Abstract
A major proportion of carcinomas induced by mouse mammary tumour virus (MMTV) show evidence for proviral activation of a cellular gene, int-2, on chromosome 7. The sequence of 7869 bp of DNA spanning the transcription unit of int-2 was determined and compared with that of a series of int-2-specific cDNA clones derived from mammary tumour RNA. The predicted positions of intron-exon boundaries, established by alignment of cDNA and chromosomal DNA sequences, indicate that the gene comprises at least three exons. An open reading frame capable of encoding a protein of 245 amino acids with an estimated mol. wt of 27 kd, is flanked by substantial non-coding segments at both 5' and 3' ends. Comparison of the chromosomal DNA sequence and the predicted amino acid sequence with available data-bases has revealed no homology to other known genes. These results are discussed in relation to the status of int-2 as a candidate proto-oncogene.
Full text
PDF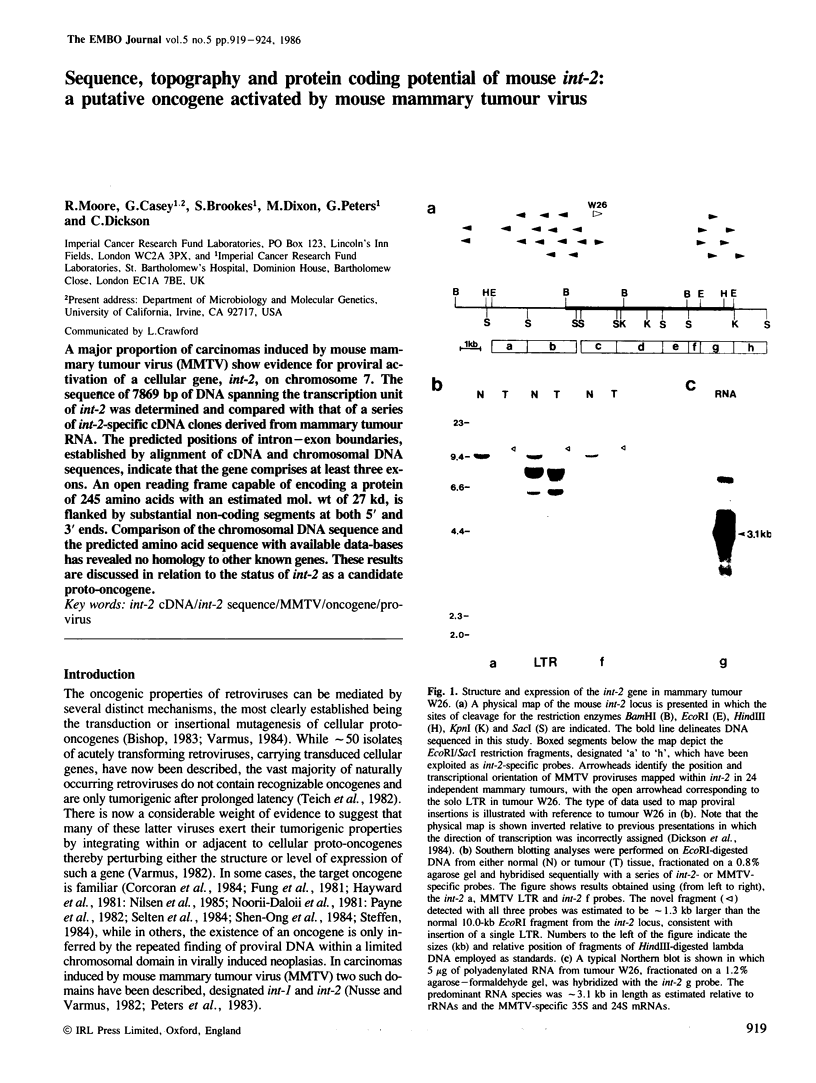





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Smith R., Brookes S., Peters G. Tumorigenesis by mouse mammary tumor virus: proviral activation of a cellular gene in the common integration region int-2. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Fadly A. M., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. On the mechanism of retrovirus-induced avian lymphoid leukosis: deletion and integration of the proviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3418–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequences at host-proviral junctions for mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):253–258. doi: 10.1038/289253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. J., Jones M. B., Elkington J. A., Williams J. G. Polyadenylation of the Xenopus beta 1 globin mRNA at a downstream minor site in the absence of the major site and utilization of an AAUACA polyadenylation signal. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):205–211. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02337.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Crittenden L. B., Raines M. A., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in ALV-induced erythroblastosis: novel RNA processing and promoter insertion result in expression of an amino-truncated EGF receptor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noori-Daloii M. R., Swift R. A., Kung H. J., Crittenden L. B., Witter R. L. Specific integration of REV proviruses in avian bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):574–576. doi: 10.1038/294574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Brookes S., Smith R., Dickson C. Tumorigenesis by mouse mammary tumor virus: evidence for a common region for provirus integration in mammary tumors. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Kozak C., Dickson C. Mouse mammary tumor virus integration regions int-1 and int-2 map on different mouse chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):375–378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Zijlstra M., Melief C., Berns A. Involvement of c-myc in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in mice: frequency and mechanisms of activation. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3215–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Potter M., Mushinski J. F., Lavu S., Reddy E. P. Activation of the c-myb locus by viral insertional mutagenesis in plasmacytoid lymphosarcomas. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1077–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.6093260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. Proviruses are adjacent to c-myc in some murine leukemia virus-induced lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2097–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. The molecular genetics of cellular oncogenes. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:553–612. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]