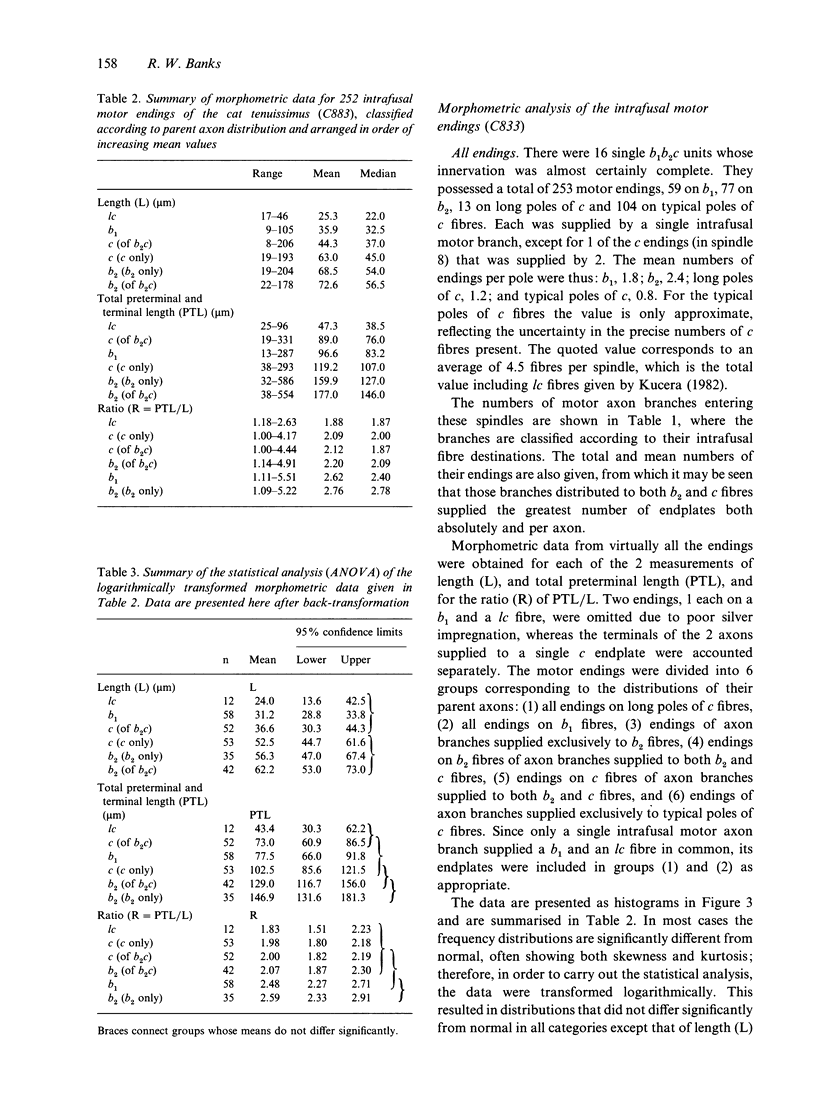
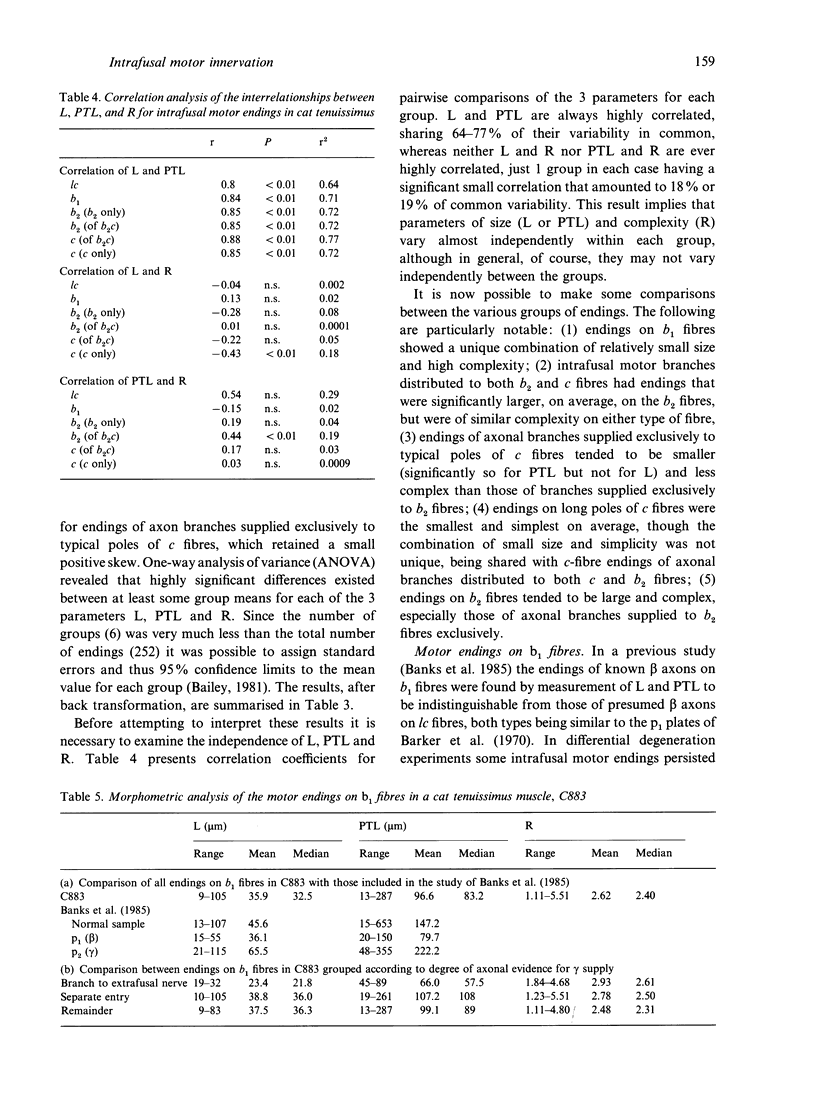
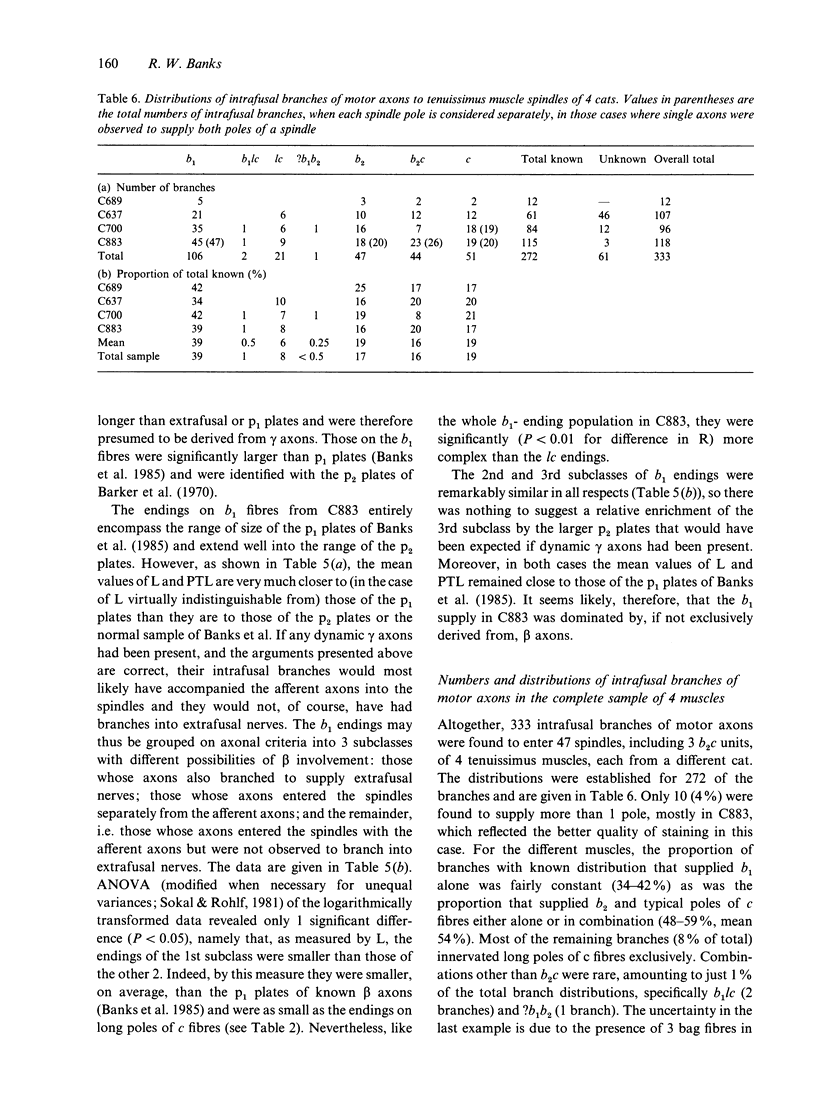
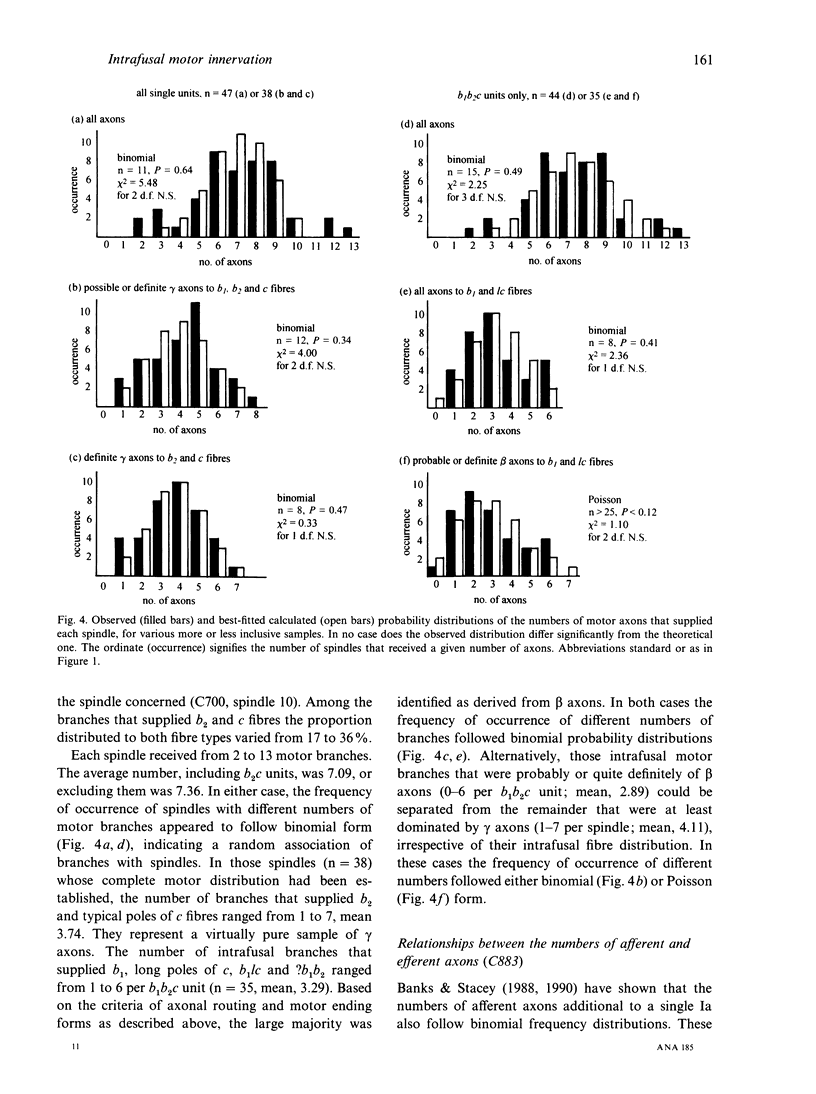
Abstract
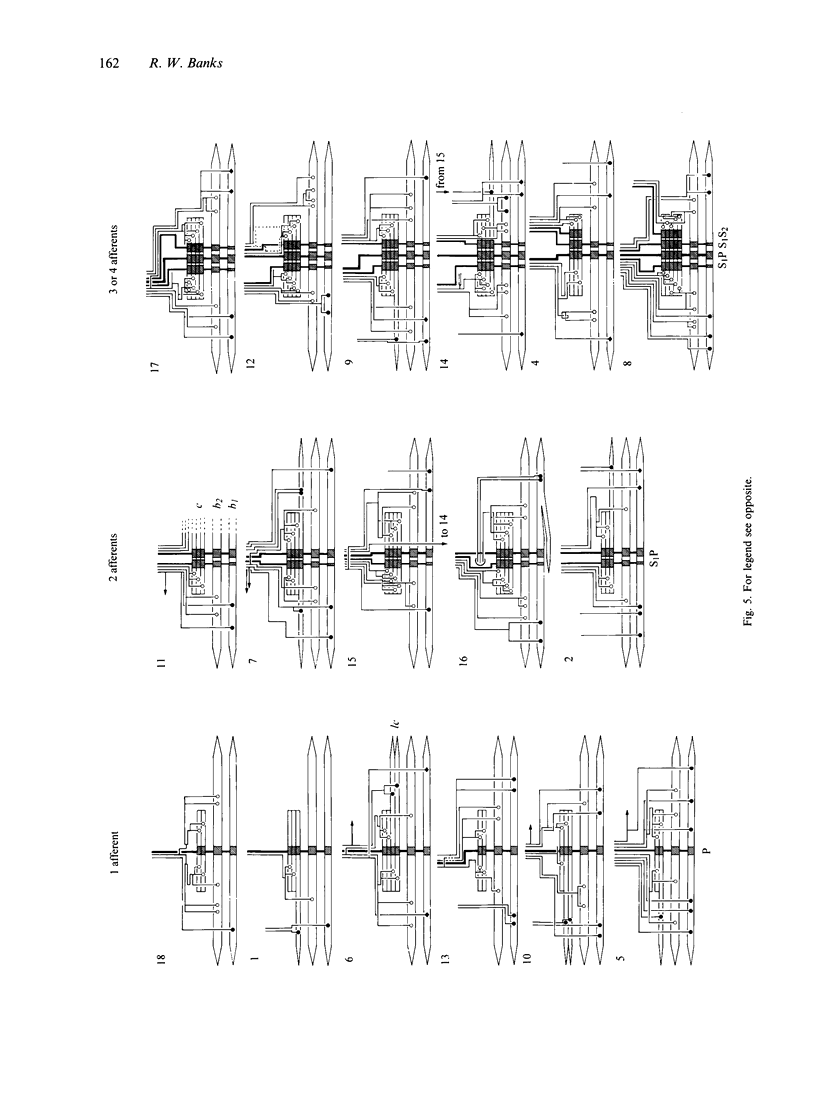
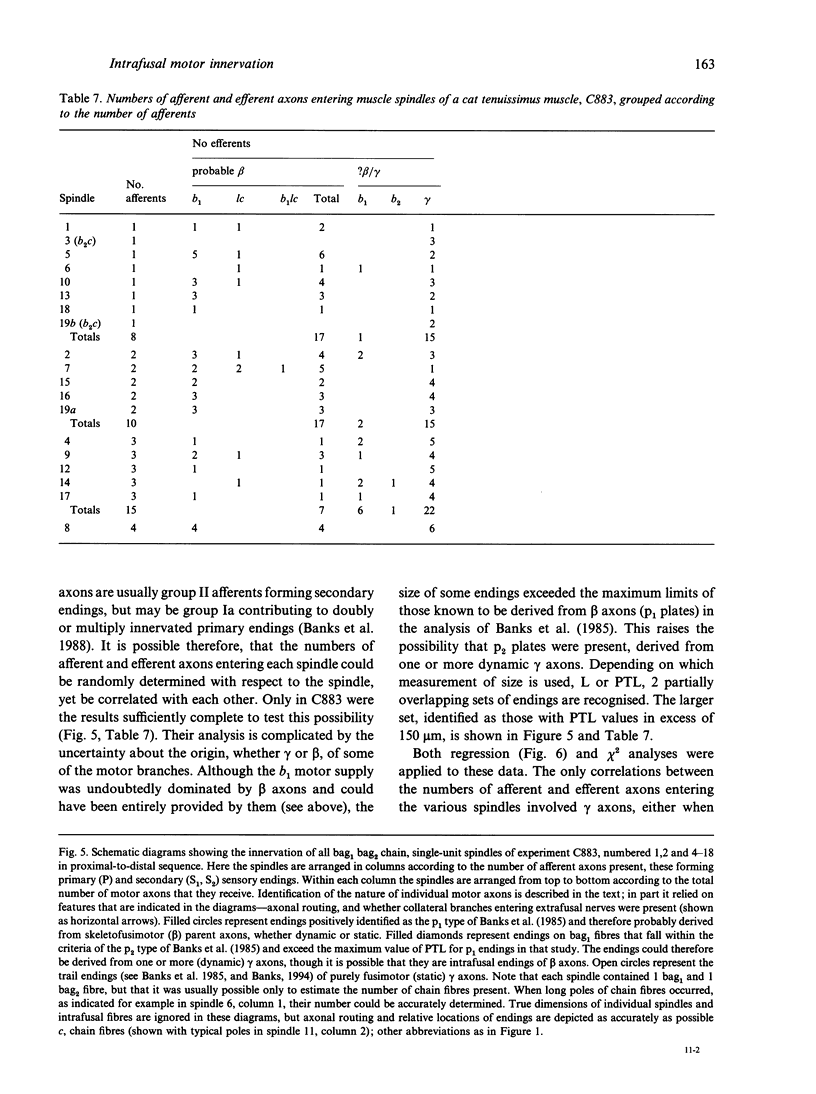
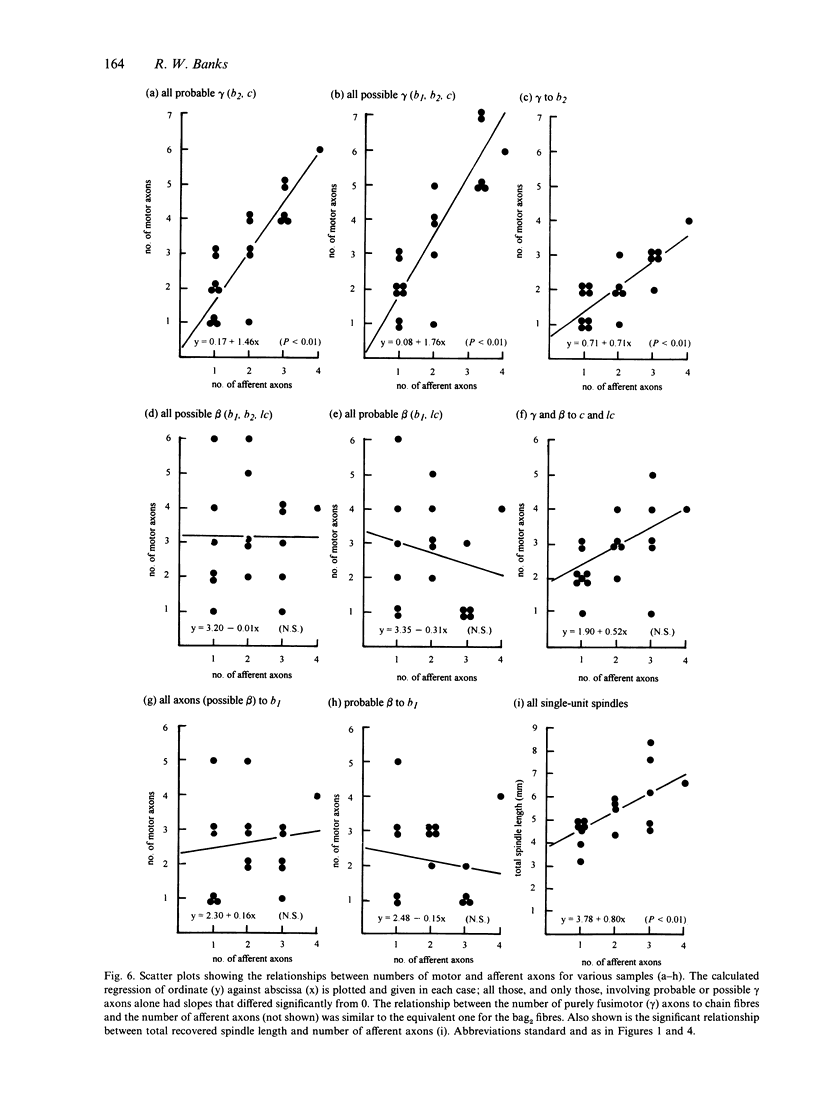
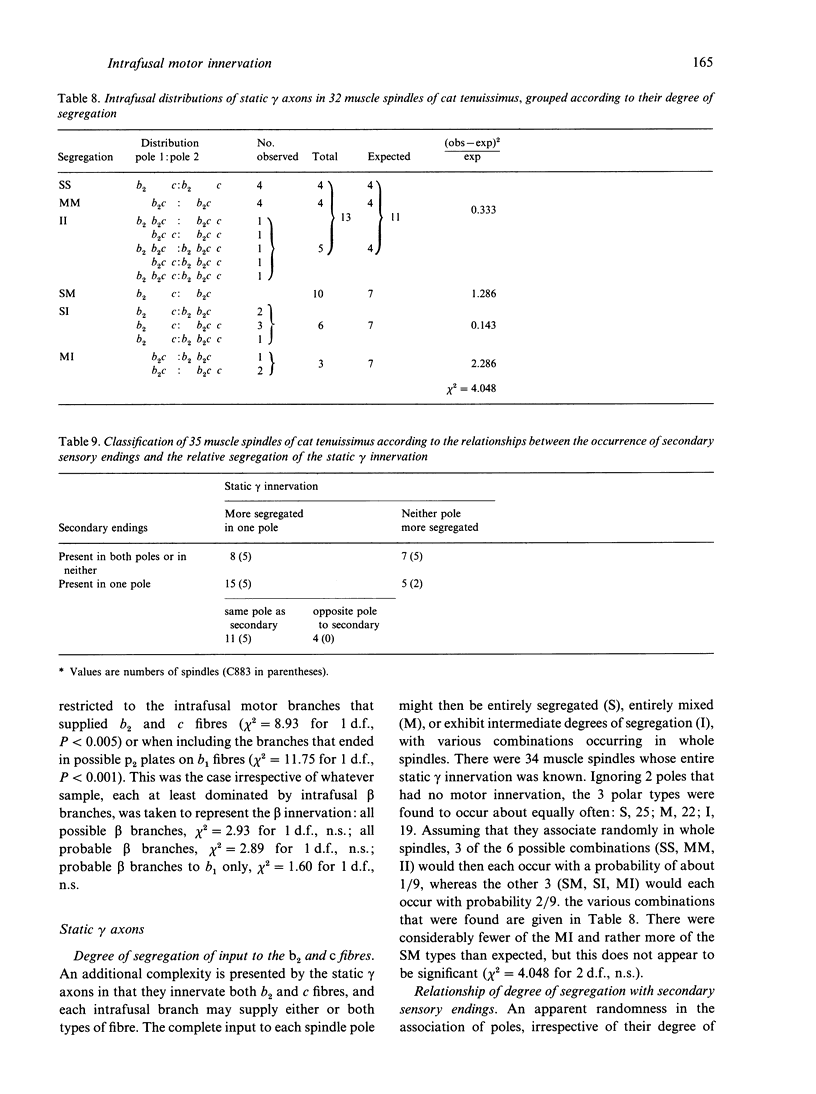
A quantitative analysis of the motor innervation of intrafusal muscle fibres is described, based on teased silver-impregnated spindles of the tenuissimus muscle of the cat. Included in the analysis are the number and distribution of intrafusal branches of both skeletofusimotor (beta) and purely fusimotor (gamma) axons, and the form of their endings. The number of axonal branches per spindle was found to follow binomial probability distributions, as had previously been shown for the afferent axons. There was a strong correlation between the numbers of gamma intrafusal branches and afferent axons, but none for the intrafusal branches of beta axons. The degree of segregation of gamma input to bag2 and chain fibres was assessed and was found, among other things, to be related to the presence of secondary sensory endings in the same pole. In this and other respects it did not appear to have the properties that would be expected if independent activation of the bag2 and chain fibres were to be functionally important. Morphometric analysis of the motor endings supplied to bag2 or chain fibres by gamma axons revealed some differences between those of intrafusal branches with segregated as opposed to unsegregated distributions, but this cannot be taken as evidence of more than one type of static gamma motoneuron because of the likely contribution of other influential factors such as fibre size. Finally, the relevance of studies on intrafusal motor innervation to the concept of the motor unit and its development are discussed.
Full text
PDF
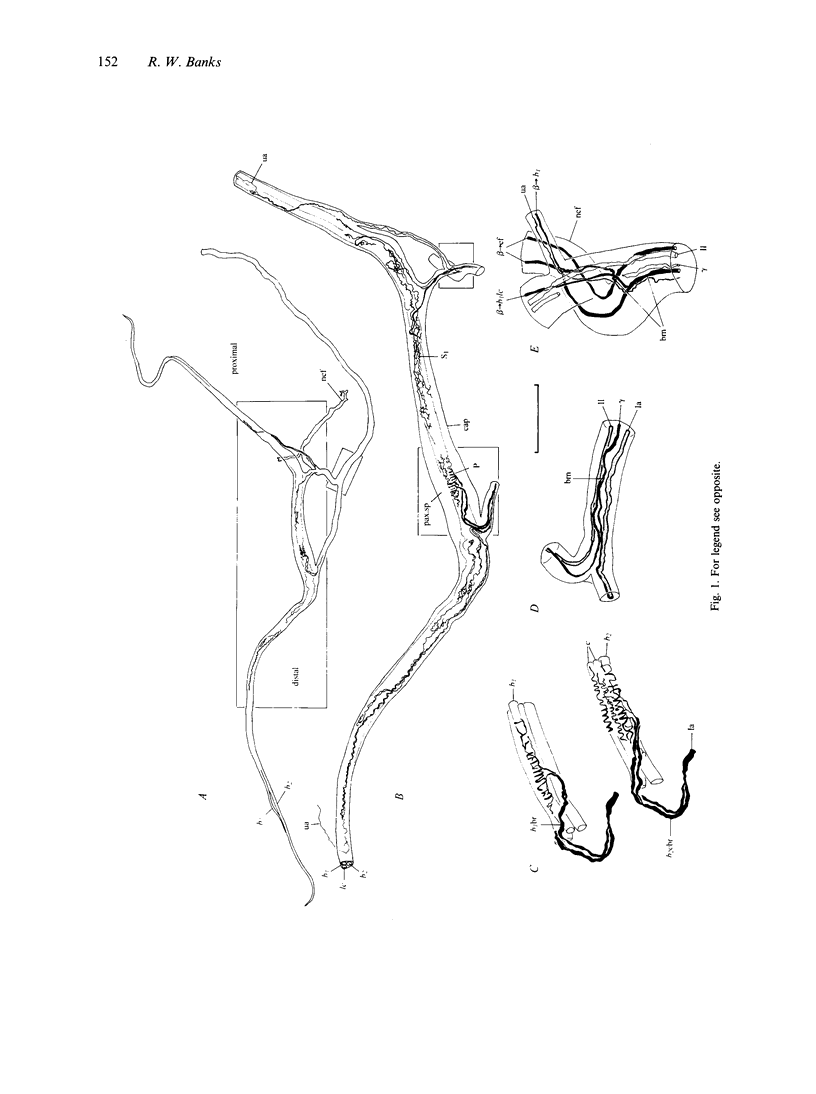

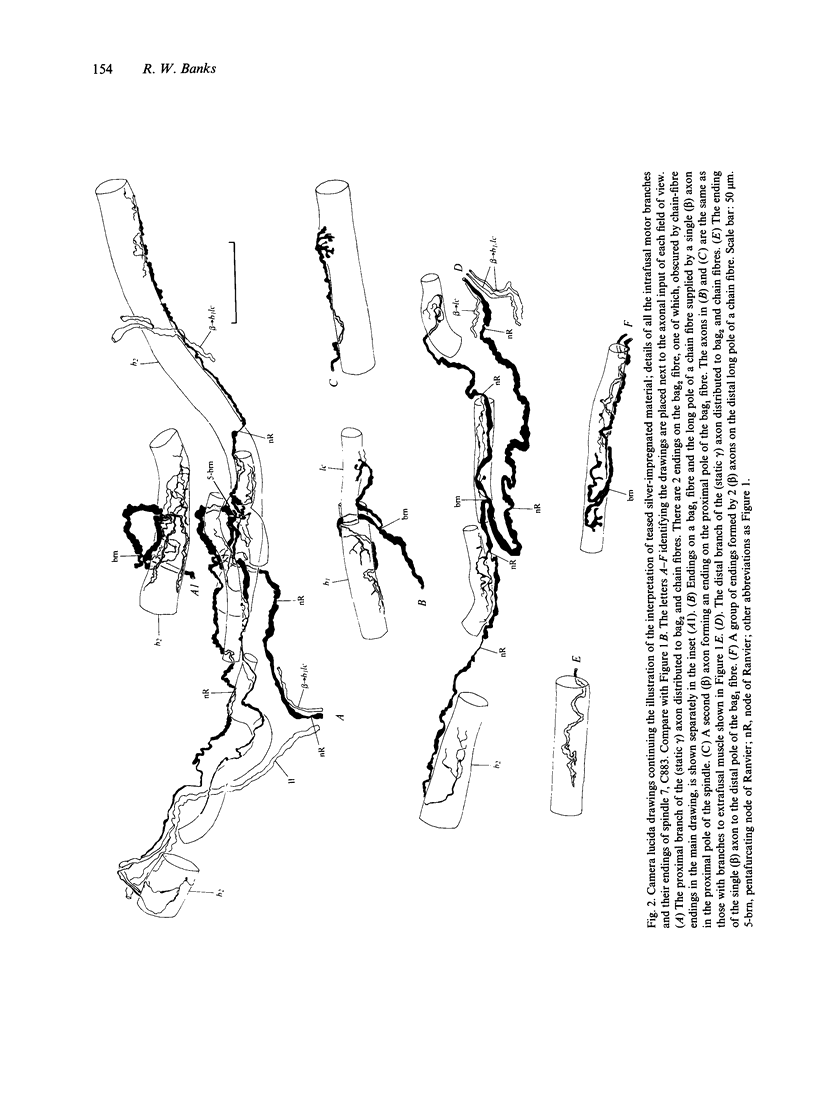


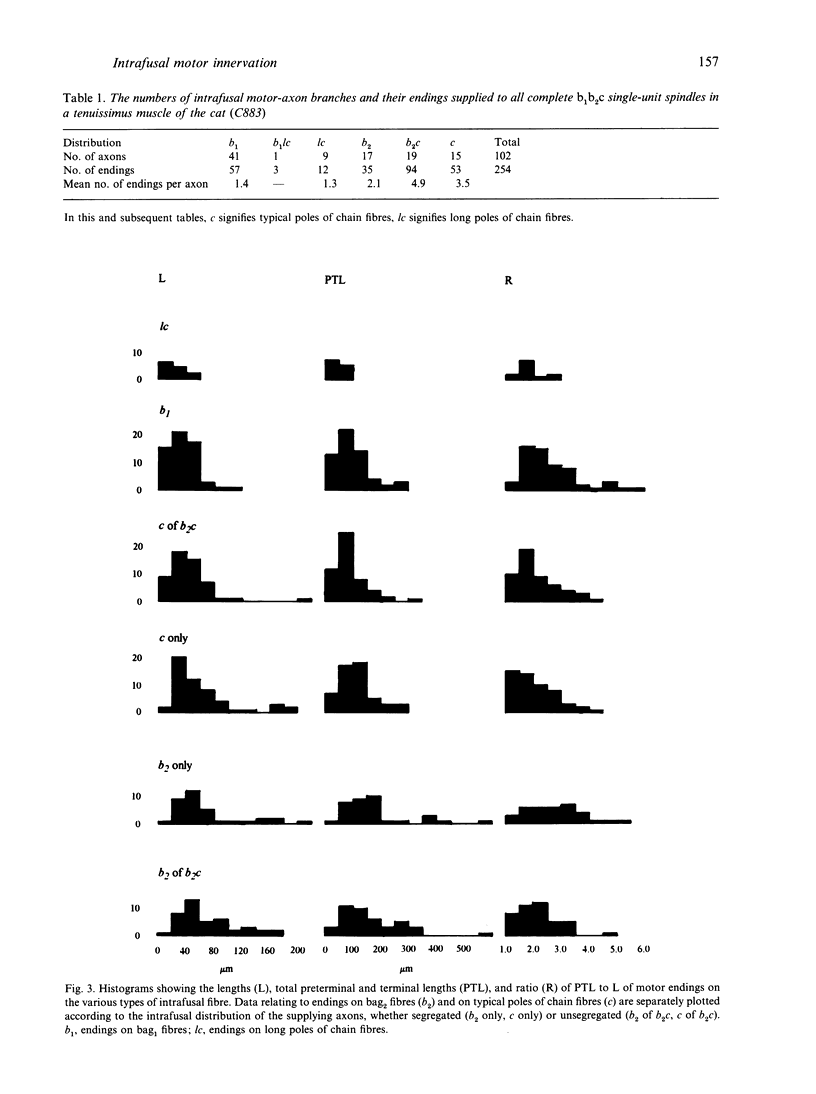







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott E. R., Gladden M. H., Sutherland F. I. Diversity and homogeneity within endplates associated with physiologically identified static gamma-axons in cat tenuissimus muscle. Exp Physiol. 1992 May;77(3):443–453. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W. A histological study of the motor innervation of the cat's muscle spindle. J Anat. 1981 Dec;133(Pt 4):571–591. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W., Barker D., Bessou P., Pagès B., Stacey M. J. Histological analysis of cat muscle spindles following direct observation of the effects of stimulating dynamic and static motor axons. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:605–619. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W., Barker D., Stacey M. J. Form and classification of motor endings in mammalian muscle spindles. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Aug 22;225(1239):195–212. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W., Barker D., Stacey M. J. Form and distribution of sensory terminals in cat hindlimb muscle spindles. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Nov 4;299(1096):329–364. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W. The distribution of static gamma-axons in the tenuissimus muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1991 Oct;442:489–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Banks R. W., Harker D. W., Milburn A., Stacey M. J. Studies of the histochemistry, ultrastructure, motor innervation, and regeneration of mammalian intrafusal muscle fibres. Prog Brain Res. 1976;44:67–88. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60724-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Bessou P., Jankowska E., Pagès B., Stacey M. J. Identification of intrafusal muscle fibres activated by single fusimotor axons and injected with fluorescent dye in cat tenuissimus spindles. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:149–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y. Distribution of fusimotor axons to intrafusal muscle fibres in cat tenuissimus spindles as determined by the glycogen-depletion method. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):49–69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Scott J. J., Stacey M. J. A study of glycogen depletion and the fibre-type composition of cat skeleto-fusimotor units. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:565–579. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Scott J. J., Stacey M. J. Sensory reinnervation of cat peroneus brevis muscle spindles after nerve crush. Brain Res. 1985 Apr 29;333(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A., Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N., Ward J. Control of dynamic and static nuclear bag fibres and nuclear chain fibres by gamma and beta axons in isolated cat muscle spindels. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):133–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A. Two types of static gamma-axon in cat muscle spindles. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Apr;71(2):307–327. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N. The activity of intrafusal muscle fibres during cortical stimulation in the cat [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):28P–29P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N. The activity of intrafusal muscle fibres in anaesthetized, decerebrate and spinal cats [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):49P–50P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H. Structural features relative to the function of intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. Prog Brain Res. 1976;44:51–59. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60722-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jami L., Lan-Couton D., Malmgren K., Petit J. "Fast" and "slow" skeleto-fusimotor innervation in cat tenuissimus spindles; a study with the glycogen-depletion method. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Jul;103(3):284–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jami L., Lan-Couton D., Malmgren K., Petit J. Histophysiological observations on fast skeleto-fusimotor axons. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 23;164:53–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Fladby T. The perinatal reorganization of the innervation of skeletal muscle in mammals. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;34(1):39–90. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90025-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. P., Ridge R. M., Rowlerson A. Rat muscle during post-natal development: evidence in favour of no interconversion between fast- and slow-twitch fibres. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:395–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. P., Ridge R. M., Rowlerson A. The non-selective innervation of muscle fibres and mixed composition of motor units in a muscle of neonatal rat. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:377–394. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J., Hammar K., Meek B. Ultrastructure of dynamic and static skeletofusimotor endings in a cat muscle spindle. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;238(1):151–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00215156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Histochemical study of long nuclear chain fibers in the cat muscle spindle. Anat Rec. 1980 Dec;198(4):567–580. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091980403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Histological identification of (static) skeletofusimotor innervation to a cat muscle spindle. Brain Res. 1984 Mar 5;294(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J., Hughes R. Histological study of motor innervation to long nuclear chain intrafusal fibers in the muscle spindle of the cat. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;228(3):535–547. doi: 10.1007/BF00211474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Morphometric studies on tenuissimus muscle spindles in the cat. J Morphol. 1982 Feb;171(2):137–150. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051710203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J., Walro J. M. Factors that determine the form of neuromuscular junctions of intrafusal fibers in the cat. Am J Anat. 1986 May;176(1):97–117. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001760108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J., Walro J. M. Origin of intrafusal muscle fibers in the rat. Histochemistry. 1990;93(6):567–580. doi: 10.1007/BF00272199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J., Walro J. M., Reichler J. Innervation of developing intrafusal muscle fibers in the rat. Am J Anat. 1988 Dec;183(4):344–358. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001830408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS P. B. The differentiation of two types of fusimotor fibre by their effects on the dynamic response of muscle spindle primary endings. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1962 Oct;47:324–333. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1962.sp001616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn A. Stages in the development of cat muscle spindles. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1984 Aug;82:177–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. R., Hammond G. R. The locomotor discharge characteristics of ankle flexor gamma-motoneurones in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:59–70. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. R., Stein R. B., Taylor J. Phasic and tonic modulation of impulse rates in gamma-motoneurons during locomotion in premammillary cats. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Aug;52(2):228–243. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.52.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walro J. M., Kucera J. Motor innervation of intrafusal fibers in rat muscle spindles: incomplete separation of dynamic and static systems. Am J Anat. 1985 May;173(1):55–68. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001730105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]