Abstract
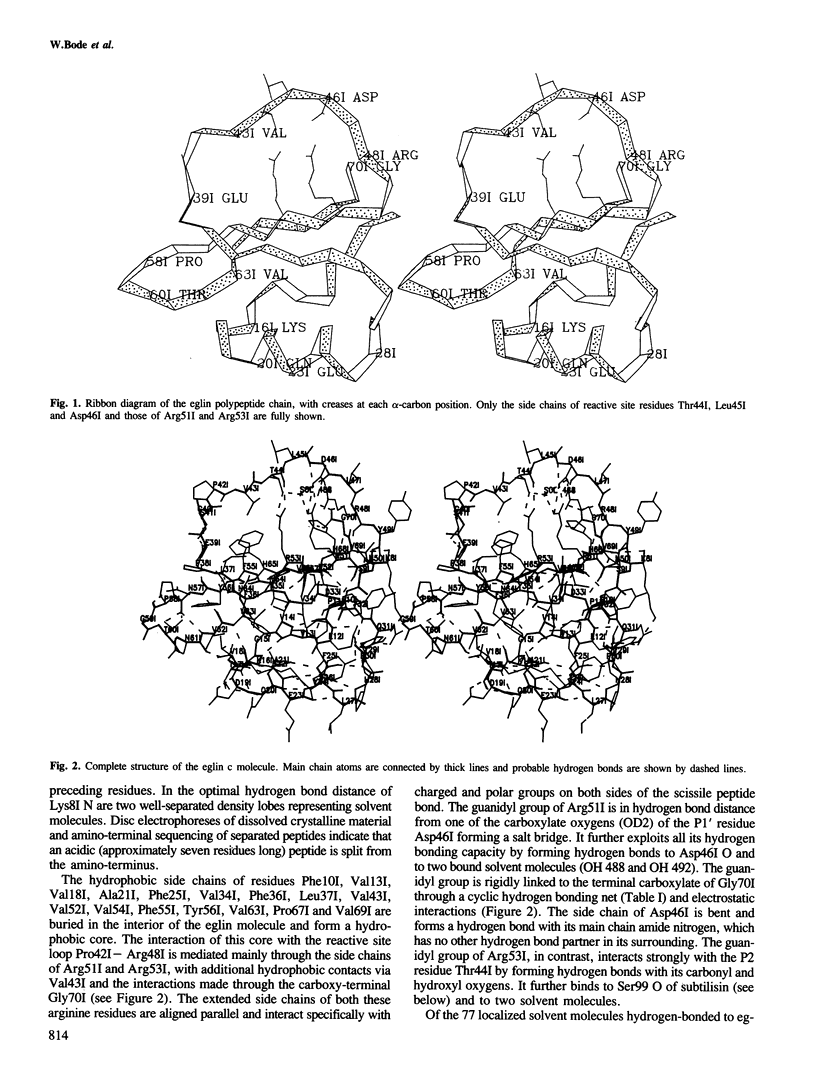
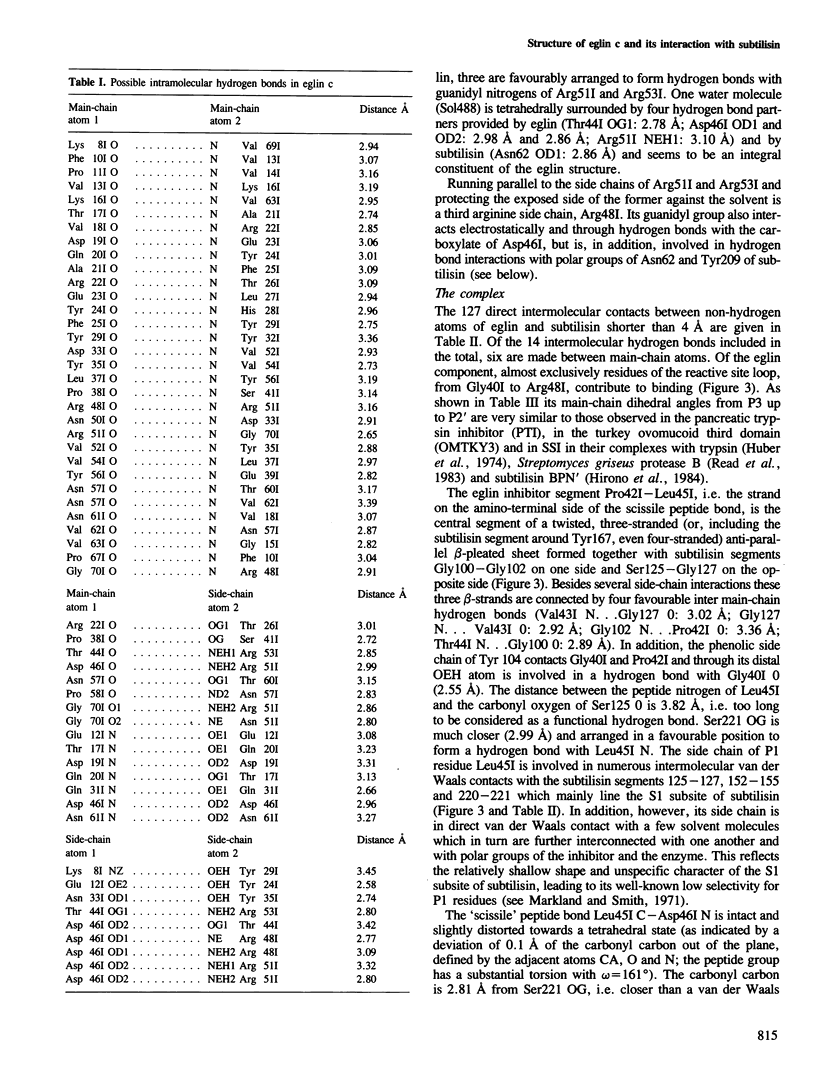
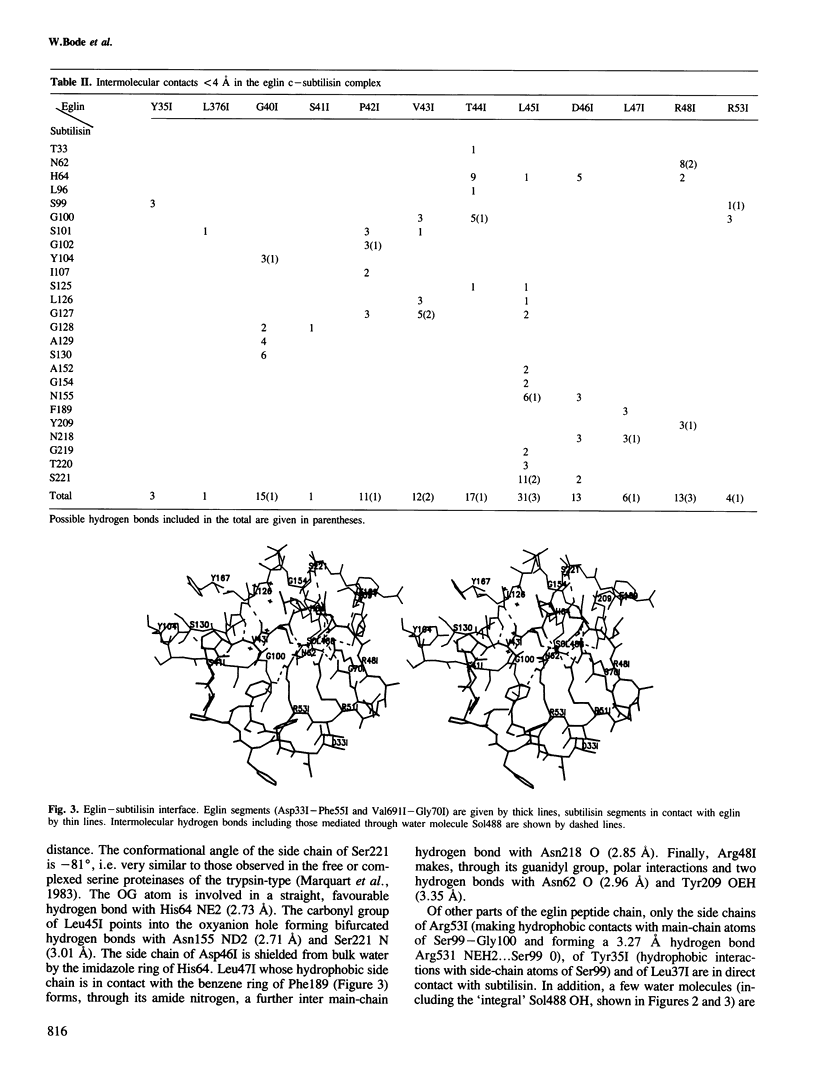
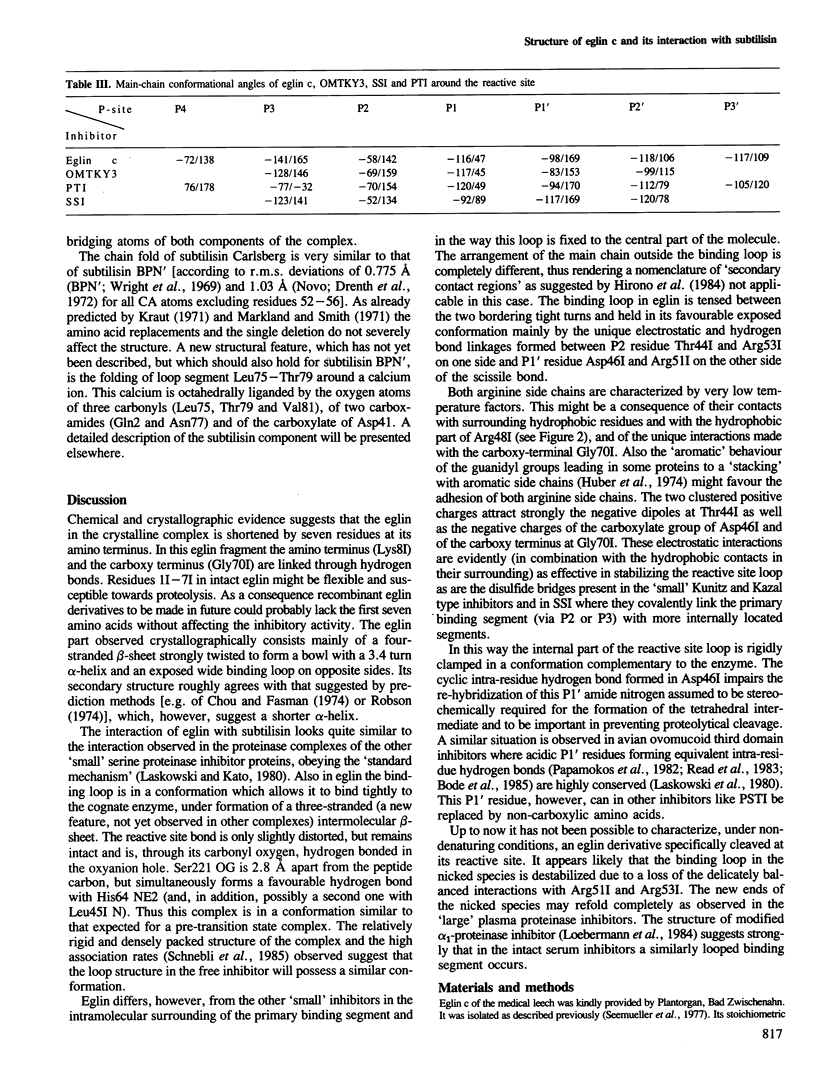
The crystal structure of the complex formed between eglin c, an elastase inhibitor from the medical leech, and subtilisin Carlsberg has been determined at 1.2 A resolution by a combination of Patterson search methods and isomorphous replacement techniques. The structure has been refined to a crystallographic R-value of 0.18 (8-1.2 A). Eglin consists of a four-stranded beta-sheet with an alpha-helical segment and the protease-binding loop fixed on opposite sides. This loop, which contains the reactive site Leu45I--Asp46I, is mainly held in its conformation by unique electrostatic/hydrogen bond interactions of Thr44I and Asp46I with the side chains of Arg53I and Arg51I which protrude from the hydrophobic core of the molecule. The conformation around the reactive site is similar to that found in other proteinase inhibitors. The nine residues of the binding loop Gly40I--Arg48I are involved in direct contacts with subtilisin. In this interaction, eglin segment Pro42I--Thr44I forms a three-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet with subtilisin segments Gly100--Gly102 and Ser125--Gly127. The reactive site peptide bond of eglin is intact, and Ser221 OG of the enzyme is 2.81 A apart from the carbonyl carbon.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Epp O., Huber R., Laskowski M., Jr, Ardelt W. The crystal and molecular structure of the third domain of silver pheasant ovomucoid (OMSVP3). Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):387–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Schirmer T. Determination of the protein content of crystals formed by Mastigocladus laminosus C-phycocyanin, Chroomonas spec. phycocyanin-645 and modified human fibrinogen using an improved Ficoll density gradient method. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Mar;366(3):287–295. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.1.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. Y., Knecht R., Maschler R., Seemüller U. Elastase-cathepsin G inhibitors eglin b and eglin c differ by a single Tyr----His substitution. A micro-method for the identification of amino-acid substitution. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Mar;366(3):281–286. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.1.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenth J., Hol W. G., Jansonius J. N., Koekoek R. Subtilisin Novo. The three-dimensional structure and its comparison with subtilisin BPN'. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 27;26(2):177–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirono S., Akagawa H., Mitsui Y., Iitaka Y. Crystal structure at 2.6 A resolution of the complex of subtilisin BPN' with streptomyces subtilisin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):389–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Kukla D., Bode W., Schwager P., Bartels K., Deisenhofer J., Steigemann W. Structure of the complex formed by bovine trypsin and bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. II. Crystallographic refinement at 1.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):73–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesk A. M., Hardman K. D. Computer-generated schematic diagrams of protein structures. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):539–540. doi: 10.1126/science.7071602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebermann H., Tokuoka R., Deisenhofer J., Huber R. Human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Crystal structure analysis of two crystal modifications, molecular model and preliminary analysis of the implications for function. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):531–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhalen C. A., Schnebli H. P., James M. N. Crystal and molecular structure of the inhibitor eglin from leeches in complex with subtilisin Carlsberg. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 19;188(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80873-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamokos E., Weber E., Bode W., Huber R., Empie M. W., Kato I., Laskowski M., Jr Crystallographic refinement of Japanese quail ovomucoid, a Kazal-type inhibitor, and model building studies of complexes with serine proteases. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):515–537. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read R. J., Fujinaga M., Sielecki A. R., James M. N. Structure of the complex of Streptomyces griseus protease B and the third domain of the turkey ovomucoid inhibitor at 1.8-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4420–4433. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink H., Liersch M., Sieber P., Meyer F. A large fragment approach to DNA synthesis: total synthesis of a gene for the protease inhibitor eglin c from the leech Hirudo medicinalis and its expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6369–6387. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson B. Analysis of code relating sequences to conformation in globular prtoeins. Theory and application of expected information. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):853–867. doi: 10.1042/bj1410853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnebli H. P., Seemüller U., Fritz H., Maschler R., Liersch M., Virca G. D., Bodmer J. L., Snider G. L., Lucey E. C., Stone P. G. Eglin c, a pharmacologically active elastase inhibitor. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1985;139:66–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemüller U., Eulitz M., Fritz H., Strobl A. Structure of the elastase-cathepsin G inhibitor of the leech Hirudo medicinalis. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Dec;361(12):1841–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemüller U., Meier M., Ohlsson K., Müller H. P., Fritz H. Isolation and characterisation of a low molecular weight inhibitor (of chymotrypsin and human granulocytic elastase and cathepsin G) from leeches. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Sep;358(9):1105–1107. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.2.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. L., DeLange R. J., Evans W. H., Landon M., Markland F. S. Subtilisin Carlsberg. V. The complete sequence; comparison with subtilisin BPN'; evolutionary relationships. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2184–2191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. S., Alden R. A., Kraut J. Structure of subtilisin BPN' at 2.5 angström resolution. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):235–242. doi: 10.1038/221235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


