Abstract
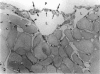
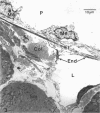
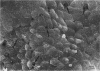
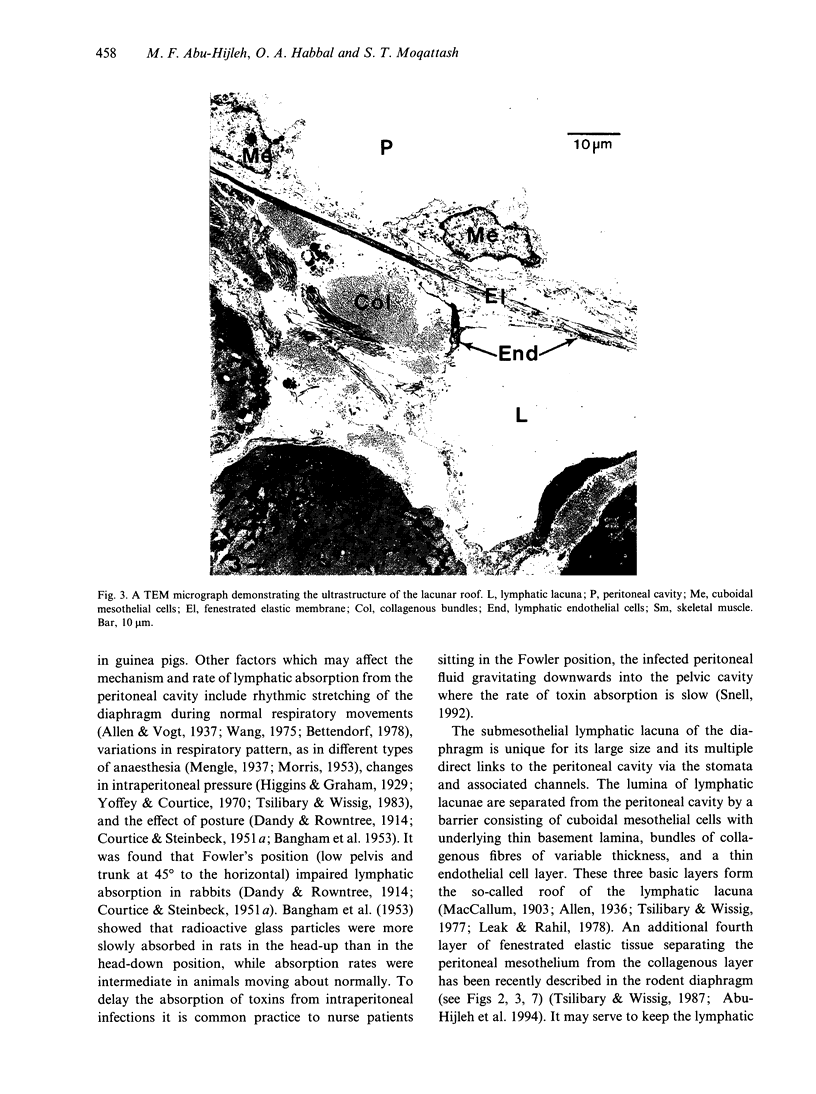
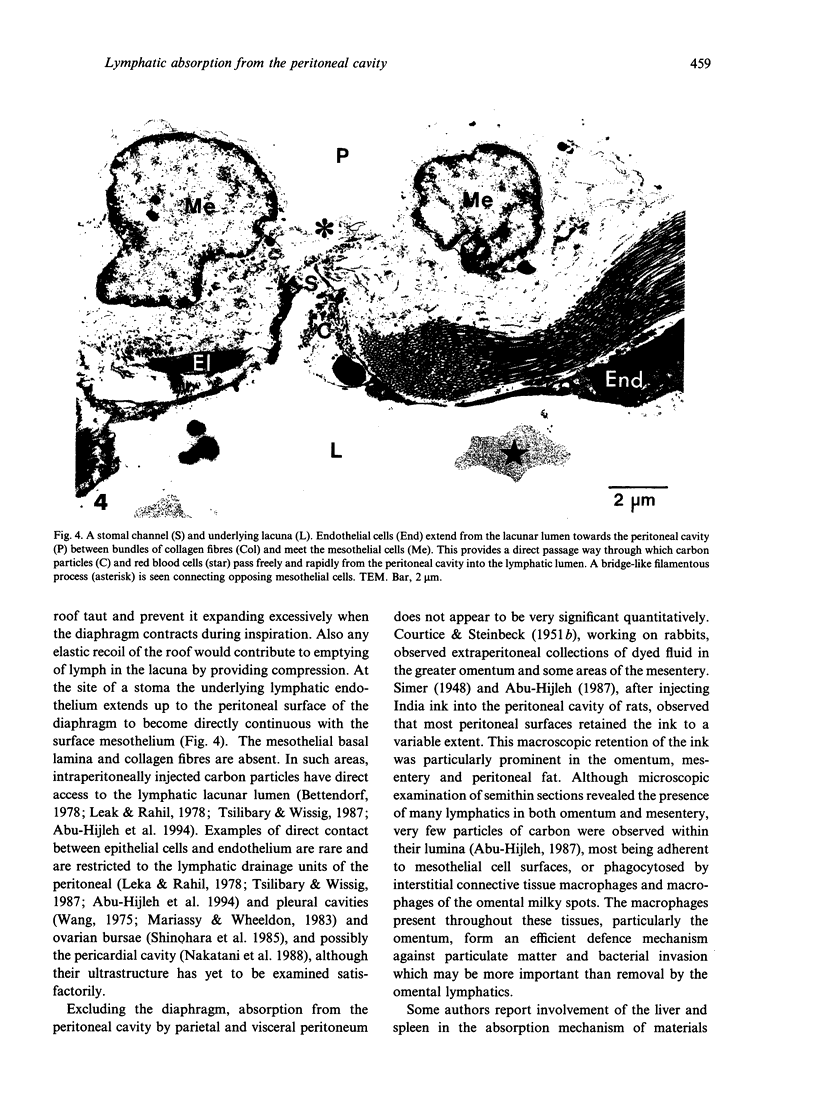
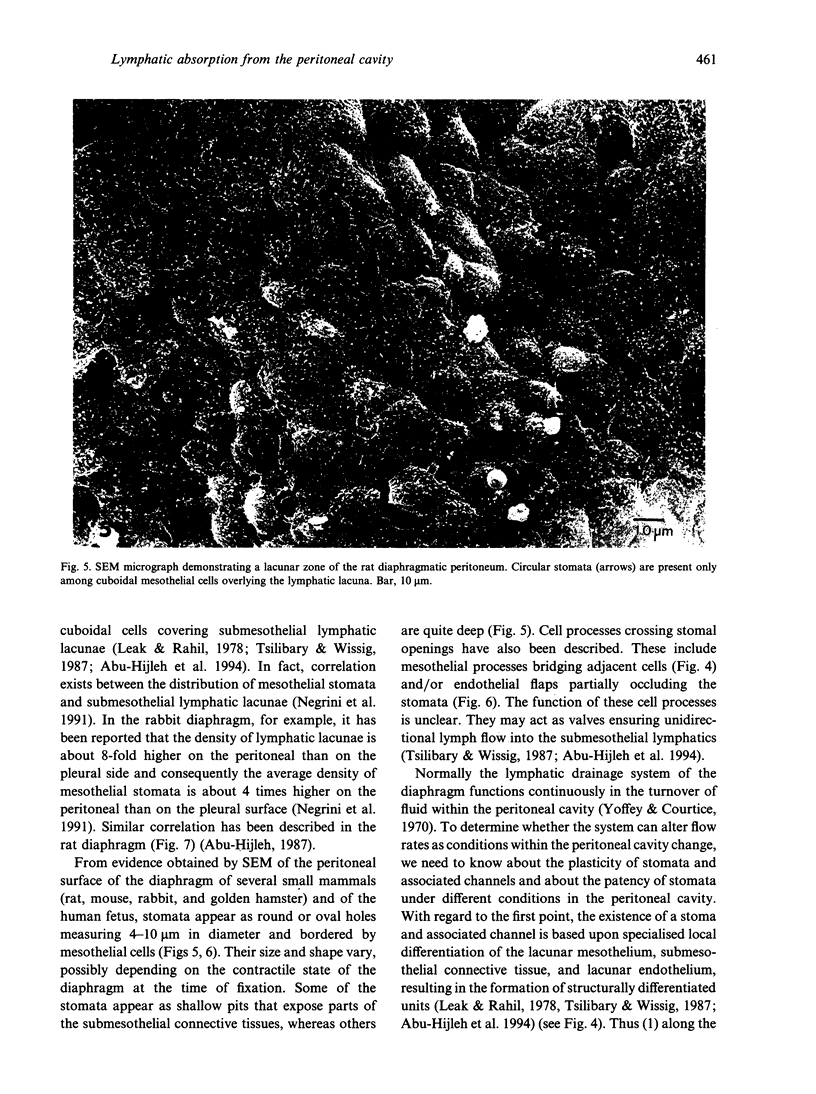
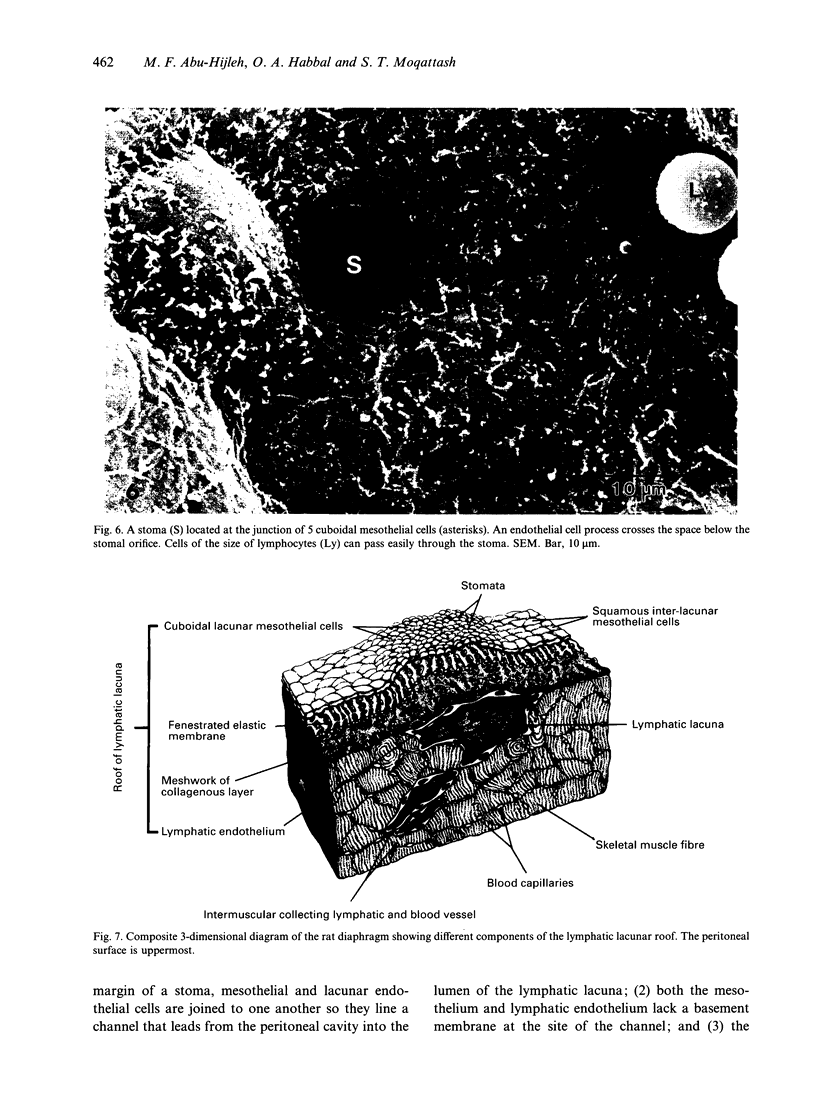
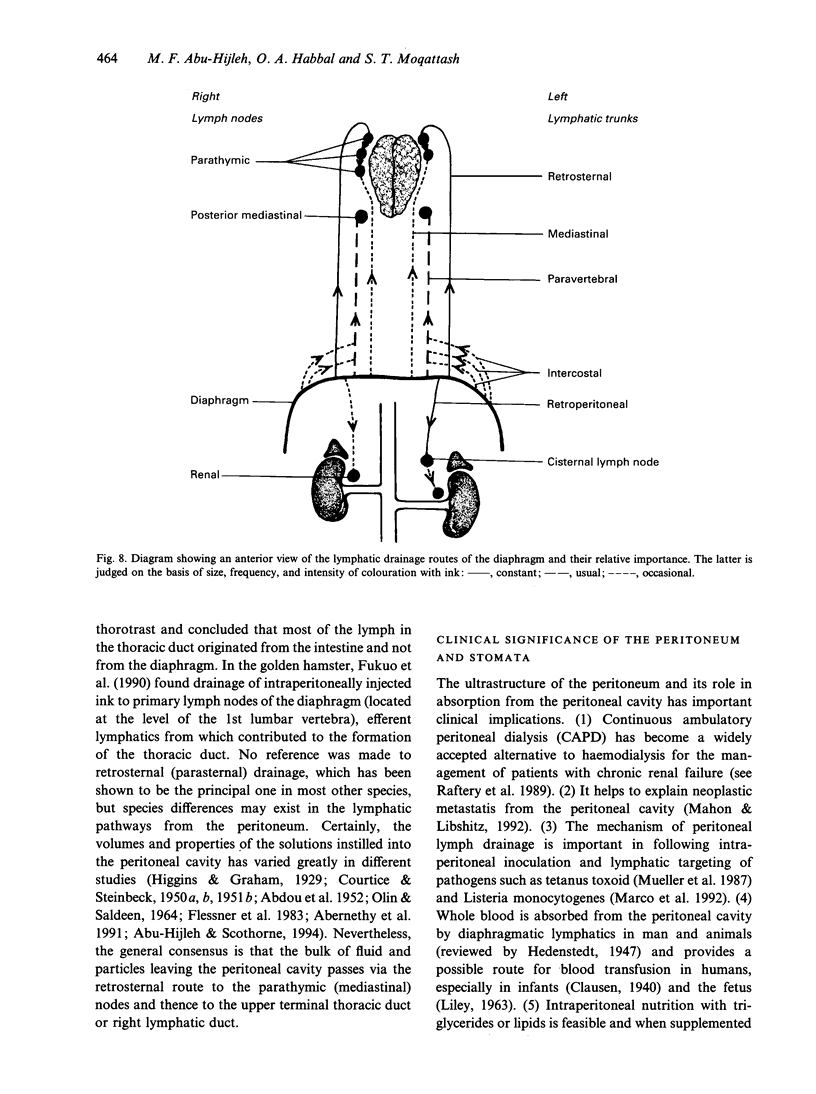
Lymphatics in the diaphragm form a specialised system draining fluid from the peritoneal cavity and returning it to the vascular system. Fluid enters subperitoneal lymphatic lacunae, between muscle fibres of the diaphragm, the lacunae being separated from the peritoneal cavity by a barrier comprising, successively, lymphatic endothelium, a layer of collagenous fibres, a thin fenestrated layer of elastic tissue, and the peritoneal mesothelium. To reach the lacunae, peritoneal fluid passes through stomata located between cuboidal mesothelial cells of the lacunar roof. Whilst the distribution of mesothelial stomata and subjacent lymphatic lacunae varies in different species, stomata appear to be exclusive to the diaphragm and may serve as the main drainage channels for absorption from the peritoneal cavity. Clinically, they may provide escape for tumour cells, pathogens and toxins from the peritoneal cavity. They could provide access for blood transfusions, for intraperitoneal chemotherapy to treat malignancies, and for peritoneal dialysis in treating chronic renal failure. From the lacunae, fluid traverses the diaphragm via intrinsic lymphatics to reach collecting lymphatics beneath the diaphragmatic pleura. Both intrinsic and collecting lymphatics contain valves. The collecting lymphatics drain principally into retrosternal (parasternal) lymphatic trunks that carry lymph to the great veins after it filters through mediastinal lymph nodes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABDOU I. A., REINHARDT W. O., TARVER H. Plasma protein. III. The equilibrium between blood and lymph protein. J Biol Chem. 1952 Jan;194(1):15–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alavi N., Lianos E., Andres G., Bentzel C. J. Effect of protamine on the permeability and structure of rat peritoneum. Kidney Int. 1982 Jan;21(1):44–53. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen L. Lymphatics and lymphoid tissues. Annu Rev Physiol. 1967;29:197–224. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.29.030167.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. M., Porter K. R. The ultrastructural morphology and possible functional significance of mesothelial microvilli. Anat Rec. 1973 Nov;177(3):409–426. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091770307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., MAGEE P. N., OSBORN S. B. The effect of inflammation and other factors on the movement of radioactive glass particles from the peritoneal cavity. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Feb;34(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARADI A. F., HOPE J. OBSERVATIONS ON ULTRASTRUCTURE OF RABBIT MESOTHELIUM. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Mar;34:33–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baradi A. F., Rayns D. G. Mesothelial intercellular junctions and pathways. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Oct 1;173(1):133–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00219271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettendorf U. Electronmicroscopic studies on the peritoneal resorption of intraperitoneally injected latex particles via the diaphragmatic lymphatics. Lymphology. 1979 Jun;12(2):66–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettendorf U. Lymph flow mechanism of the subperitoneal diaphragmatic lymphatics. Lymphology. 1978 Sep;11(3):111–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull H. A., Pittilo R. M., Drury J., Pollock J. G., Clarke J. M., Woolf N., Marston A., Machin S. J. Effects of autologous mesothelial cell seeding on prostacyclin production within Dacron arterial prostheses. Br J Surg. 1988 Jul;75(7):671–674. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASCARANO J., RUBIN A. D., CHICK W. L., ZWEIFACH B. W. METABOLICALLY INDUCED PERMEABILITY CHANGES ACROSS MESOTHELIUM AND ENDOTHELIUM. Am J Physiol. 1964 Feb;206:373–382. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURTICE F. C., HARDING J., STEINBECK A. W. The removal of free red blood cells from the peritoneal cavity of animals. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1953 Jun;31(3):215–225. doi: 10.1038/icb.1953.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURTICE F. C., STEINBECK A. W. Absorption of protein from the peritoneal cavity. J Physiol. 1951 Jul;114(3):336–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURTICE F. C., STEINBECK A. W. The effects of lymphatic obstruction and of posture on the absorption of protein from the peritoneal cavity. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1951 Nov;29(6):451–458. doi: 10.1038/icb.1951.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURTICE F. C., STEINBECK A. W. The lymphatic drainage of plasma from the peritoneal cavity of the cat. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1950 Mar;28(2):161–169. doi: 10.1038/icb.1950.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURTICE F. C., STEINBECK A. W. The rate of absorption of heparinized plasma and of 0.9 p.c. NaCl from the peritoneal cavity of the rabbit and guinea-pig. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1950 Mar;28(2):171–182. doi: 10.1038/icb.1950.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casley-Smith J. R. An electron microscopical study of the passage of ions through the endothelium of lymphatic and blood capillaries, and through the mesothelium. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1967 Apr;52(2):105–113. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1967.sp001892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Karnovsky M. J. Ultrastructural studies on the permeability of the mesothelium to horseradish peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1968 Apr;37(1):123–137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandy W. E., Rowntree L. G. X. Peritoneal and Pleural Absorption, with Reference to Postural Treatment. Ann Surg. 1914 Apr;59(4):587–596. doi: 10.1097/00000658-191404000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick R. L. Theoretical and experimental bases of intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Semin Oncol. 1985 Sep;12(3 Suppl 4):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digenis G. E., Rabinovich S., Medline A., Rodella H., Wu G., Oreopoulos D. G. Electron microscopic study of the peritoneal kinetics of iron dextran during peritoneal dialysis in the rabbit. Nephron. 1984;37(2):108–112. doi: 10.1159/000183224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbie J. W., Zaki M., Wilson L. Ultrastructural studies on the peritoneum with special reference to chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Scott Med J. 1981 Jul;26(3):213–223. doi: 10.1177/003693308102600305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. The cause and prevention of postoperative intraperitoneal adhesions. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1971 Sep;133(3):497–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKATA H. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY ON NORMAL RAT PERITONEAL MESOTHELIUM AND ITS CHANGES IN ABSORPTION OF PARTICULATE IRON DEXTRAN COMPLEX. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1963 Oct;13:309–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1963.tb03161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flessner M. F., Parker R. J., Sieber S. M. Peritoneal lymphatic uptake of fibrinogen and erythrocytes in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):H89–H96. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.244.1.H89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuo Y., Shinohara H., Matsuda T. The distribution of lymphatic stomata in the diaphragm of the golden hamster. J Anat. 1990 Apr;169:13–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudio E., Casale N., Pannarale L., Priori A., Marinozzi G. A scanning electron microscopy morphometric study of the rabbit peritoneal surface. Anat Rec. 1990 Oct;228(2):145–150. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092280206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervin A. S., Puckett C. L., Silver D. Serosal hypofibrinolysis. A cause of postoperative adhesions. Am J Surg. 1973 Jan;125(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(73)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotloib L., Digenis G. E., Rabinovich S., Medline A., Oreopoulos D. G. Ultrastructure of normal rabbit mesentery. Nephron. 1983;34(4):248–255. doi: 10.1159/000183024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A. G., Claeys M., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Biosynthesis of prostaglandin (PGI2) and 12L-hydroxy-5,8,10,14-eicosatetraenoic acid (HETE) by pericardium, pleura, peritoneum and aorta of the rabbit. Prostaglandins. 1979 Sep;18(3):439–452. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(79)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge T., Hovig T. The ultrastructure of human and rat pericardium. I. Parietal and visceral mesothelium. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;71(4):529–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb05175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. INTRAUTERINE TRANSFUSION OF FOETUS IN HAEMOLYTIC DISEASE. Br Med J. 1963 Nov 2;2(5365):1107–1109. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5365.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leak L. V., Rahil K. Permeability of the diaphragmatic mesothelium: the ultrastructural basis for "stomata". Am J Anat. 1978 Apr;151(4):557–593. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001510409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill S. R., Parsons R. H., Buhac I. Permeability of the diaphragm and fluid resorption from the peritoneal cavity in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):997–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS B. The effect of diaphragmatic movement on the absorption of protein and of red cells from the peritoneal cavity. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1953 Jun;31(3):239–246. doi: 10.1038/icb.1953.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison L. D., Bergstrom-Porter B., Torres A. R., Shelton E. Regulation of surface topography of mouse peritoneal cells. Formation of microvilli and vesiculated pits on omental mesothelial cells by serum and other proteins. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):783–797. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahedero G., Morán J. M., Salas J., Blanco M. Absorption of Intralipid and interferences from nutrients infused into the peritoneal cavity of the rat. Am J Surg. 1992 Jul;164(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80644-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahon T. G., Libshitz H. I. Mediastinal metastases of infradiaphragmatic malignancies. Eur J Radiol. 1992 Sep;15(2):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0720-048x(92)90138-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marco A. J., Domingo M., Ruberte J., Carretero A., Briones V., Dominguez L. Lymphatic drainage of Listeria monocytogenes and Indian ink inoculated in the peritoneal cavity of the mouse. Lab Anim. 1992 Jul;26(3):200–205. doi: 10.1258/002367792780740549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariassy A. T., Wheeldon E. B. The pleura: a combined light microscopic, scanning, and transmission electron microscopic study in the sheep. I. Normal pleura. Exp Lung Res. 1983 May;4(4):293–314. doi: 10.3109/01902148309055016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miserocchi G., Mariani E., Negrini D. Role of the diaphragm in setting liquid pressure in serous cavities. Respir Physiol. 1982 Dec;50(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(82)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miserocchi G., Negrini D., Mukenge S., Turconi P., Del Fabbro M. Liquid drainage through the peritoneal diaphragmatic surface. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Apr;66(4):1579–1585. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.4.1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C., Tschumper A., Tschumper J. C., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Parathymic lymph node: oriented proliferative response of the murine thymic cortex to intraperitoneal stimulation. Thymus. 1987;9(1):3–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani T., Shinohara H., Fukuo Y., Morisawa S., Matsuda T. Pericardium of rodents: pores connect the pericardial and pleural cavities. Anat Rec. 1988 Feb;220(2):132–137. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092200204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrini D., Del Fabbro M., Gonano C., Mukenge S., Miserocchi G. Distribution of diaphragmatic lymphatic lacunae. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Mar;72(3):1166–1172. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.3.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrini D., Mukenge S., Del Fabbro M., Gonano C., Miserocchi G. Distribution of diaphragmatic lymphatic stomata. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Apr;70(4):1544–1549. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.70.4.1544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The localization by electron microscopy of nucleoside phosphatase activity in guinea pig phagocytic cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Sep;16(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODOR D. L. Observations of the rat mesothelium with the electron and phase microscopes. Am J Anat. 1954 Nov;95(3):433–465. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000950304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIN T., SALDEEN T. THE LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS FROM THE PERITONEAL CAVITY: A LYMPHANGIOGRAPHIC STUDY IN THE RAT. Cancer Res. 1964 Nov;24:1700–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery A. T. An enzyme histochemical study of mesothelial cells in rodents. J Anat. 1973 Sep;115(Pt 3):365–373. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery A. T. Regeneration of peritoneum: a fibrinolytic study. J Anat. 1979 Oct;129(Pt 3):659–664. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbe E. B., Alm P., Hallberg E., Norgren L. E. Evaluation of peritoneal tube grafts in the inferior vena cava of the pig. Br J Surg. 1988 Apr;75(4):357–360. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara H., Nakatani T., Matsuda T. The presence of lymphatic stomata in the ovarian bursa of the golden hamster. Anat Rec. 1985 Sep;213(1):44–52. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092130107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu M., Simionescu N. Organization of cell junctions in the peritoneal mesothelium. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):98–110. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N. Cellular aspects of transcapillary exchange. Physiol Rev. 1983 Oct;63(4):1536–1579. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.4.1536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsilibary E. C., Wissig S. L. Absorption from the peritoneal cavity: SEM study of the mesothelium covering the peritoneal surface of the muscular portion of the diaphragm. Am J Anat. 1977 May;149(1):127–133. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001490111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsilibary E. C., Wissig S. L. Light and electron microscope observations of the lymphatic drainage units of the peritoneal cavity of rodents. Am J Anat. 1987 Oct;180(2):195–207. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001800209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsilibary E. C., Wissig S. L. Lymphatic absorption from the peritoneal cavity: regulation of patency of mesothelial stomata. Microvasc Res. 1983 Jan;25(1):22–39. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(83)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N. S. The preformed stomas connecting the pleural cavity and the lymphatics in the parietal pleura. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Jan;111(1):12–20. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B. G., Mather S. J., Hawkins L. R., Crowther M. E., Shepherd J. H., Granowska M., Britton K. E., Slevin M. L. Localization of radioiodine conjugated to the monoclonal antibody HMFG2 in human ovarian carcinoma: assessment of intravenous and intraperitoneal routes of administration. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4719–4723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Singh H., Webb J. Phagocytosis of colloidal carbon by the fixed tissue and peritoneal macrophages of New Zealand mice. Scott Med J. 1972 Dec;17(21):382–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker D., Papadimitriou J. M., Walters M. The mesothelium: its fibrinolytic properties. J Pathol. 1982 Apr;136(4):291–299. doi: 10.1002/path.1711360404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]