Abstract
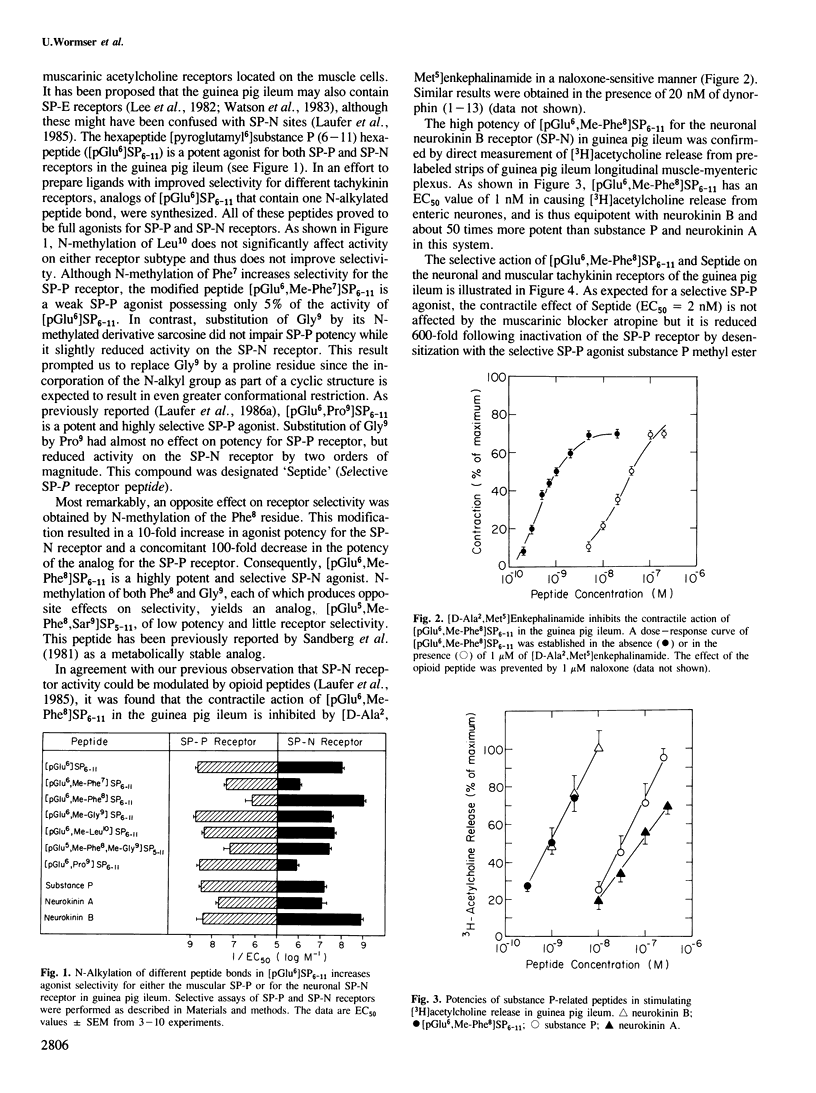
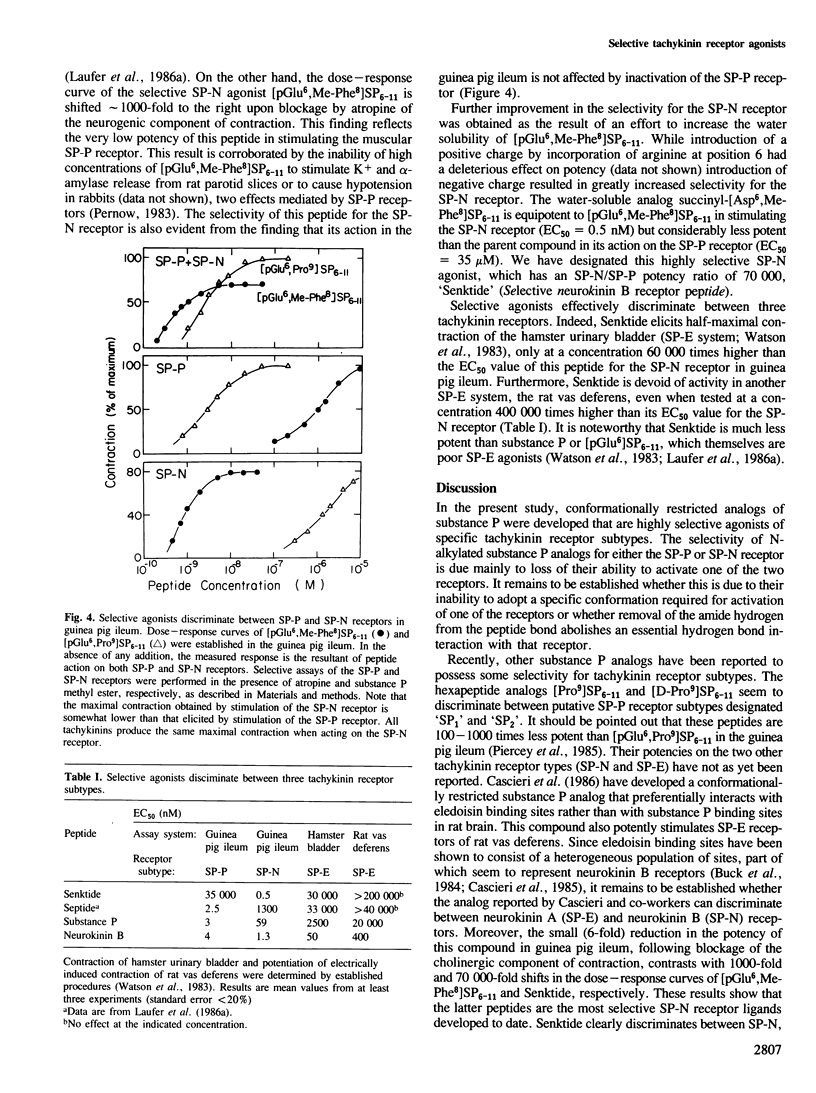
The existence of a third tachykinin receptor (SP-N) in the mammalian nervous system was demonstrated by development of highly selective agonists. Systematic N-methylation of individual peptide bonds in the C-terminal hexapeptide of substance P gave rise to agonists which specifically act on different receptor subtypes. The most selective analog of this series, succinyl-[Asp6,Me-Phe8]SP6-11, elicits half-maximal contraction of the guinea pig ileum through the neuronal SP-N receptor at a concentration of 0.5 nM. At least 60,000-fold higher concentrations of this peptide are required to stimulate the other two tachykinin receptors (SP-P and SP-E). The action of selective SP-N agonists in the guinea pig ileum is antagonized by opioid peptides, suggesting a functional counteraction between opiate and SP-N receptors. These results indicate that the tachykinin receptors are distinct entities which may mediate different physiological functions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthó L., Holzer P. Search for a physiological role of substance P in gastrointestinal motility. Neuroscience. 1985 Sep;16(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck S. H., Burcher E., Shults C. W., Lovenberg W., O'Donohue T. L. Novel pharmacology of substance K-binding sites: a third type of tachykinin receptor. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):987–989. doi: 10.1126/science.6095447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri M. A., Chicchi G. G., Freidinger R. M., Colton C. D., Perlow D. S., Williams B., Curtis N. R., McKnight A. T., Maguire J. J., Veber D. F. Conformationally constrained tachykinin analogs which are selective ligands for the eledoisin binding site. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;29(1):34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri M. A., Chicchi G. G., Liang T. Demonstration of two distinct tachykinin receptors in rat brain cortex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darman P. S., Landis G. C., Smits J. R., Hirning L. D., Gulya K., Yamamura H. I., Burks T. F., Hruby V. J. Conformationally restricted cyclic analogues of substance P: insight into the receptor binding process. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):656–662. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio J., Nguyen T. M., Lemieux C., Schiller P. W. Synthesis and pharmacological characterization in vitro of cyclic enkephalin analogues: effect of conformational constraints on opiate receptor selectivity. J Med Chem. 1982 Dec;25(12):1432–1438. doi: 10.1021/jm00354a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer-Petsche U., Schimek E., Amann R., Lembeck F. In vivo and in vitro actions of mammalian tachykinins. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;330(2):130–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00499905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P., Lippe I. T., Barthó L., Lembeck F. [D-Met2, Pro5]enkephalinamide and dynorphin-(1-13) inhibit the cholinergic contraction induced in the guinea-pig ileum by substance P. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jul 15;91(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90365-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Minamino N., Fukuda A., Matsuo H. Neuromedin K: a novel mammalian tachykinin identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):533–540. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90813-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Chorev M., Gilon C., Friedman Z. Y., Wormser U., Selinger Z. Persistent action of N-methylated analogs of substance P on rat parotid slices. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80311-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. Characterization of a neurokinin B receptor site in rat brain using a highly selective radioligand. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10257–10263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. [pGlu6,Pro9]SP6-11, a selective agonist for the substance P P-receptor subtype. J Med Chem. 1986 Jul;29(7):1284–1288. doi: 10.1021/jm00157a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Wormser U., Friedman Z. Y., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. Neurokinin B is a preferred agonist for a neuronal substance P receptor and its action is antagonized by enkephalin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7444–7448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Iversen L. L., Hanley M. R., Sandberg B. E. The possible existence of multiple receptors for substance P. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;318(4):281–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00501166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manavalan P., Momany F. A. Conformational energy studies on N-methylated analogs of thyrotropin releasing hormone, enkephalin, and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. Biopolymers. 1980 Nov;19(11):1943–1973. doi: 10.1002/bip.1980.360191103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Gee K., Yamamura H. I., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F. Bis-penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5871–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Doteuchi M., Igano K., Inouye K., Nakanishi S. Substance K: a novel mammalian tachykinin that differs from substance P in its pharmacological profile. Life Sci. 1984 Mar 19;34(12):1153–1160. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Schenker C., Leeman S. E. Substance P as a transmitter candidate. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:227–268. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osakada F., Kubo K., Goto K., Kanazawa I., Munekata E. The contractile activities of neurokinin A, B and related peptides on smooth muscles. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 21;120(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90541-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Zar M. A. The origin of acetylcholine released from guinea-pig intestine and longitudinal muscle strips. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):13–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow B. Substance P. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Jun;35(2):85–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piercey M. F., Dobry-Schreur P. J., Masiques N., Schroeder L. A. Stereospecificity of SP1 and SP2 substance P receptors. Life Sci. 1985 Feb 25;36(8):777–780. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg B. E., Lee C. M., Hanley M. R., Iversen L. L. Synthesis and biological properties of enzyme-resistant analogues of substance P. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Neurotransmitter receptor binding and drug discovery. J Med Chem. 1983 Dec;26(12):1667–1672. doi: 10.1021/jm00366a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodoropoulos D., Poulos C., Gatos D., Cordopatis P., Escher E., Mizrahi J., Regoli D., Dalietos D., Furst A., Lee T. D. Conformationally restricted C-terminal peptides of substance P. Synthesis, mass spectral analysis and pharmacological properties. J Med Chem. 1985 Oct;28(10):1536–1539. doi: 10.1021/jm00148a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrens Y., Lavielle S., Chassaing G., Marquet A., Glowinski J., Beaujouan J. C. Neuromedin K, a tool to further distinguish two central tachykinin binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 13;102(2):381–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran V. T., Beal M. F., Martin J. B. Two types of somatostatin receptors differentiated by cyclic somatostatin analogs. Science. 1985 Apr 26;228(4698):492–495. doi: 10.1126/science.2858917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veber D. F., Freidlinger R. M., Perlow D. S., Paleveda W. J., Jr, Holly F. W., Strachan R. G., Nutt R. F., Arison B. H., Homnick C., Randall W. C. A potent cyclic hexapeptide analogue of somatostatin. Nature. 1981 Jul 2;292(5818):55–58. doi: 10.1038/292055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Bartho L. Presynaptic modulation by noradrenaline and an opioid of the substance P-induced release of [3H]acetylcholine from the myenteric plexus. Regul Pept. 1985 Nov 28;12(4):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(85)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Sandberg B. E., Hanley M. R., Iversen L. L. Tissue selectivity of substance P alkyl esters: suggesting multiple receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 28;87(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


