Abstract
The human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), a ubiquitous pathogen of the herpesvirus group, has a linear double-stranded DNA genome of 235 kb. The expression of its major immediate early gene (IE1) is entirely dependent on host factors, presumably proteins binding to DNA elements in the regulatory regions of the gene. We have identified four high-affinity binding sites for nuclear factor 1 (NF1) in the promoter upstream region of IE1 gene between nucleotides -780 and -610, and an additional, even stronger, binding site in the first intron near nucleotide +350. NF1 activity is found in a wide range of species and binds to the sequence 5' TGGC/ANNNNNGCCAA3' on double-stranded DNA, protecting approximately 25 bp from DNase I digestion; its functional importance has been found first in the necessity for adenovirus DNA replication, where it may be important in mediating the binding of other proteins. The regulatory significance of NF1 recognition elements within other genes is unknown. The NF1 binding sites in the HCMV IE1 gene coincide with regions that had been shown to be sensitive to DNase I in the active gene but not sensitive in the silent gene; there was, however, no NF1 binding in the strong and constitutively DNase I-hypersensitive transcription enhancer of the IE1 gene. This suggests that the specific protein--DNA interaction described is important in the regulated control of the IE1 gene.
Full text
PDF


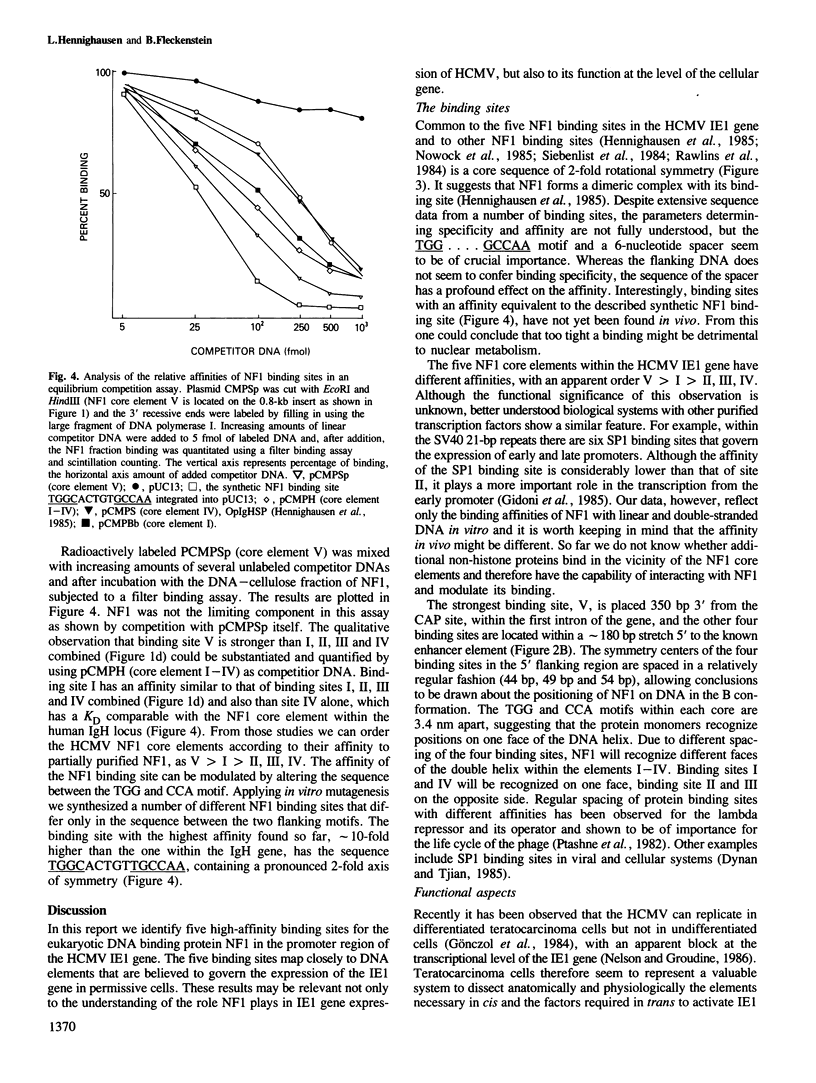

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borgmeyer U., Nowock J., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA-binding protein: a eukaryotic nuclear protein recognizing a symmetrical sequence on double-stranded linear DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4295–4311. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarchi J. M. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: restriction enzyme cleavage maps and map locations for immediate-early, early, and late RNAs. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnick M., Chou J., Petes T. D., Farber R. A. Relationships among DNA sequences of the 1.3 kb EcoRI family of mouse DNA. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(2):115–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02300749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling A., Keil G., Nowak B., Fleckenstein B., Berthelot N., Sheldrick P. Genome structure and virion polypeptides of the primate herpesviruses Herpesvirus aotus types 1 and 3: comparison with human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):715–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.715-726.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Sippel A. E., Igo-Kemenes T. Nuclease-hypersensitive sites in the chromatin domain of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3467–3485. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Adhya S., Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Site-specific DNA binding of nuclear factor I: analyses of cellular binding sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):964–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gönczöl E., Andrews P. W., Plotkin S. A. Cytomegalovirus replicates in differentiated but not in undifferentiated human embryonal carcinoma cells. Science. 1984 Apr 13;224(4645):159–161. doi: 10.1126/science.6322309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L., Siebenlist U., Danner D., Leder P., Rawlins D., Rosenfeld P., Kelly T., Jr High-affinity binding site for a specific nuclear protein in the human IgM gene. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):289–292. doi: 10.1038/314289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn G., Knust E., Schmolla H., Sarre T., Nelson J. A., McDougall J. K., Fleckenstein B. Predominant immediate-early transcripts of human cytomegalovirus AD 169. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):363–370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.363-370.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leegwater P. A., van der Vliet P. C., Rupp R. A., Nowock J., Sippel A. E. Functional homology between the sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins nuclear factor I from HeLa cells and the TGGCA protein from chicken liver. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):381–386. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Spector D. H. Transcription in human fibroblasts permissively infected by human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Enomoto T., Lichy J. H., Hurwitz J. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: identification of a host factor that stimulates synthesis of the preterminal protein-dCMP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Groudine M. Transcriptional regulation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene is associated with induction of DNase I-hypersensitive sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):452–461. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowock J., Borgmeyer U., Püschel A. W., Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA protein binds to the MMTV-LTR, the adenovirus origin of replication, and the BK virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2045–2061. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. A genetic switch in a bacterial virus. Sci Am. 1982 Nov;247(5):128-30, 132, 134-40. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1182-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Wides R. J., Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J., Jr Structure and function of the adenovirus origin of replication. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weststrate M. W., Geelen J. L., van der Noordaa J. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: physical maps for restriction endonucleases BglII, hindIII and XbaI. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



