Abstract
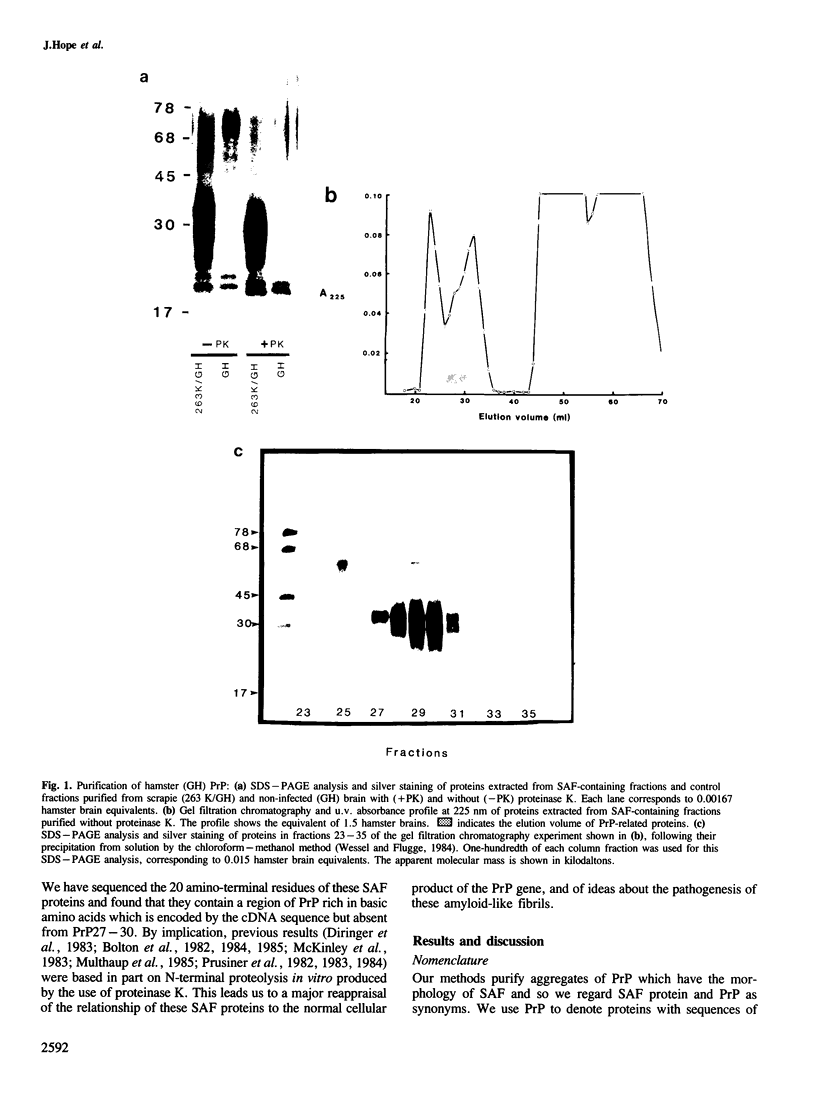
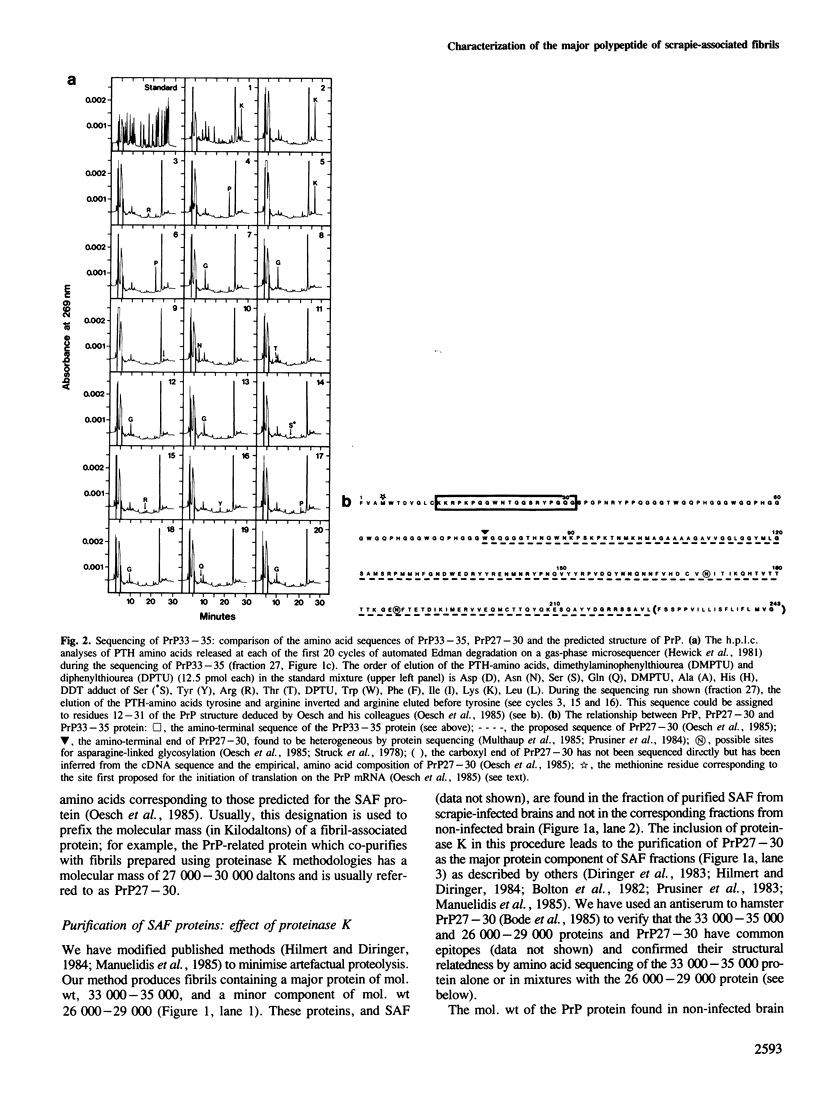
Scrapie-associated fibrils (SAF) are unique structures characteristic of the group of unconventional slow infections which includes scrapie and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. A major component of hamster fibrils has been described as a protease-resistant glycoprotein with an apparent mol. wt of 27,000-30,000 (PrP27-30). However, we report here that if fibrils are prepared by procedures designed to minimise proteolysis the PrP proteins co-purifying with hamster SAF have mol. wts of 33,000-35,000 (PrP33-35) and 26,000-29,000 (PrP26-29). We find a Lys-Lys-Arg-Pro-Lys sequence at the amino terminus of these SAF proteins, that is absent from PrP27-30, and which has recently been predicted to be the N-terminal sequence of the native PrP protein of uninfected brain. The major SAF protein (PrP33-35) and its normal brain homologue are shown to have the same apparent mol. wt and ionic charge distribution by two-dimensional gel analysis, silver staining and immunoblotting. These results support our view that PrP33-35 and the normal brain PrP protein may have the same covalent structure, and that the PrP protein is recruited into these amyloid-like SAF or into association with a non-protein component of SAF by an irreversible event initiated directly or indirectly by scrapie infection.
Full text
PDF
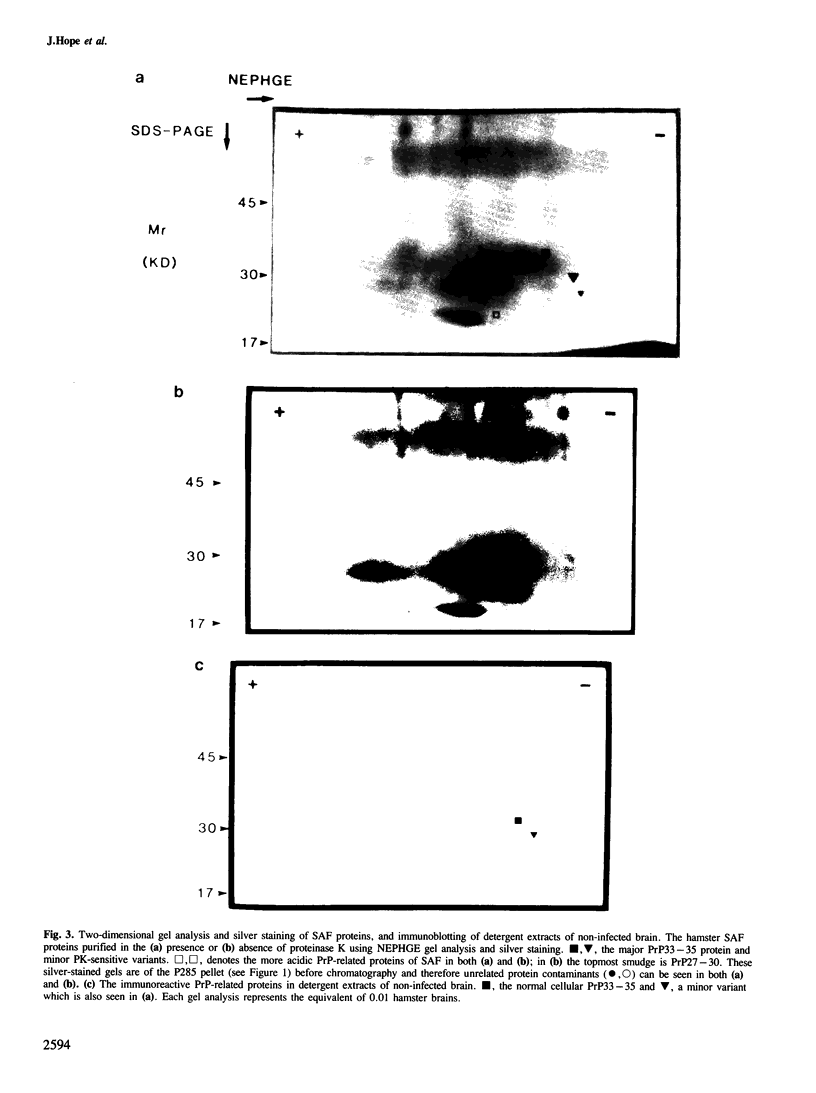



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bode L., Pocchiari M., Gelderblom H., Diringer H. Characterization of antisera against scrapie-associated fibrils (SAF) from affected hamster and cross-reactivity with SAF from scrapie-affected mice and from patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2471–2478. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Molecular characteristics of the major scrapie prion protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):5898–5906. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Meyer R. K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie PrP 27-30 is a sialoglycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):596–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.596-606.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Race R., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Bloom M., Lechner D., Bergstrom S., Robbins K., Mayer L., Keith J. M. Identification of scrapie prion protein-specific mRNA in scrapie-infected and uninfected brain. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):331–333. doi: 10.1038/315331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J. Antibody to scrapie-associated fibril protein identifies a cellular antigen. J Gen Virol. 1986 Feb;67(Pt 2):243–253. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., McKinley M. P., Barry R. A., Braunfeld M. B., McColloch J. R., Prusiner S. B. Identification of prion amyloid filaments in scrapie-infected brain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90076-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Gelderblom H., Hilmert H., Ozel M., Edelbluth C., Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie infectivity, fibrils and low molecular weight protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):476–478. doi: 10.1038/306476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1283–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilmert H., Diringer H. A rapid and efficient method to enrich SAF-protein from scrapie brains of hamsters. Biosci Rep. 1984 Feb;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1007/BF01120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kascsak R. J., Rubenstein R., Merz P. A., Carp R. I., Wisniewski H. M., Diringer H. Biochemical differences among scrapie-associated fibrils support the biological diversity of scrapie agents. J Gen Virol. 1985 Aug;66(Pt 8):1715–1722. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-8-1715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie: how much do we really understand? Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1986 Mar-Apr;12(2):131–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1986.tb00046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H., Walker C. A. Evidence that the transmission of one source of scrapie agent to hamsters involves separation of agent strains from a mixture. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jun;39(3):487–496. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-3-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar H. A., Prusiner S. B., Stowring L. E., DeArmond S. J. Scrapie prion proteins are synthesized in neurons. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jan;122(1):1–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Langer-Safer P. R., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of satellite DNA using biotin-labeled DNA probes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):619–625. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Valley S., Manuelidis E. E. Specific proteins associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie share antigenic and carbohydrate determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4263–4267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Bolton D. C., Prusiner S. B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Rohwer R. G., Kascsak R., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):437–440. doi: 10.1126/science.6377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Iqbal K. Abnormal fibrils from scrapie-infected brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;54(1):63–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00691333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Scrapie-associated fibrils in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):474–476. doi: 10.1038/306474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Braunfeld M. B., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Multhaup G., Diringer H., Hilmert H., Prinz H., Heukeshoven J., Beyreuther K. The protein component of scrapie-associated fibrils is a glycosylated low molecular weight protein. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1495–1501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Bolton D. C., Groth D. F., Bowman K. A., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P. Further purification and characterization of scrapie prions. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6942–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Bolton D. C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Purification and structural studies of a major scrapie prion protein. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90533-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein R., Kascsak R. J., Merz P. A., Papini M. C., Carp R. I., Robakis N. K., Wisniewski H. M. Detection of scrapie-associated fibril (SAF) proteins using anti-SAF antibody in non-purified tissue preparations. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):671–681. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville R. A., Merz P. A., Carp R. I. Partial copurification of scrapie-associated fibrils and scrapie infectivity. Intervirology. 1986;25(1):48–55. doi: 10.1159/000149654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Lennarz W. J., Brew K. Primary structural requirements for the enzymatic formation of the N-glycosidic bond in glycoproteins. Studies with alpha-lactalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5786–5794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Prusiner S. B. Conservation of the cellular gene encoding the scrapie prion protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2035–2044. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]