Abstract
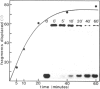
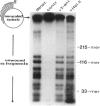
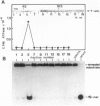
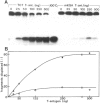
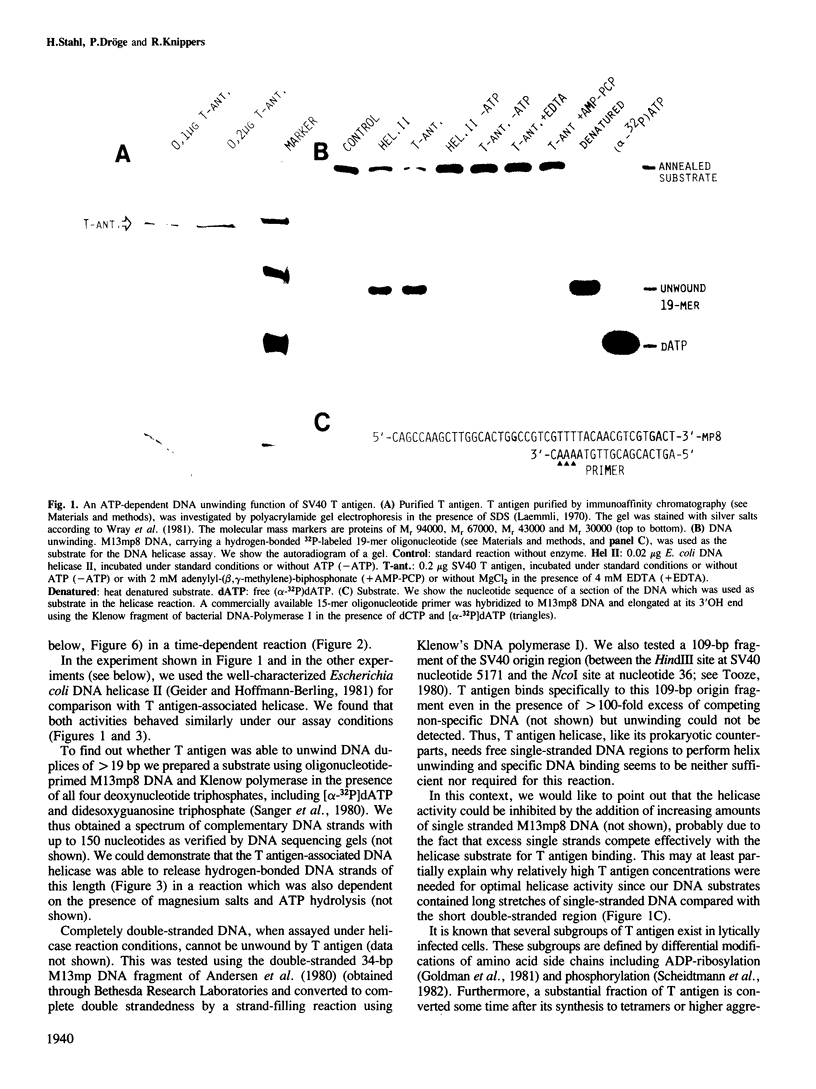
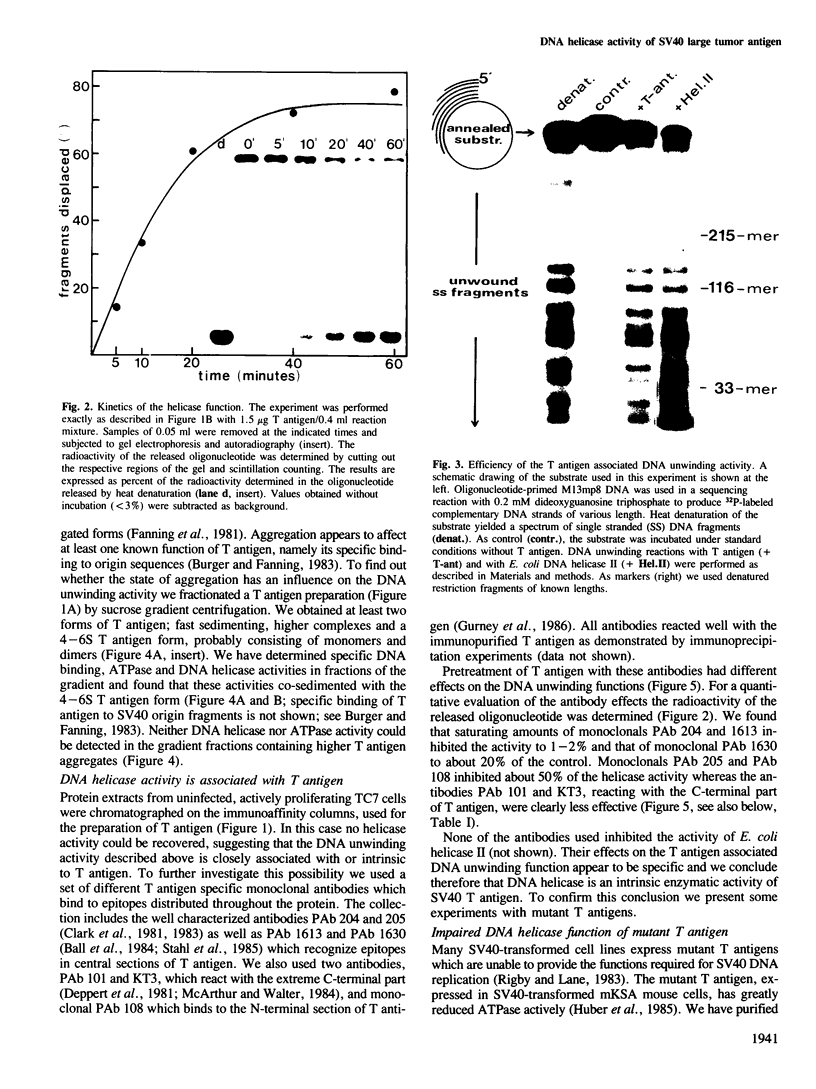
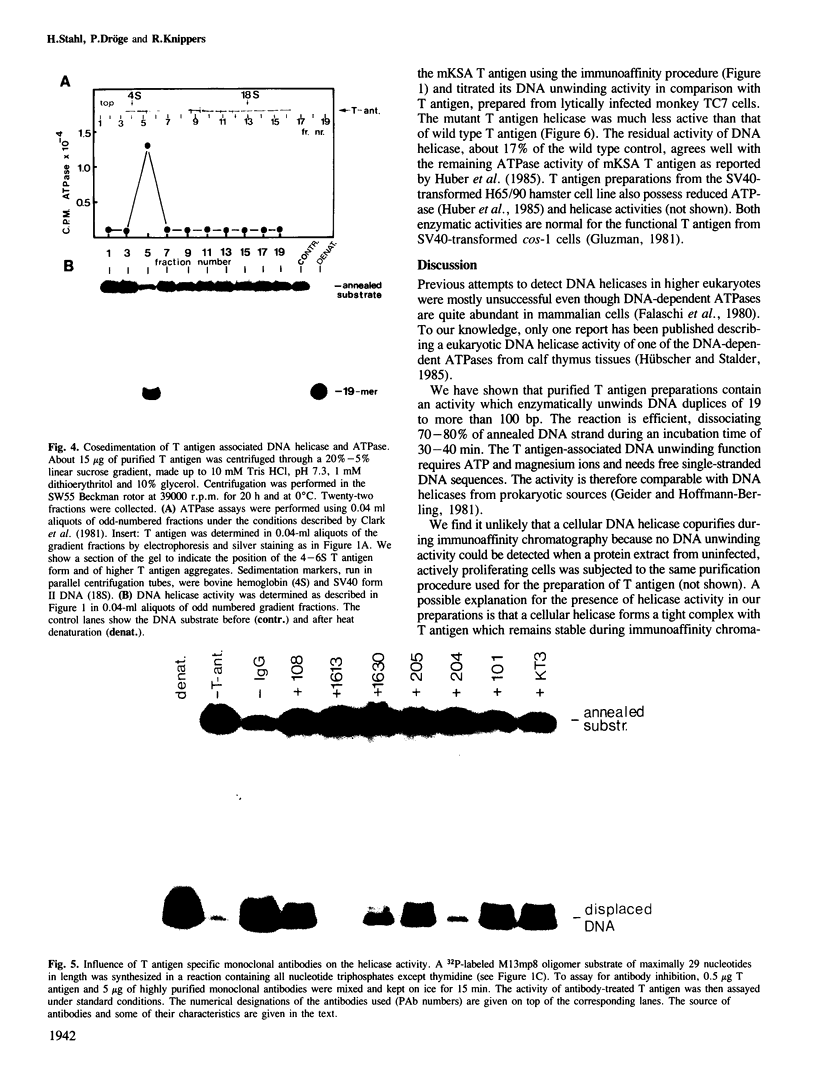
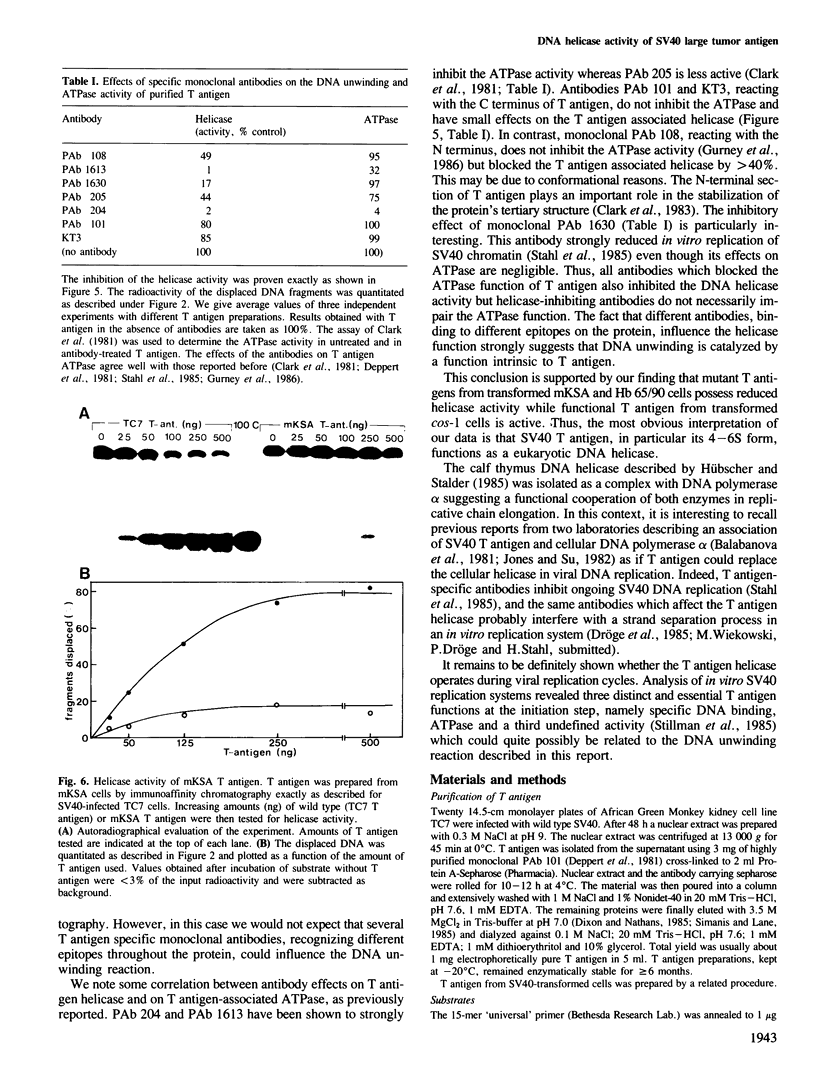
Large tumor antigen (T antigen) was extracted from SV40-infected African Green Monkey cells and purified to homogeneity by immunoaffinity chromatography. The purified T antigen preparations unwind DNA duplices of greater than 120 bp in a reaction which is dependent on magnesium ions and ATP hydrolysis. Based on these and other properties of the reaction we classify this newly discovered enzymatic activity as a eukaryotic DNA helicase. The helicase and the known ATPase function of T antigen cosediment with the mono- or dimeric 4-6 S form of T antigen, but not with higher T antigen aggregates. The helicase activity seems to be an intrinsic function of SV40 T antigen. First, several different T antigen-specific monoclonal antibodies interfere with the DNA unwinding activity; monoclonals which are known to reduce the T antigen-specific ATPase most strongly inhibited the helicase reaction. Second, mutant T antigens with impaired ATPase function also showed a reduced DNA unwinding activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Gait M. J., Mayol L., Young I. G. A short primer for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded phage vector M13mp2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1731–1743. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balabanova H., Fridlender B. R., Anderer F. A. Stimulation of DNA polymerase alpha by a nuclear DNA/protein complex. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;16(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380160102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball R. K., Siegl B., Quellhorst S., Brandner G., Braun D. G. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 nuclear large T tumour antigen: epitope mapping, papova virus cross-reaction and cell surface staining. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1485–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann E. A., Hand R. Protein kinase activity associated with the D2 hybrid protein related to simian virus 40 T antigen: some characteristics of the reaction products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3688–3692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M., Riboli B., Magni G. E. coli recA protein possesses a strand separating activity on short duplex DNAs. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):3025–3030. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04039.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger C., Fanning E. Specific DNA binding activity of T antigen subclasses varies among different SV40-transformed cell lines. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Lane D. P., Tjian R. Use of monoclonal antibodies as probes of simian virus 40 T antigen ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11854–11858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Peden K., Pipas J. M., Nathans D., Tjian R. Biochemical activities of T-antigen proteins encoded by simian virus 40 A gene deletion mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):220–228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Tornow J., Clark R., Tjian R. Properties of the simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigens encoded by SV40 mutants with deletions in gene A. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):539–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.539-546.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 tumor antigens: analysis of antigenic binding sites, using adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):478–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.478-482.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Nathans D. Purification of simian virus 40 large T antigen by immunoaffinity chromatography. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1001–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1001-1004.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge P., Sogo J. M., Stahl H. Inhibition of DNA synthesis by aphidicolin induces supercoiling in simian virus 40 replicative intermediates. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3241–3246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Nowak B., Burger C. Detection and characterization of multiple forms of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):92–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.92-102.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geider K., Hoffmann-Berling H. Proteins controlling the helical structure of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:233–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacherio D., Hager L. P. A poly(dT)-stimulated ATPase activity associated with simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8113–8116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman N., Brown M., Khoury G. Modification of SV40 T antigen by poly ADP-ribosylation. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):567–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Tamowski S., Deppert W. Antigenic binding sites of monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1168–1172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1168-1172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber B., Vakalopoulou E., Burger C., Fanning E. Identification and biochemical analysis of DNA replication-defective large T antigens from SV40-transformed cells. Virology. 1985 Oct 30;146(2):188–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Stalder H. P. Mammalian DNA helicase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5471–5483. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Su R. T. DNA polymerase alpha from the nuclear matrix of cells infected with simian virus 40. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5517–5532. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Smith A. E. In vitro mutagenesis of a putative DNA binding domain of SV40 large-T. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):109–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur H., Walter G. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the carboxy terminus of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):483–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.483-491.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Nathans D. Mutants of simian virus 40 with base substitutions at the origin of DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):663–668. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Lane D. P. An immunoaffinity purification procedure for SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillman T., Giacherio D., Hager L. P. Single strand DNA binding of simian virus 40 tumor antigen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3100–3104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Zentgraf H., Knippers R. A large-tumor-antigen-specific monoclonal antibody inhibits DNA replication of simian virus 40 minichromosomes in an in vitro elongation system. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):473–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.473-482.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Knippers R. Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen on replicating viral chromatin: tight binding and localization on the viral genome. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):65–76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.65-76.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B., Gerard R. D., Guggenheimer R. A., Gluzman Y. T antigen and template requirements for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2933–2939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Robbins A., Clark R. Catalytic properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):103–111. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Robbins A. Enzymatic activities associated with a purified simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):610–614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]