Abstract
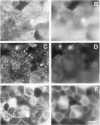
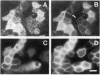
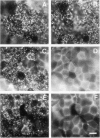
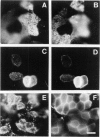
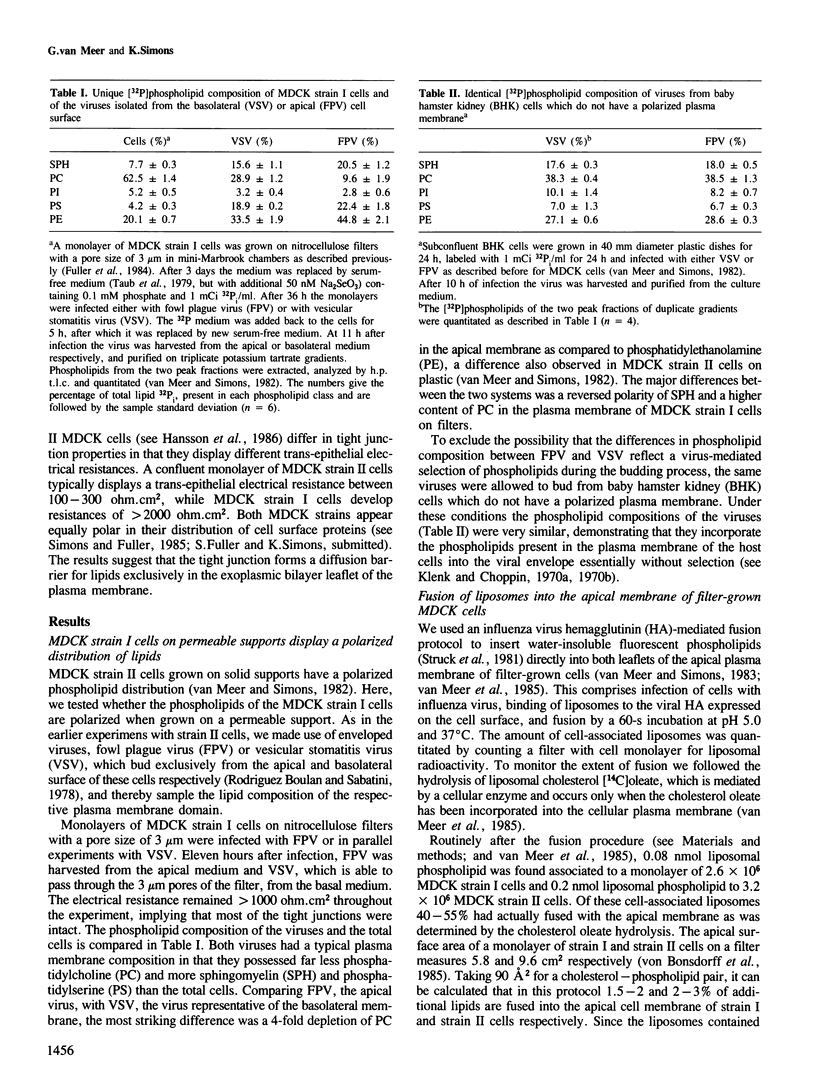
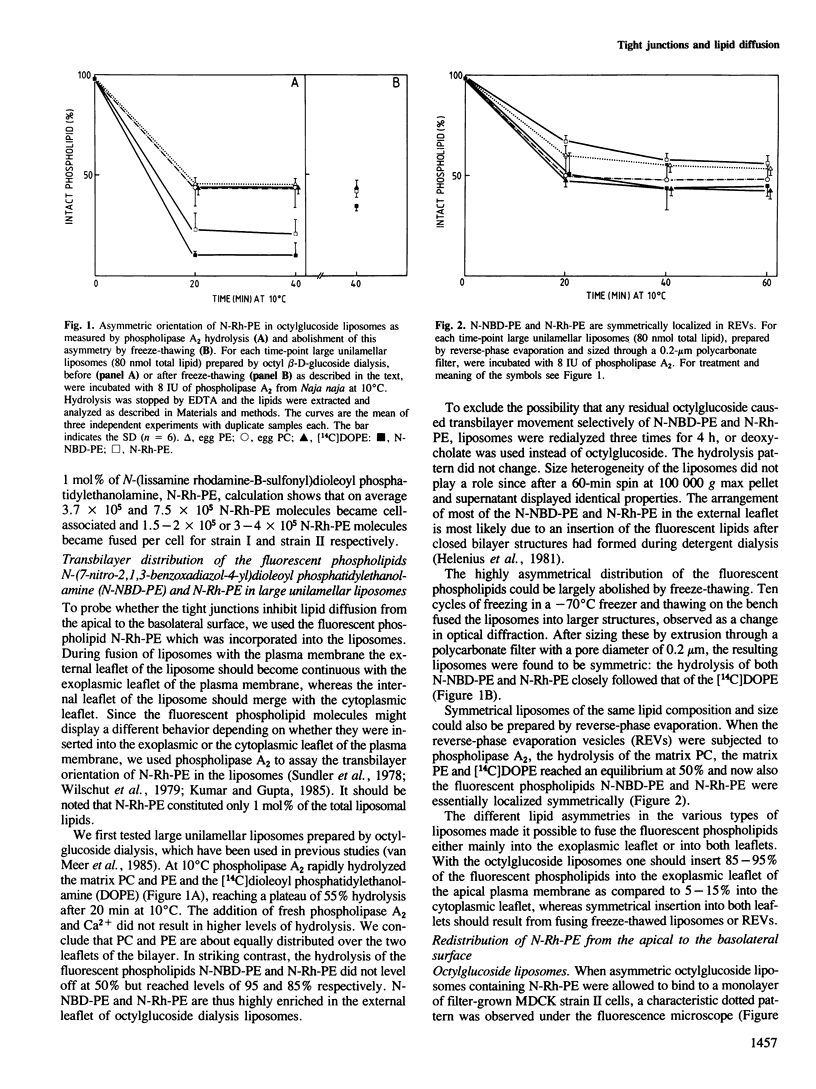
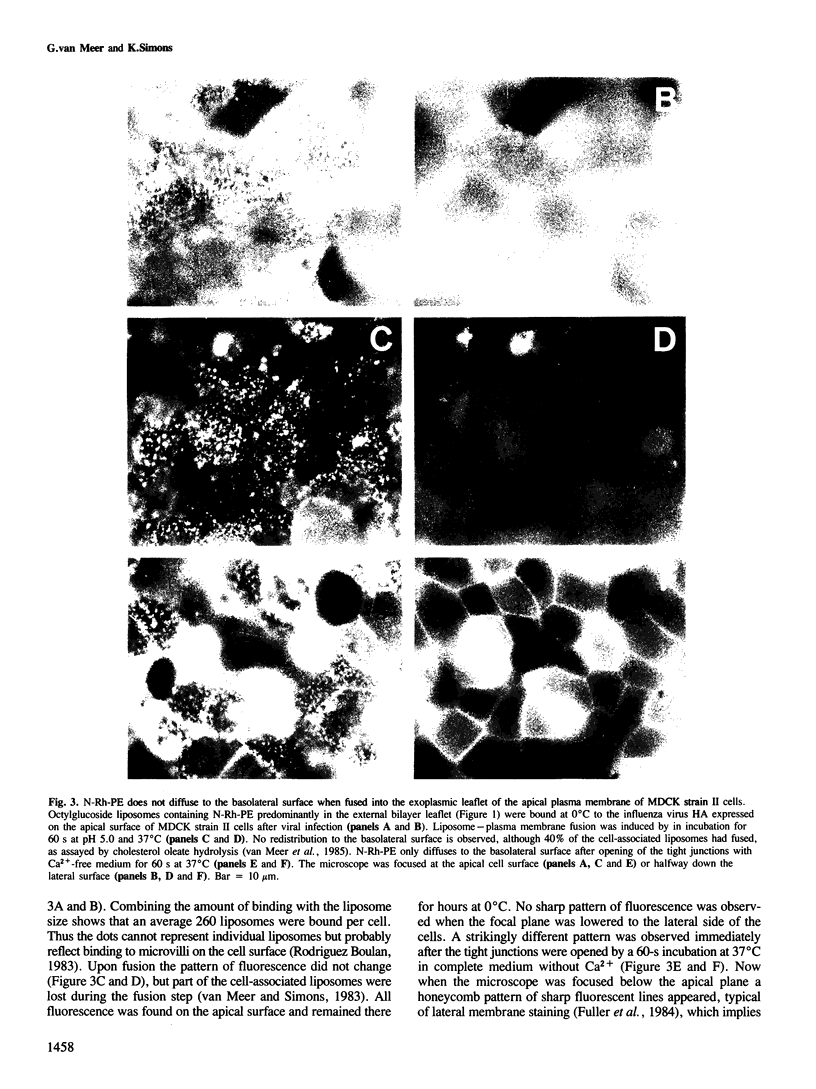
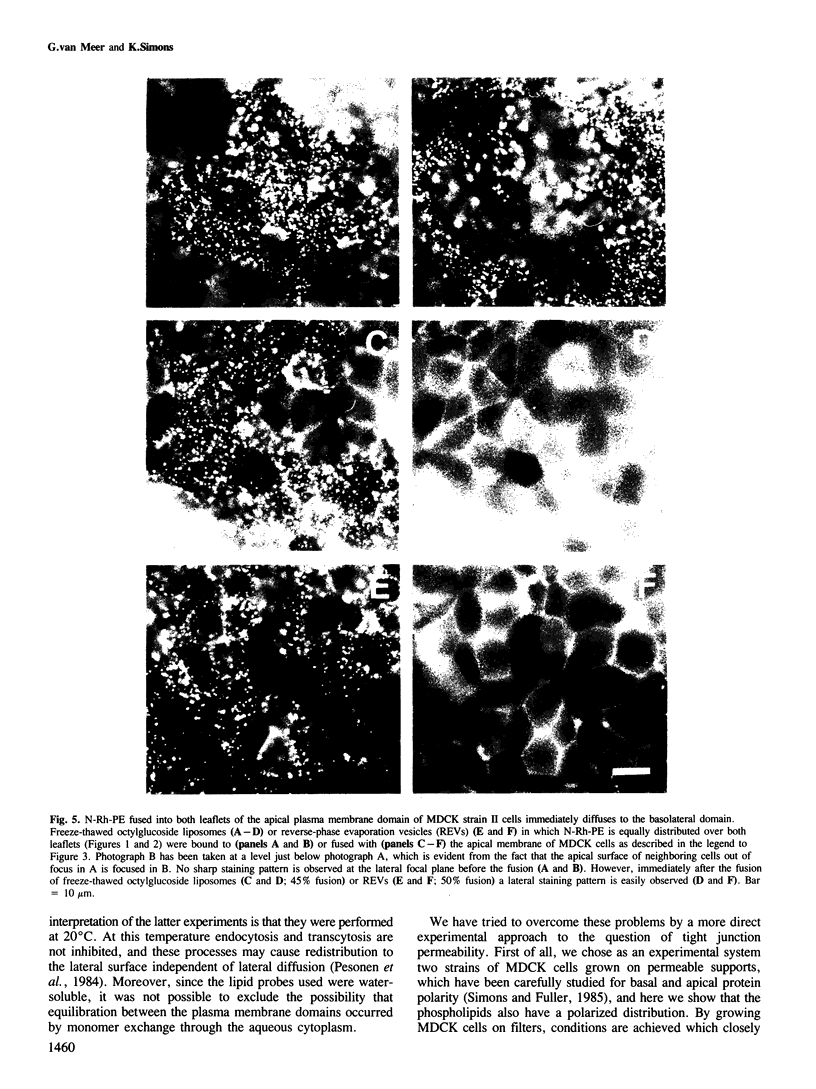
Tight junctions in epithelial cells have been postulated to act as barriers inhibiting lateral diffusion of lipids and proteins between the apical and basolateral plasma membrane domains. To study the fence function of the tight junction in more detail, we have fused liposomes containing the fluorescent phospholipid N-Rh-PE into the apical plasma membrane of MDCK cells. Liposome fusion was induced by low pH and mediated by the influenza virus hemagglutinin, which was expressed on the apical cell surface after viral infection. Redistribution of N-Rh-PE to the basolateral surface, monitored at 0 degree C by fluorescence microscopy, appeared to be dependent on the transbilayer orientation of the fluorescent lipids in the plasma membrane. Asymmetric liposomes containing over 85% of the N-Rh-PE in the external bilayer leaflet, as shown by a phospholipase A2 assay, were generated by octyl beta-D-glucoside dialysis. When these asymmetric liposomes were fused with the apical plasma membrane, fluorescent lipid did not move to the basolateral side. Symmetric liposomes which contained the marker in both leaflets were obtained by freeze-thawing asymmetric liposomes or by reverse-phase evaporation. Upon fusion of these with the apical membrane, redistribution to the basolateral membrane occurred immediately. Redistribution could be observed with asymmetric liposomes only when the tight junctions were opened by incubation in a Ca2+-free medium. During the normal experimental manipulations the tight junctions remained intact since a high trans-epithelial electrical resistance was maintained over the cell monolayer. We conclude that the tight junction acts as a diffusion barrier for the fluorescent phospholipid N-Rh-PE in the exoplasmic leaflet of the plasma membrane but not in the cytoplasmic leaflet.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasitus T. A., Schachter D. Lipid dynamics and lipid-protein interactions in rat enterocyte basolateral and microvillus membranes. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2763–2769. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Phosphatidyl-ethanolamine: differential labelling in intact cells and cell ghosts of human erythrocytes by a membrane-impermeable reagent. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):523–528. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel G., Rodrigue F., Carrière S., Le Grimellec C. Composition and physical properties of lipids from plasma membranes of dog kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 27;818(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereijido M., Robbins E. S., Dolan W. J., Rotunno C. A., Sabatini D. D. Polarized monolayers formed by epithelial cells on a permeable and translucent support. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):853–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapelle S., Gilles-Baillien M. Phospholipids and cholesterol in brush border and basolateral membranes from rat intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 20;753(2):269–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Twenty-first Bowditch lecture. The epithelial junction: bridge, gate, and fence. Physiologist. 1977 Feb;20(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragsten P. R., Blumenthal R., Handler J. S. Membrane asymmetry in epithelia: is the tight junction a barrier to diffusion in the plasma membrane? Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):718–722. doi: 10.1038/294718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:375–412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G., Wherrett J. R. Plasma membrane and mucosal glycosphingolipids in the rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 21;306(3):446–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S., von Bonsdorff C. H., Simons K. Vesicular stomatitis virus infects and matures only through the basolateral surface of the polarized epithelial cell line, MDCK. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griepp E. B., Dolan W. J., Robbins E. S., Sabatini D. D. Participation of plasma membrane proteins in the formation of tight junctions by cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):693–702. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B., Simons K. A functional assay for proteins involved in establishing an epithelial occluding barrier: identification of a uvomorulin-like polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):457–468. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. C., Simons K., van Meer G. Two strains of the Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell line have distinct glycosphingolipid compositions. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):483–489. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Sarvas M., Simons K. Asymmetric and symmetric membrane reconstitution by detergent elimination. Studies with Semliki-Forest-virus spike glycoprotein and penicillinase from the membrane of Bacillus licheniformis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. The intramembrane structure of tight junctions: an experimental analysis of the single-fibril and two-fibril models using the quick-freeze method. J Ultrastruct Res. 1982 Sep;80(3):288–301. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(82)80042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hise M. K., Mantulin W. W., Weinman E. J. Fluidity and composition of brush border and basolateral membranes from rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 2):F434–F439. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.3.F434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., de Boer T., Klappe K., Wilschut J. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5675–5681. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachar B., Reese T. S. Evidence for the lipidic nature of tight junction strands. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):464–466. doi: 10.1038/296464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai K., Fujita M., Nakao M. Lipid components of two different regions of an intestinal epithelial cell membrane of mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 18;369(2):222–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Glycosphingolipids of plasma membranes of cultured cells and an enveloped virus (SV5) grown in these cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):57–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Plasma membrane lipids and parainfluenza virus assembly. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremmer T., Wisher M. H., Evans W. H. The lipid composition of plasma membrane subfractions originating from the three major functional domains of the rat hepatocyte cell surface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Gupta C. M. Transbilayer phosphatidylcholine distributions in small unilamellar sphingomyelin-phosphatidylcholine vesicles: effect of altered polar head group. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5157–5163. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Dharmsathaphorn K. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., Sztul E. S., Reuben A., Boyer J. L. Structural and functional polarity of canalicular and basolateral plasma membrane vesicles isolated in high yield from rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):991–1000. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitoris B. A., Simon F. R. Renal cortical brush-border and basolateral membranes: cholesterol and phospholipid composition and relative turnover. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(3):207–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01868695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A. Lipid asymmetry in membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:47–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Ansorge W., Simons K. Transcytosis of the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus after implantation into the apical plasma membrane of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. I. Involvement of endosomes and lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):796–782. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Kachar B. On tight-junction structure. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkonen O., Gahmberg C. G., Simons K., Käriäinen L. The lipids of the plasma membranes and endoplasmic reticulum from cultured baby hamster kidney cells (BHK21). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):66–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Boulan E., Sabatini D. D. Asymmetric budding of viruses in epithelial monlayers: a model system for study of epithelial polarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel S., Blumenthal R., Fishman P. H., Handler J. S. Gangliosides do not move from apical to basolateral plasma membrane in cultured epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 5;821(2):310–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Goodenough D. A. Zonulae occludentes in junctional complex-enriched fractions from mouse liver: preliminary morphological and biochemical characterization. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1209–1221. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Hoekstra D., Pagano R. E. Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4093–4099. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler R., Alberts A. W., Vagelos P. R. Phospholipases as probes for membrane sideness. Selective analysis of the outer monolayer of asymmetric bilayer vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5299–5304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4194–4198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub M., Chuman L., Saier M. H., Jr, Sato G. Growth of Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell (MDCK) line in hormone-supplemented, serum-free medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3338–3342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson T. E., Tillack T. W. Organization of glycosphingolipids in bilayers and plasma membranes of mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:361–386. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Thompson J., Sariban-Sohraby S., Handler J. S. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of epithelial membrane polarization. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2173–2180. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilschut J. C., Regts J., Scherphof G. Action of phospholipase A2 on phospholipid vesicles. Preservation of the membrane permeability barrier during asymmetric bilayer degradation. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 1;98(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalc B., Helwig J. J., Ghandour M. S., Sarlieve L. Sulfatide in the kidney: how is this lipid involved in sodium chloride transport? FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 1;92(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80729-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Davoust J., Simons K. Parameters affecting low-pH-mediated fusion of liposomes with the plasma membrane of cells infected with influenza virus. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3593–3602. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Simons K. An efficient method for introducing defined lipids into the plasma membrane of mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1365–1374. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Simons K. Viruses budding from either the apical or the basolateral plasma membrane domain of MDCK cells have unique phospholipid compositions. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):847–852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bonsdorff C. H., Fuller S. D., Simons K. Apical and basolateral endocytosis in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells grown on nitrocellulose filters. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2781–2792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]