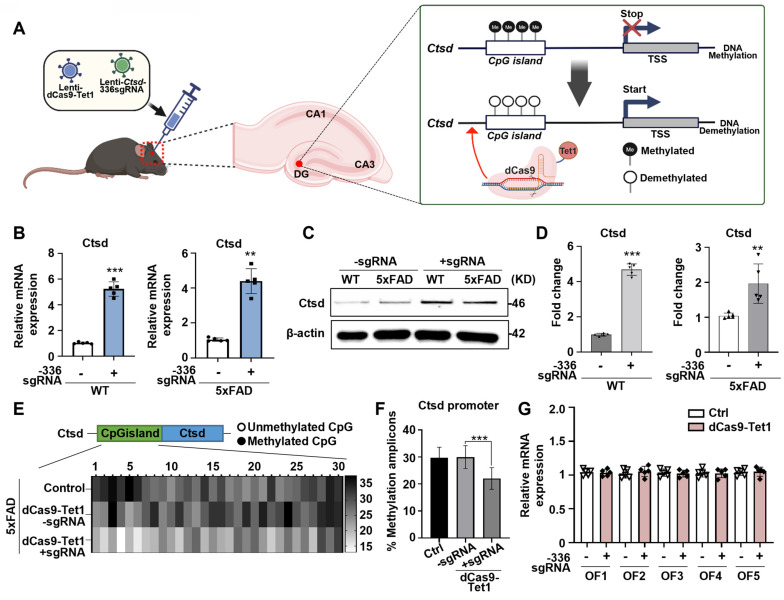
Figure 3.
dCas9-Tet1-Mediated demethylation of Ctsd in mouse brain. (A) Schematic representation of the dCas9-Tet1-mediated demethylation system targeting the Ctsd promoter in the mouse brain in vivo. (B) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of Ctsd expression in the brains of WT and 5xFAD mice injected with -336 sgRNA and dCas9-Tet1. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 5). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, two-tailed unpaired t-tests. (C-D) Western blot analysis of Ctsd in the brains of WT and 5xFAD mice injected with -336 sgRNA and dCas9-Tet1. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, two-tailed unpaired t-tests. (E) Bisulfite sequencing analysis of the Ctsd promoter region in the brain of 5xFAD mice injected with -336 sgRNA and dCas9-Tet1. (F) Quantificationof demethylated amplicons. A total of 10 to 30 sequences were analyzed across three independent experiments. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. (G) Evaluation of off-target effects using Cas-offinder in the hippocampus of WT mice injected with -336 sgRNA and dCas9-Tet1. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5). *p < 0.05, two-tailed unpaired t-tests. Image in panel C is representative of three or more similar experiments.