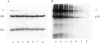Abstract
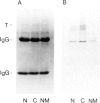
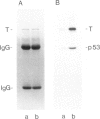
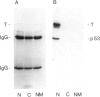
Large T antigen (large T) extracted from SV40-infected or transformed cells exhibits an in vitro protein kinase activity, whose origin and biological significance up to now had been obscure. We have addressed the questions of whether this activity is intrinsic to large T or arises by association with a cellular kinase, and, furthermore, whether this activity might play a biological role in vivo. Instead of analyzing large T from whole-cell lysates, where non-specific association of a cellular kinase(s) with large T might easily occur, we analyzed individual cellular subclasses of large T, isolated from their in vivo locations. In contrast to large T isolated from whole-cell lysates which was always kinase positive, none of the cellular subclasses of large T prepared by in situ fractionation of SV40-transformed mKSA cells exhibited detectable in vitro kinase activity. We could demonstrate that our fractionation conditions neither inactivated the large T-associated kinase activity nor dissociated it from large T when they were applied to kinase-positive large T isolated from whole-cell lysates. We conclude that large T does not contain an intrinsic kinase activity. This conclusion was further supported by our finding that it was possible to remove the large T-associated kinase activity from kinase-positive large T preparations and to reconstitute it by incubating the kinase-negative large T with cell lysates from various cell lines. Therefore, the simplest way of interpreting our results is that the in vitro kinase activity measured with large T preparations from whole-cell lysates is the result of an in vitro association of a cellular kinase(s) with large T during certain conditions of cell lysis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann E. A., Hand R. Protein kinase activity associated with the D2 hybrid protein related to simian virus 40 T antigen: some characteristics of the reaction products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3688–3692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Viral oncogenes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. Relationship of oligomerization to enzymatic and DNA-binding properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Gurney E. G., Goodfellow P., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Detection of a common feature in several human tumor cell lines--a 53,000-dalton protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo A. B., Shiku H., Takahashi T., John M., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of chemically induced sarcomas of the mouse. I. Murine leukemia virus-related antigens and alloantigens on cultured fibroblasts and sarcoma cells: description of a unique antigen on BALB/c Meth A sarcoma. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):720–734. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W. SV40 T-antigen-related surface antigen: correlated expression with nuclear T-antigen in cells transformed by an SV40 A-gene mutant. Virology. 1980 Jul 30;104(2):497–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacherio D., Hager L. P. A poly(dT)-stimulated ATPase activity associated with simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8113–8116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Spangler G., Livingston D. M. Protein kinase activity associated with simian virus 40 T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2610–2614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Khoury G., DeLeo A. B., Dippold W. G., Old L. J. p53 transformation-related protein: detection of an associated phosphotransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Kurimura T., Dubbs D. R. Transplantable mouse tumor line induced by injection of SV40-transformed mouse kidney cells. Int J Cancer. 1969 Jul 15;4(4):384–392. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910040403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockmann U., Deppert W. Acylated simian virus 40 large T-antigen: a new subclass associated with a detergent-resistant lamina of the plasma membrane. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockmann U., Deppert W. Evidence for transmembrane orientation of acylated simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):541–548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.541-548.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Cellular oncogenes and multistep carcinogenesis. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):771–778. doi: 10.1126/science.6356358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmark P. Events at the surface of the cell. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):380–380. doi: 10.1038/317380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIGEN IN SV40-TRANSFORMED CELLS BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:121–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F., BUTEL J. S., MELNICK J. L. VIRUS-INDUCED INTRANUCLEAR ANTIGEN IN CELLS TRANSFORMED BY PAPOVAVIRUS SV40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:1131–1135. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Boss M. A., Baltimore D. Increased concentration of an apparently identical cellular protein in cells transformed by either Abelson murine leukemia virus or other transforming agents. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):336–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.336-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soule H. R., Butel J. S. Subcellular Localization of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):523–532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.523-532.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M., Deppert W. Different structural systems of the nucleus are targets for SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M., Deppert W. Preparation of nuclear matrices from cultured cells: subfractionation of nuclei in situ. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1886–1894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Robbins A., Clark R. Catalytic properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):103–111. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Robbins A. Enzymatic activities associated with a purified simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):610–614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Protein kinase activities in immune complexes of simian virus 40 large T-antigen and transformation-associated cellular p53 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):232–239. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Bibring T., Osborn M. Specific visualization of tubulin-containing structures in tissue culture cells by immunofluorescence. Cytoplasmic microtubules, vinblastine-induced paracrystals, and mitotic figures. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 1;95(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90615-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]