., Ishikawa H. Cytoskeletal network underlying the human erythrocyte membrane. Thin-section electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):567–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Branton D. Rotary shadowing of extended molecules dried from glycerol. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 May;71(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungewickell E., Gratzer W. Self-association of human spectrin. A thermodynamic and kinetic study. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):379–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursitti J. A., Pumplin D. W., Wade J. B., Bloch R. J. Ultrastructure of the human erythrocyte cytoskeleton and its attachment to the membrane. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;19(4):227–243. doi: 10.1002/cm.970190402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursitti J. A., Wade J. B. Ultrastructure and immunocytochemistry of the isolated human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;25(1):30–42. doi: 10.1002/cm.970250105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Fischman D. A., Steck T. L. Selective solubilization of proteins and phospholipids from red blood cell membranes by nonionic detergents. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):233–248. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]