Abstract
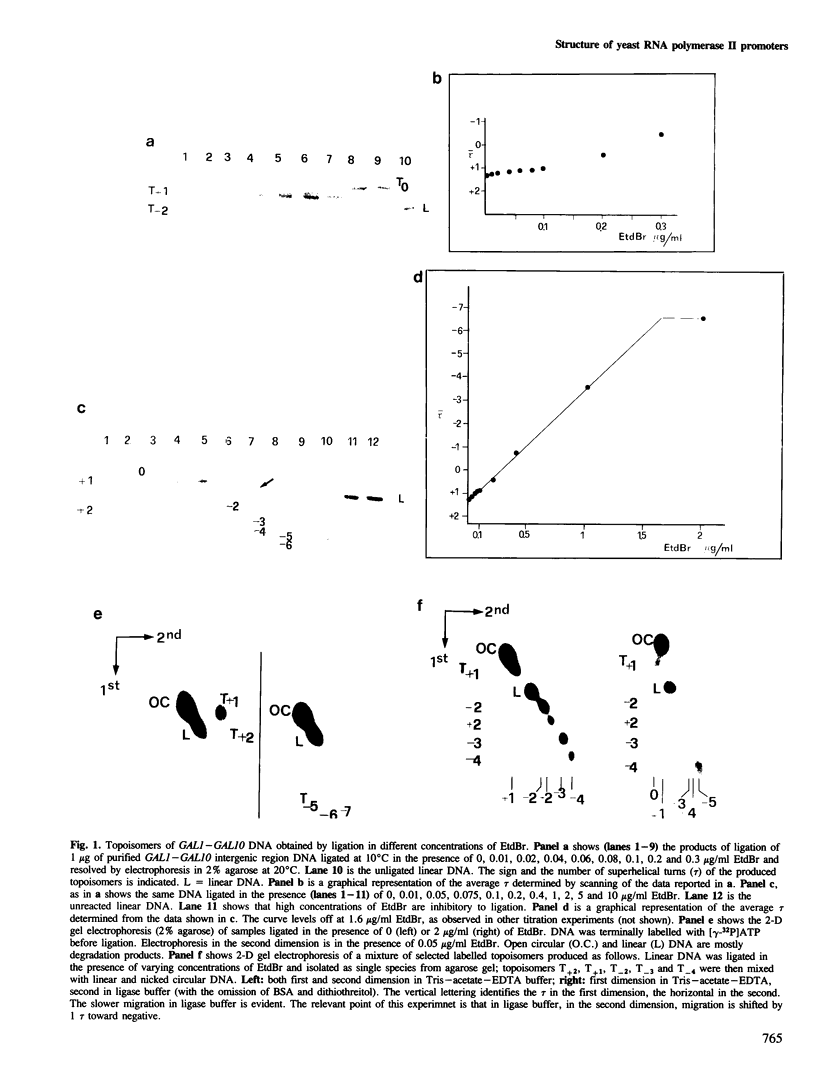
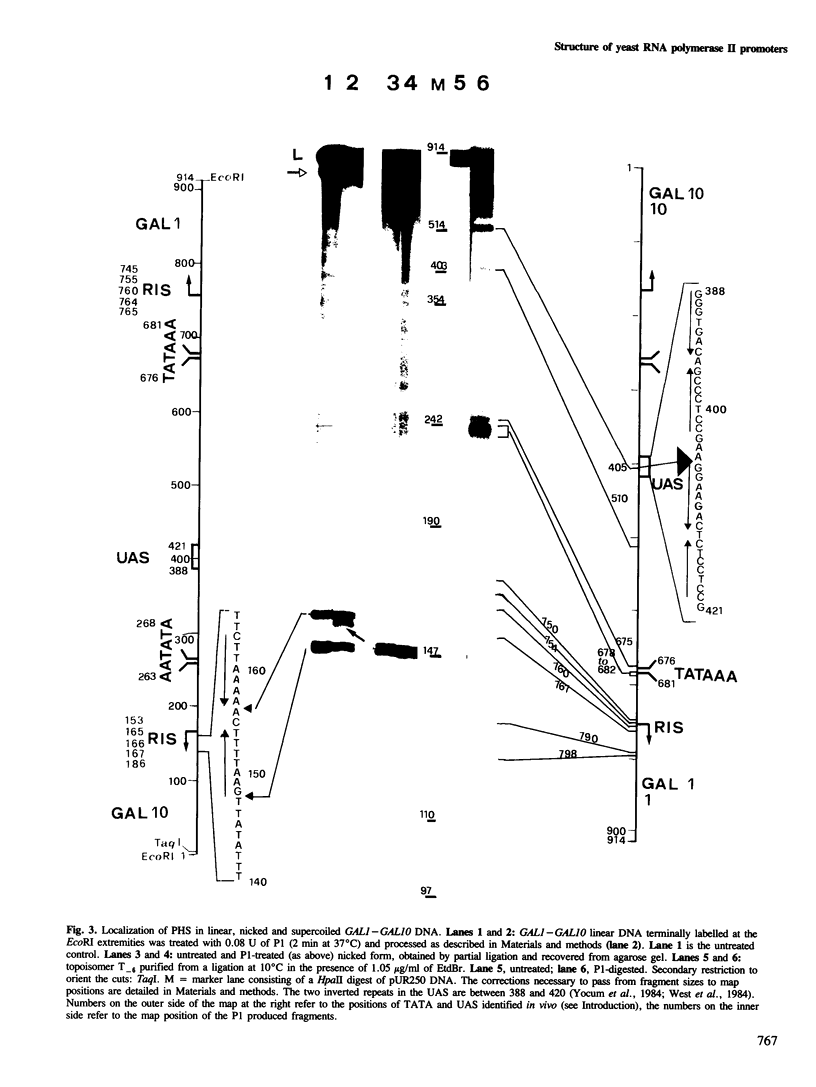
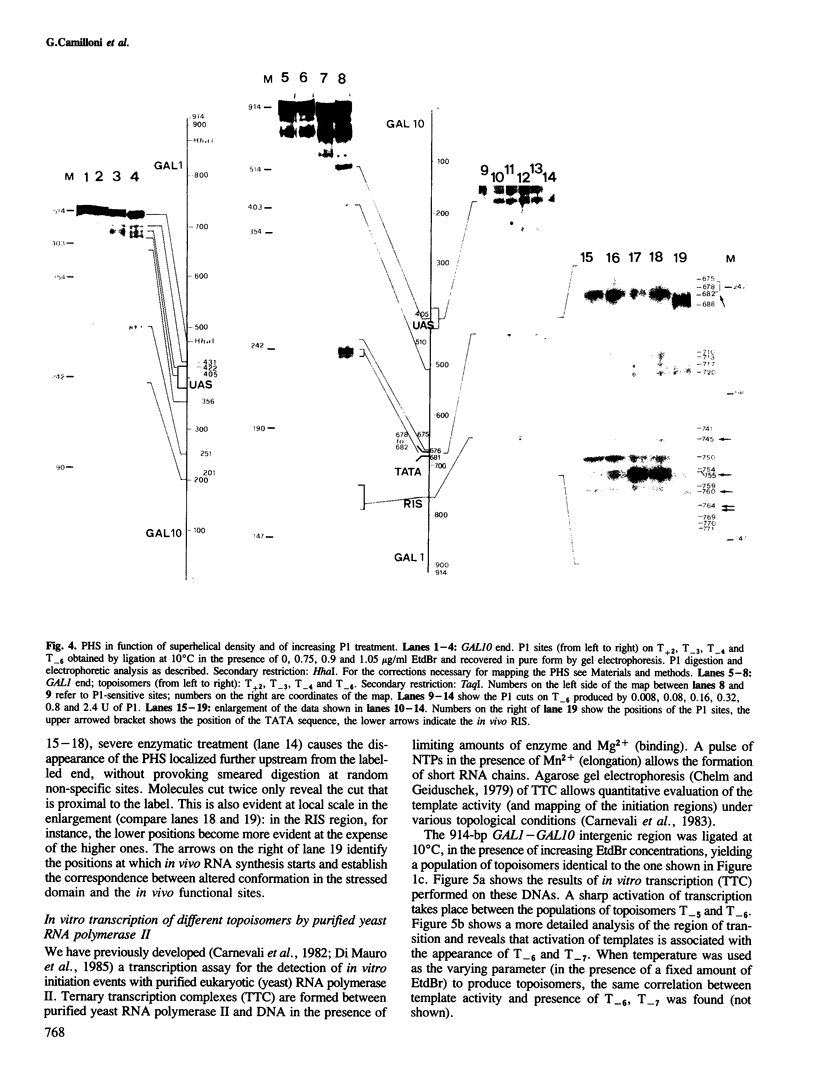
A DNA fragment encompassing the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1--GAL10 divergent promoters (914 bp) has been circularized in vitro with T4 DNA ligase. We have defined a set of conditions that allows the production of a series of nine topoisomers covering a range from relaxed to highly negatively supercoiled DNA. Topoisomers were recovered in pure form from agarose gels and were analysed singly for the presence of sites sensitive to the single strand-specific endonuclease Pl. In this way, the occurrence of conformational alterations as a function of the linking deficiency of the closed DNA domain has been determined. Interestingly, sites of Pl hypersensitivity localize on the three sequences identified as relevant for the in vitro transcription of the GAL1 moiety of the divergent promoter: the upstream activator sequence (UAS), the TATA sequence, and the RNA initiation site (RIS). In vitro transcription with purified S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase II shows that activation of transcription parallels the appearance of conformational alterations on the UAS, the TATA and the RIS sequences.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J., Feldman J., Nasmyth K. A., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Broach J. R., Hicks J. B. Sites required for position-effect regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):989–998. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akrigg A., Cook P. R. DNA gyrase stimulates transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):845–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballario P., Buongiorno-Nardelli M., Carnevali F., Di Mauro E., Pedone F. Selective in vitro transcription by purified yeast RNA polymerase II on cloned 2 micron DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3959–3978. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. J. Stable cruciform formation at inverted repeat sequences in supercoiled DNA. Biopolymers. 1982 Mar;21(3):679–696. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. J. Statistical mechanical analysis of competing conformational transitions in superhelical DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):219–227. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Worcel A. Isolation, characterization, and structure of the folded interphase genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina-Stein M., Vogel T., Singer D. S., Singer M. F. H5 Histone and DNA-relaxing enzyme of chicken erythrocytes. Interaction with superhelical DNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7363–7366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A bacterial repressor protein or a yeast transcriptional terminator can block upstream activation of a yeast gene. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):612–615. doi: 10.1038/312612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Efstratiadis A. Possible structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine S1-hypersensitive sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8059–8072. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnevali F., Caserta M., Di Mauro E. In vitro transcription by purified yeast RNA polymerase II. Coarse promoter mapping on homologous cloned genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3195–3209. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnevali F., Caserta M., Di Mauro E. Topological modifications and template activation are induced in chimaeric plasmids by inserted sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 25;165(1):59–77. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnevali F., Caserta M., Di Mauro E. Transitions in topological organization of supercoiled DNA domains as a potential regulatory mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12633–12643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelm B. K., Geiduschek E. P. Gel electrophoretic separation of transcription complexes: an assay for RNA polymerase selectivity and a method for promoter mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1851–1867. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Wang J. C. Cruciform formation in a negatively supercoiled DNA may be kinetically forbidden under physiological conditions. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew D. E., Wang J. C. Conformational fluctuations of DNA helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Mauro E., Caserta M., Negri R., Carnevali F. Activation of in vitro transcription and topology of closed DNA domains. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):152–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Sternglanz R., Reynolds A. E., Wright A. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants have compensatory mutations in DNA gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Anatomy of hypersensitive sites. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):213–214. doi: 10.1038/309213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Schon E., Gora-Maslak G., Patterson J., Efstratiadis A. S1-hypersensitive sites in eukaryotic promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8043–8058. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Mizuuchi K. Slow cruciform transitions in palindromic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5545–5549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Weintraub H., McKnight S. L. Transcription of circular and linear DNAs in amphibian oocytes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):958–963. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Hopper J. E. Isolation of the yeast regulatory gene GAL4 and analysis of its dosage effects on the galactose/melibiose regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Characterization of purified DNA-relaxing enzyme from human tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2550–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Asai K. Reverse gyrase--a topoisomerase which introduces positive superhelical turns into DNA. Nature. 1984 Jun 21;309(5970):677–681. doi: 10.1038/309677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski D. Changes in site specificity of single-strand-specific endonucleases on supercoiled PM2 DNA with temperature and ionic environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7071–7086. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Cheng S. M., Adolph K. W., Paulson J. R., Brown J. A., Baumbach W. R. Metaphase chromosome structure: the role of nonhistone proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):351–360. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the GAL4 gene, a positive regulator of transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6827–6831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bret M. Catastrophic variation of twist and writhing of circular DNAs with constraint? Biopolymers. 1979 Jul;18(7):1709–1725. doi: 10.1002/bip.1979.360180710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescure B., Williamson V., Sentenac A. Efficient and selective initiation by yeast RNA polymerase B in a dinucleotide-primed reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):31–45. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. Eukaryotic genes--are they under torsional stress? Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):276–277. doi: 10.1038/305276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. Hairpin-loop formation by inverted repeats in supercoiled DNA is a local and transmissible property. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1271–1289. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace H. A., Pelham H. R., Travers A. A. Association of an S1 nuclease-sensitive structure with short direct repeats 5' of Drosophila heat shock genes. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):555–557. doi: 10.1038/304555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. DNA conformation at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porschke D., Hillen W., Takahashi M. The change of DNA structure by specific binding of the cAMP receptor protein from rotation diffusion and dichroism measurements. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2873–2878. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. C., Reeder R. H. Effect of topological constraint on transcription of ribosomal DNA in Xenopus oocytes. Comparison of plasmid and endogenous genes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):121–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90368-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Manes S. H., Drlica K. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants: increased supercoiling is corrected by mutations near gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F., Gottesfeld J. M. 5S rRNA gene transcription factor IIIA alters the helical configuration of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1862–1866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A. Right-handed and left-handed DNA: conformational information in genetic material. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):1–12. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selleck S. B., Elgin S. C., Cartwright I. L. Supercoil-dependent features of DNA structure at Drosophila locus 67B1. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 5;178(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Baldwin R. L. Energetics of DNA twisting. I. Relation between twist and cyclization probability. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):957–981. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Baldwin R. L. Energetics of DNA twisting. II. Topoisomer analysis. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):983–1007. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. DNA supercoiling: another level for regulating gene expression. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd J., Lebowitz J., Watson R. Early and late helix-coil transitions in closed circular DNA. The number of superhelical turns in polyoma DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):173–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Anshelevich V. V., Lukashin A. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Statistical mechanics of supercoils and the torsional stiffness of the DNA double helix. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):294–298. doi: 10.1038/280294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Peck L. J., Becherer K. DNA supercoiling and its effects on DNA structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):85–91. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Goodman T. C., Hillen W., Horn G. T., Klein R. D., Larson J. E., Müller U. R., Neuendorf S. K., Panayotatos N., Stirdivant S. M. DNA structure and gene regulation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:167–267. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60674-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Hanley S., West R., Jr, Ptashne M. Use of lacZ fusions to delimit regulatory elements of the inducible divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1985–1998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]