Abstract
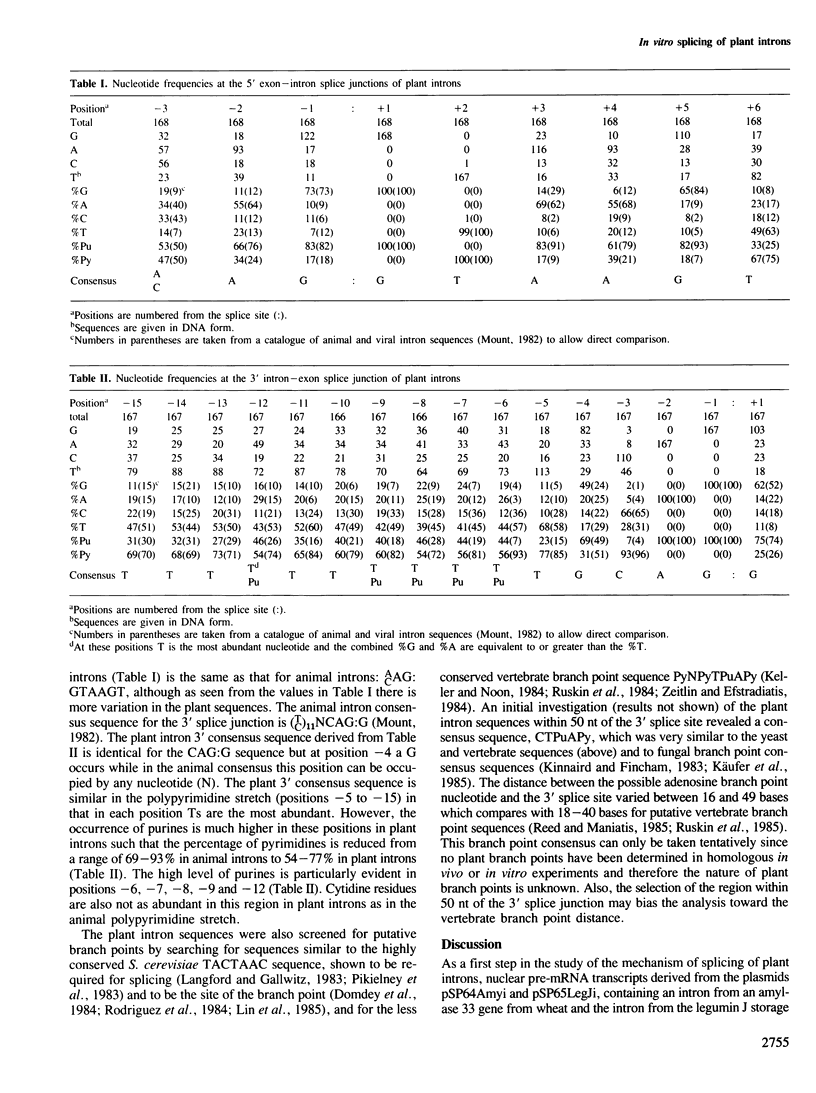
Two plant introns along with flanking exon sequences have been isolated from an amylase gene of wheat and a legumin gene of pea and cloned behind the phage SP6 promoter. Pre-mRNAs produced by in vitro transcription with SP6 RNA polymerase were tested for their ability to be spliced in a HeLa cell nuclear extract. The plant introns were accurately spliced and the predicted splice junctions were used. Lariat RNAs were observed as both intermediates and final products during the splicing reaction. The branch points were mapped to adenosine residues lying within sequences that showed good homology to the animal branch point consensus. Consensus sequences for the 5' and 3' splice junctions and for putative branch point sequences of plants were derived from an analysis of 168 plant intron sequences.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachy R. N., Chen Z. L., Horsch R. B., Rogers S. G., Hoffmann N. J., Fraley R. T. Accumulation and assembly of soybean beta-conglycinin in seeds of transformed petunia plants. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3047–3053. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M., Barker R., Goldsbrough A., Jarvis M., Kavanagh T., Iturriaga G. The structure and transcription start site of a major potato tuber protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4625–4638. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. Ribonucleoprotein complex formation during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2582–2592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutry M., Chua N. H. A nuclear gene encoding the beta subunit of the mitochondrial ATP synthase in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2159–2165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03910.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bown D., Levasseur M., Croy R. R., Boulter D., Gatehouse J. A. Sequence of a pseudogene in the legumin gene family of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4527–4538. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Annesi F., Beccari E., Fragapane P., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F. Splicing of Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein RNAs is inhibited in vivo by antisera to ribonucleoproteins containing U1 small nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson N., Verma D. P. Soybean leghemoglobin gene family: normal, pseudo, and truncated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4055–4059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E., Abelson J. The "spliceosome": yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3890181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broglie R., Coruzzi G., Fraley R. T., Rogers S. G., Horsch R. B., Niedermeyer J. G., Fink C. L., Chua N. H. Light-regulated expression of a pea ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit gene in transformed plant cells. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):838–843. doi: 10.1126/science.6719112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäumlein H., Wobus U., Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. The legumin gene family: structure of a B type gene of Vicia faba and a possible legumin gene specific regulatory element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2707–2720. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Black D. L., LeMaster D. M., Steitz J. A. The 3' splice site of pre-messenger RNA is recognized by a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1344–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2933810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Fractionation and characterization of a yeast mRNA splicing extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2387–2391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Edwards C., Chua N. H. Tissue-specific and light-regulated expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1671–1679. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. S., Sachs M. M., Gerlach W. L., Finnegan E. J., Peacock W. J. Molecular analysis of the alcohol dehydrogenase 2 (Adh2) gene of maize. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):727–743. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradin A., Jove R., Hemenway C., Keiser H. D., Manley J. L., Prives C. Splicing pathways of SV40 mRNAs in X. laevis oocytes differ in their requirements for snRNPs. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):927–936. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Definition of a novel promoter for the major adenovirus-associated virus mRNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. F., Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Cofactor requirements of splicing of purified messenger RNA precursors. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):375–377. doi: 10.1038/308375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Keller W. Splicing of in vitro synthesized messenger RNA precursors in HeLa cell extracts. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Jensen E. O., Paludan K., Wiborg O., Garrett R., Jørgensen P., Marcker K. A. The primary structures of two leghemoglobin genes from soybean. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):689–701. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltwasser G., Spitzer S. G., Goldenberg C. J. Assembly in an in vitro splicing reaction of a mouse insulin messenger RNA precursor into a 60-40S ribonucleoprotein complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3687–3701. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin-Neumann G. A., Kohorn B. D., Thornber J. P., Tobin E. M. A chlorophyll a/b-protein encoded by a gene containing an intron with characteristics of a transposable element. J Mol Appl Genet. 1985;3(1):45–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinakis P., Verma D. P. Nodulin-24 gene of soybean codes for a peptide of the peribacteroid membrane and was generated by tandem duplication of a sequence resembling an insertion element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4157–4161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E. B., Noon W. A. Intron splicing: a conserved internal signal in introns of animal pre-mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7417–7420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaird J. H., Fincham J. R. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Neurospora crassa am (NADP-specific glutamate dehydrogenase) gene. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Tóth M., Solymosy F. Plant small nuclear RNAs. Nucleolar U3 snRNA is present in plants: partial characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):259–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Characterization of the branch site in lariat RNAs produced by splicing of mRNA precursors. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):552–557. doi: 10.1038/313552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Ebel J. P., Rinke J., Luhrmann R. U1, U2 and U5 small nuclear RNAs are found in plants cells. Complete nucleotide sequence of the U5 RNA family from pea nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8583–8594. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W., Appel B., Lührmann R. The 5' terminus of the RNA moiety of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles is required for the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W. Purification of a protein required for the splicing of pre-mRNA and its separation from the lariat debranching enzyme. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3571–3581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Simanis V., Nurse P. Fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe correctly excises a mammalian RNA transcript intervening sequence. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):78–80. doi: 10.1038/318078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. J., Newman A. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Yeast mRNA splicing in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14780–14792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marco Y. A., Thanh V. H., Tumer N. E., Scallon B. J., Nielsen N. C. Cloning and structural analysis of DNA encoding an A2B1a subunit of glycinin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13436–13441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur B. J., Chui C. F. Sequence of a genomic DNA clone for the small subunit of ribulose bis-phosphate carboxylase-oxygenase from tobacco. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2373–2386. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai N., Kemp J. D., Sutton D. W., Murray M. G., Slightom J. L., Merlo D. J., Reichert N. A., Sengupta-Gopalan C., Stock C. A., Barker R. F., Hall T. C. Phaseolin gene from bean is expressed after transfer to sunflower via tumor-inducing plasmid vectors. Science. 1983 Nov 4;222(4623):476–482. doi: 10.1126/science.222.4623.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Lariat RNA's as intermediates and products in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):898–903. doi: 10.1126/science.6206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Mount S. M., Steitz J. A., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors is inhibited by antisera to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Mignery G. A., Ma D. P., Stark V. J., Park W. D. Sequence of two apparent pseudogenes of the major potato tuber protein, patatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5564–5566. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. Specific small nuclear RNAs are associated with yeast spliceosomes. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90561-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Evidence for the biochemical role of an internal sequence in yeast nuclear mRNA introns: implications for U1 RNA and metazoan mRNA splicing. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochester D. E., Winer J. A., Shah D. M. The structure and expression of maize genes encoding the major heat shock protein, hsp70. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):451–458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. R., Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. In vivo characterization of yeast mRNA processing intermediates. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. An RNA processing activity that debranches RNA lariats. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.2990042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Specific and stable intron-factor interactions are established early during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Greene J. M., Green M. R. Cryptic branch point activation allows accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin intron mutants. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):833–844. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler M. A., Schmitt E. S., Beachy R. N. Closely related families of genes code for the alpha and alpha' subunits of the soybean 7S storage protein complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8225–8244. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta-Gopalan C., Reichert N. A., Barker R. F., Hall T. C., Kemp J. D. Developmentally regulated expression of the bean beta-phaseolin gene in tobacco seed. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3320–3324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Complete nucleotide sequence of a soybean actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1022–1026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Genes encoding actin in higher plants: intron positions are highly conserved but the coding sequences are not. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):111–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Sun S. M., Hall T. C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a French bean storage protein gene: Phaseolin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumer N. E., Clark W. G., Tabor G. J., Hironaka C. M., Fraley R. T., Shah D. M. The genes encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase are expressed differentially in petunia leaves. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3325–3342. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayraghavan U., Parker R., Tamm J., Iimura Y., Rossi J., Abelson J., Guthrie C. Mutations in conserved intron sequences affect multiple steps in the yeast splicing pathway, particularly assembly of the spliceosome. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1683–1695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werr W., Frommer W. B., Maas C., Starlinger P. Structure of the sucrose synthase gene on chromosome 9 of Zea mays L. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1373–1380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiborg O., Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Jensen E. O., Paludan K., Marcker K. A. The nucleotide sequences of two leghemoglobin genes from soybean. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3487–3494. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Tollervey D., Maloney D., Swerdlow H., Dunn E. J., Guthrie C. Yeast contains small nuclear RNAs encoded by single copy genes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):743–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang V. W., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A., Flint S. J. A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein is required for splicing of adenoviral early RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1371–1375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






