Abstract
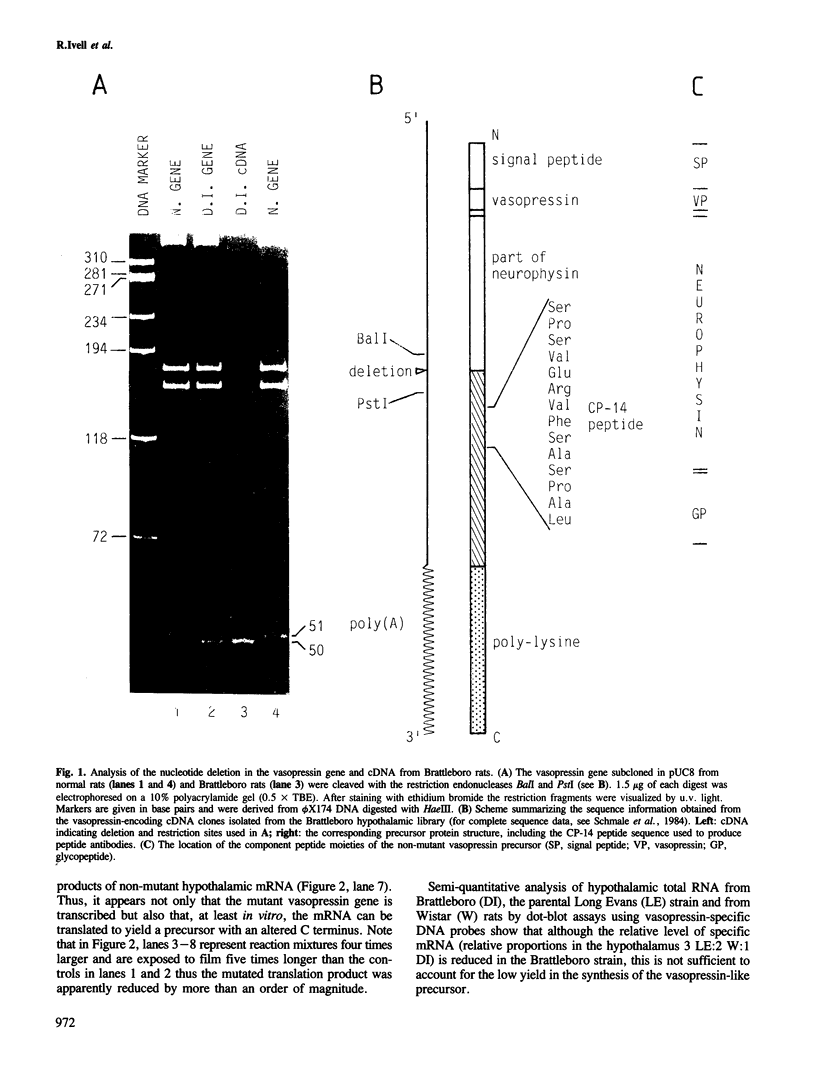
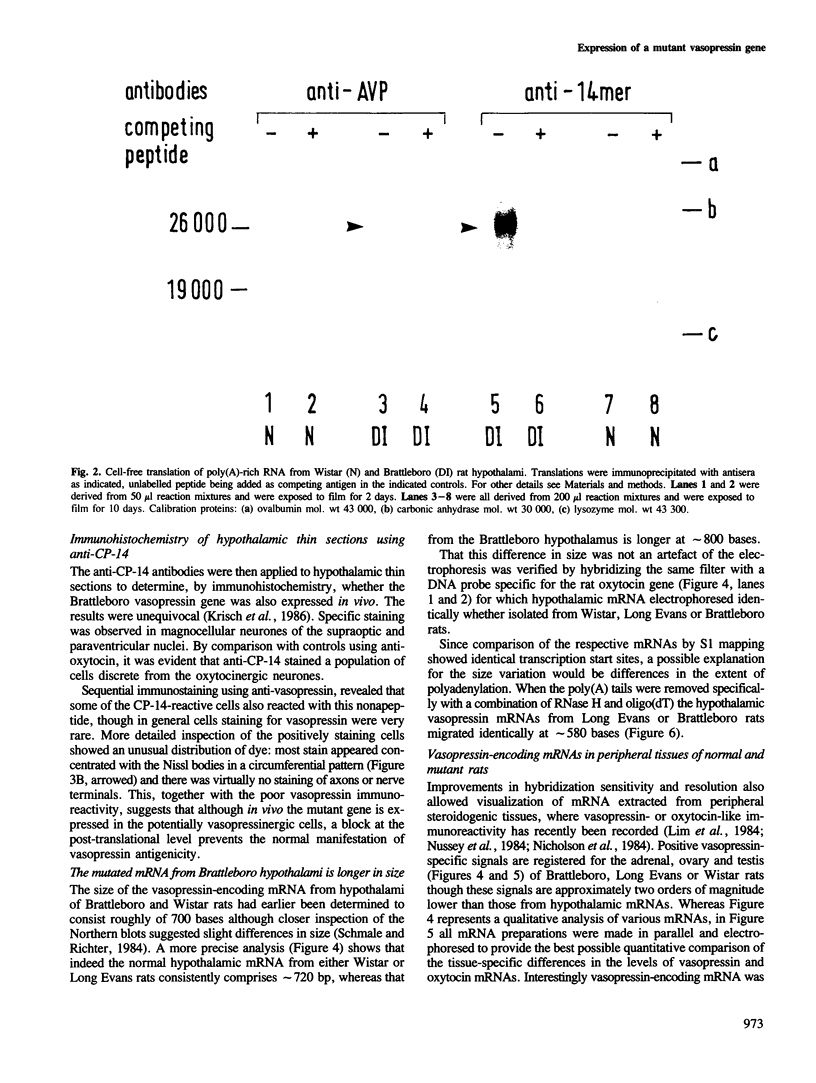
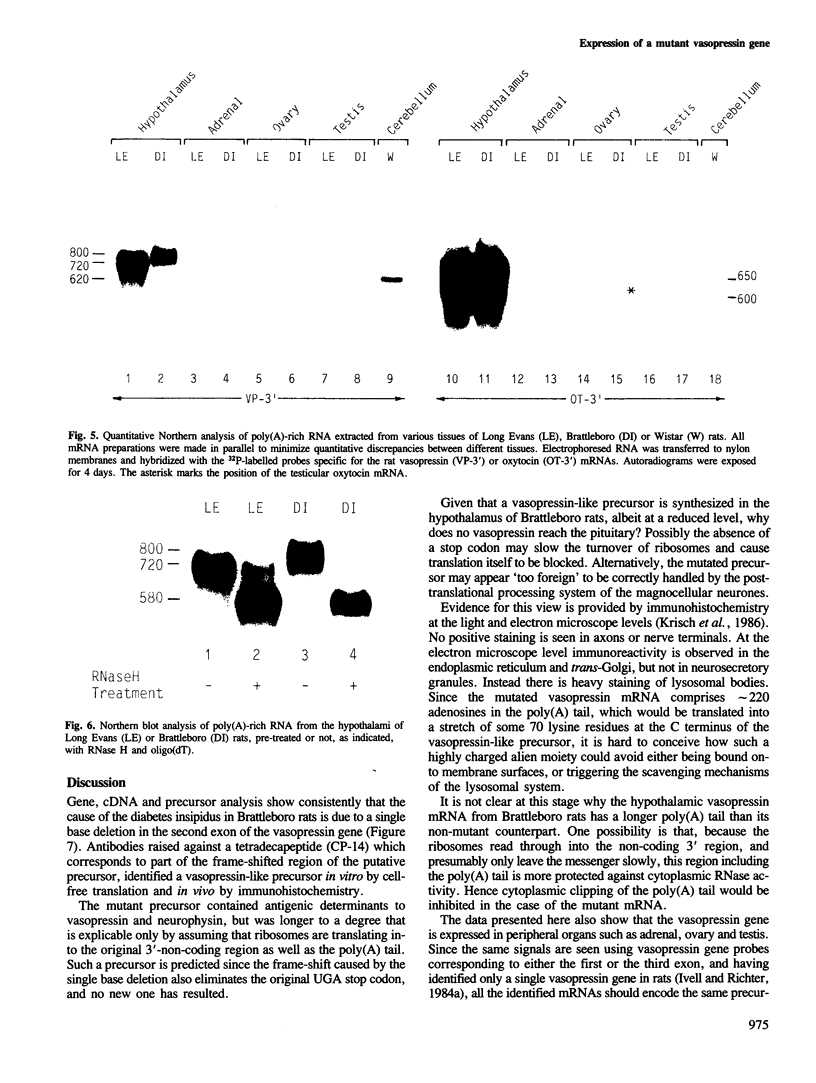
Sequence analysis of cDNA clones derived from hypothalamic mRNA of diabetes insipidus (Brattleboro) rats shows that the vasopressin gene transcript also includes the single base deletion demonstrated in the gene. This causes a frame-shift in the C terminus of the vasopressin precursor with a reading frame open through the 3' end of the mRNA including the poly(A) sequence. Antibodies raised against a synthetic tetradecapeptide (CP-14) corresponding to the frame-shifted C terminus identified a product of mol. wt approximately 26 000 in a reticulocyte lysate system programmed with Brattleboro hypothalamic mRNA. Immunohistochemical analysis indicated that a similar precursor is also present in vivo in neurones of the Brattleboro hypothalamus. Electrophoretic analysis of vasopressin mRNA from wild-type and mutant rat tissues revealed that (i) the hypothalamic mRNA from Brattleboro rats contains a longer stretch of poly(A) sequence than the wild-type strains; (ii) vasopressin mRNA is also present in the adrenal, ovary, testis and cerebellum, at very low levels; however, (iii) the extra-hypothalamic mRNA is considerably shorter than that in the hypothalamus because of a curtailed poly(A) sequence. Thus similar vasopressin gene transcripts are subject to a tissue-specific differential polyadenylation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bantle J. A., Maxwell I. H., Hahn W. E. Specificity of oligo (dT)-cellulose chromatography in the isolation of polyadenylated RNA. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:413–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. The Role of the poly(A) sequence in mammalian messenger RNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238109114634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:333–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivell R., Richter D. The gene for the hypothalamic peptide hormone oxytocin is highly expressed in the bovine corpus luteum: biosynthesis, structure and sequence analysis. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2351–2354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the Rous sarcoma virus pol gene by ribosomal frameshifting. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1237–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.2416054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
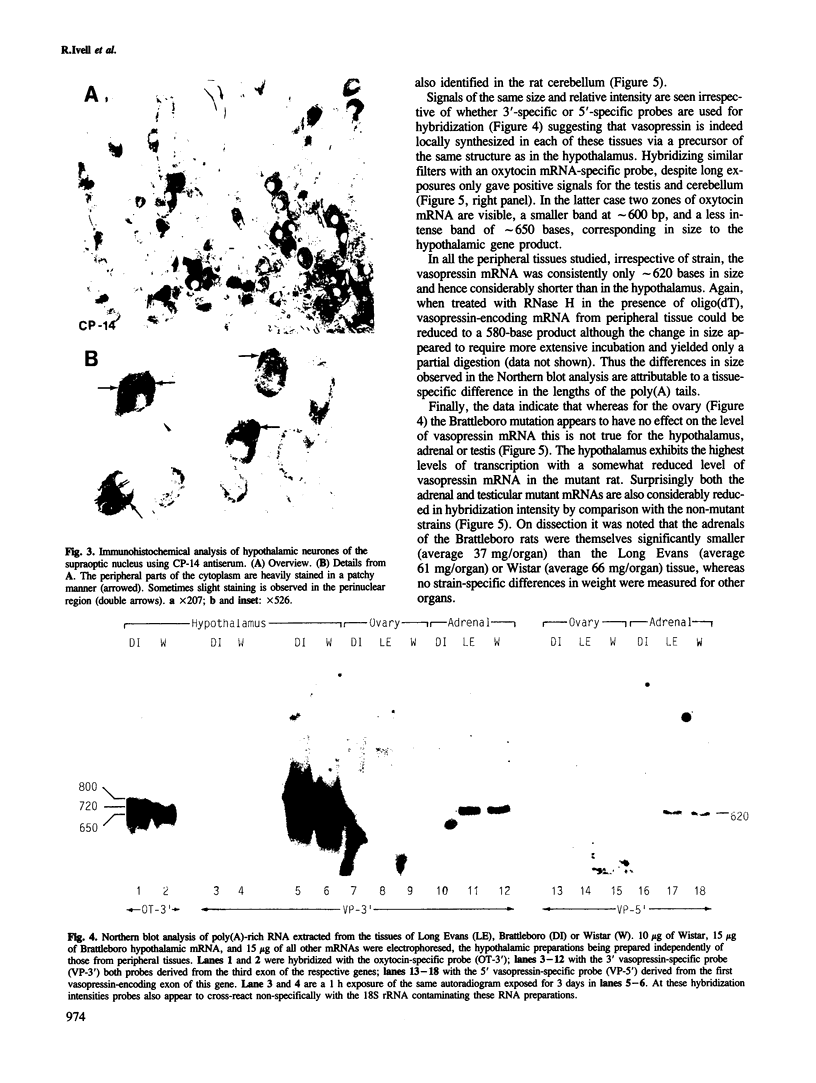
- Krisch B., Nahke P., Richter D. Immunocytochemical staining of supraoptic neurons from homozygous Brattleboro rats by use of antibodies against two domains of the mutated vasopressin precursor. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;244(2):351–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00219211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim A. T., Lolait S. J., Barlow J. W., Autelitano D. J., Toh B. H., Boublik J., Abraham J., Johnston C. I., Funder J. W. Immunoreactive arginine-vasopressin in Brattleboro rat ovary. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):61–64. doi: 10.1038/310061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson H. D., Swann R. W., Burford G. D., Wathes D. C., Porter D. G., Pickering B. T. Identification of oxytocin and vasopressin in the testis and in adrenal tissue. Regul Pept. 1984 Mar;8(2):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussey S. S., Ang V. T., Jenkins J. S., Chowdrey H. S., Bisset G. W. Brattleboro rat adrenal contains vasopressin. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):64–66. doi: 10.1038/310064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale H., Heinsohn S., Richter D. Structural organization of the rat gene for the arginine vasopressin-neurophysin precursor. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):763–767. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01497.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale H., Ivell R., Breindl M., Darmer D., Richter D. The mutant vasopressin gene from diabetes insipidus (Brattleboro) rats is transcribed but the message is not efficiently translated. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3289–3293. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale H., Richter D. Single base deletion in the vasopressin gene is the cause of diabetes insipidus in Brattleboro rats. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):705–709. doi: 10.1038/308705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]