Abstract
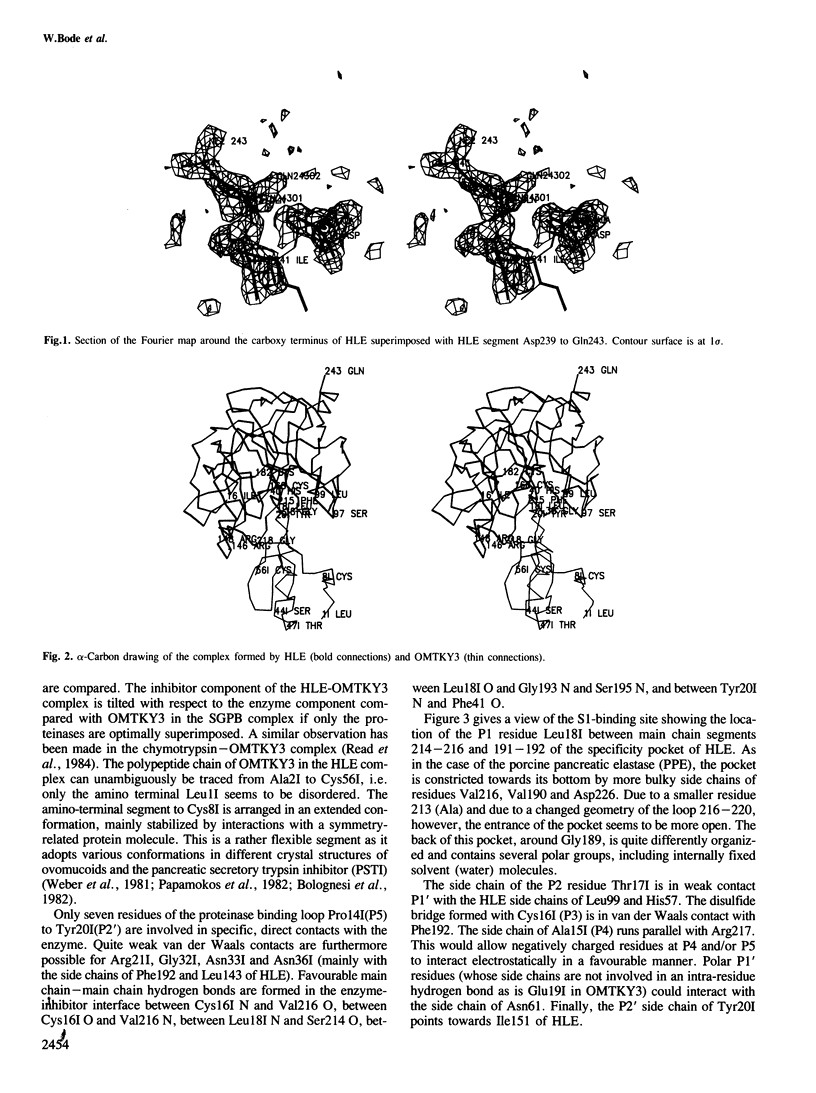
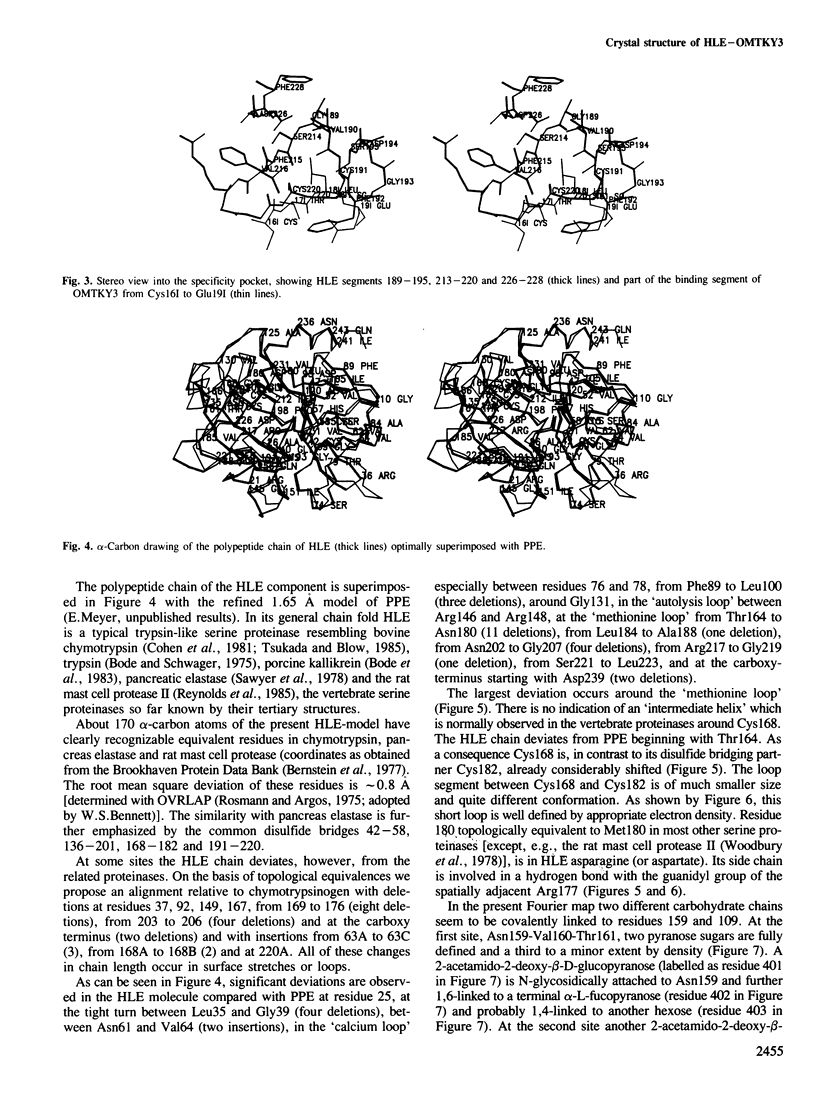
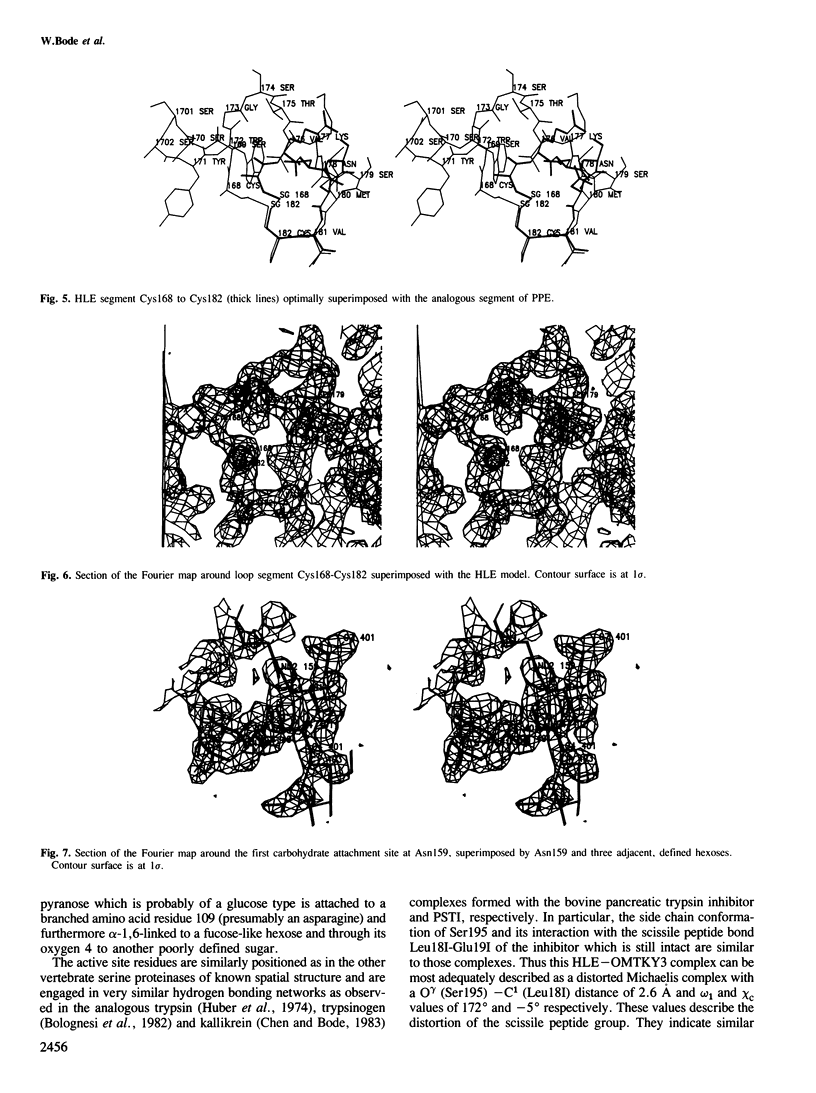
Orthorhombic crystals diffracting beyond 1.7 A resolution, have been grown from the stoichiometric complex formed between human leukocyte elastase (HLE) and the third domain of turkey ovomucoid inhibitor (OMTKY3). The crystal and molecular structure has been determined with the multiple isomorphous replacement technique. The complex has been modeled using the known structure of OMTKY3 and partial sequence information for HLE, and has been refined. The current crystallographic R-value is 0.21 for reflections from 25 to 1.8 A resolution. HLE shows the characteristic polypeptide fold of trypsin-like serine proteinases and consists of 218 amino acid residues. However, several loop segments, mainly arranged around the substrate binding site, have unique conformations. The largest deviations from the other vertebrate proteinases of known spatial structure are around Cys168. The specificity pocket is constricted by Val190, Val216 and Asp226 to preferentially accommodate medium sized hydrophobic amino acids at P1. Seven residues of the OMTKY3-binding segment are in specific contact with HLE. This interaction and geometry around the reactive site are similar as observed in other complexes. It is the first serine proteinase glycoprotein analysed, having two sugar chains attached to Asn159 and to residue 109.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardelt W., Laskowski M., Jr Thermodynamics and kinetics of the hydrolysis and resynthesis of the reactive site peptide bond in turkey ovomucoid third domain by aspergillopeptidase B. Acta Biochim Pol. 1983;30(2):115–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baugh R. J., Travis J. Human leukocyte granule elastase: rapid isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):836–841. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T., Sibanda B. L., Pearl L. Three-dimensional structure, specificity and catalytic mechanism of renin. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):273–275. doi: 10.1038/304273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Chen Z., Bartels K., Kutzbach C., Schmidt-Kastner G., Bartunik H. Refined 2 A X-ray crystal structure of porcine pancreatic kallikrein A, a specific trypsin-like serine proteinase. Crystallization, structure determination, crystallographic refinement, structure and its comparison with bovine trypsin. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):237–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Epp O., Huber R., Laskowski M., Jr, Ardelt W. The crystal and molecular structure of the third domain of silver pheasant ovomucoid (OMSVP3). Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):387–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Papamokos E., Musil D., Seemueller U., Fritz H. Refined 1.2 A crystal structure of the complex formed between subtilisin Carlsberg and the inhibitor eglin c. Molecular structure of eglin and its detailed interaction with subtilisin. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):813–818. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04286.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Schwager P. The refined crystal structure of bovine beta-trypsin at 1.8 A resolution. II. Crystallographic refinement, calcium binding site, benzamidine binding site and active site at pH 7.0. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 15;98(4):693–717. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogard W. C., Jr, Kato I., Laskowski M., Jr A Ser162/Gly162 polymorphism in Japanese quail ovomucoid. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6569–6574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi M., Gatti G., Menagatti E., Guarneri M., Marquart M., Papamokos E., Huber R. Three-dimensional structure of the complex between pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor (Kazal type) and trypsinogen at 1.8 A resolution. Structure solution, crystallographic refinement and preliminary structural interpretation. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):839–868. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90550-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Bode W. Refined 2.5 A X-ray crystal structure of the complex formed by porcine kallikrein A and the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Crystallization, Patterson search, structure determination, refinement, structure and comparison with its components and with the bovine trypsin-pancreatic trypsin inhibitor complex. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):283–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Silverton E. W., Davies D. R. Refined crystal structure of gamma-chymotrypsin at 1.9 A resolution. Comparison with other pancreatic serine proteases. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):449–479. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinaga M., Read R. J., Sielecki A., Ardelt W., Laskowski M., Jr, James M. N. Refined crystal structure of the molecular complex of Streptomyces griseus protease B, a serine protease, with the third domain of the ovomucoid inhibitor from turkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4868–4872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger R., Junk A., Jochum M. Isolation and characterization of porcine leukocyte elastase. Leukocyte elastase-inhibitor complexes in porcine blood, II. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1985 Dec;23(12):821–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer J. Comparative model-building of the mammalian serine proteases. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):1027–1042. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck L. W., Darby W. L., Hunter F. A., Bhown A., Miller E. J., Bennett J. C. Isolation, characterization, and amino-terminal amino acid sequence analysis of human neutrophil elastase from normal donors. Anal Biochem. 1985 Aug 15;149(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90488-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Kukla D., Bode W., Schwager P., Bartels K., Deisenhofer J., Steigemann W. Structure of the complex formed by bovine trypsin and bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. II. Crystallographic refinement at 1.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):73–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Elastase in tissue injury. Annu Rev Med. 1985;36:207–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.36.020185.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebermann H., Tokuoka R., Deisenhofer J., Huber R. Human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Crystal structure analysis of two crystal modifications, molecular model and preliminary analysis of the implications for function. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):531–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Olsson I. The neutral proteases of human granulocytes. Isolation and partial characterization of granulocyte elastases. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamokos E., Weber E., Bode W., Huber R., Empie M. W., Kato I., Laskowski M., Jr Crystallographic refinement of Japanese quail ovomucoid, a Kazal-type inhibitor, and model building studies of complexes with serine proteases. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):515–537. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read R. J., Fujinaga M., Sielecki A. R., James M. N. Structure of the complex of Streptomyces griseus protease B and the third domain of the turkey ovomucoid inhibitor at 1.8-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4420–4433. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Argos P. A comparison of the heme binding pocket in globins and cytochrome b5. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7525–7532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L., Shotton D. M., Campbell J. W., Wendell P. L., Muirhead H., Watson H. C. The atomic structure of crystalline porcine pancreatic elastase at 2.5 A resolution: comparisons with the structure of alpha-chymotrypsin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 15;118(2):137–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada H., Blow D. M. Structure of alpha-chymotrypsin refined at 1.68 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90314-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Papamokos E., Bode W., Huber R., Kato I., Laskowski M., Jr Crystallization, crystal structure analysis and molecular model of the third domain of Japanese quail ovomucoid, a Kazal type inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):109–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Katunuma N., Kobayashi K., Titani K., Neurath H., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. Covalent structure of a group-specific protease from rat small intestine. Appendix: crystallographic data for a group specific protease from rat intestine. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):811–819. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


