Abstract
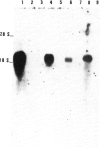
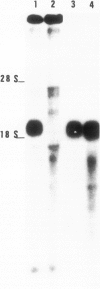
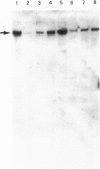
We have isolated a human genomic clone for the intermediate filament subunit vimentin with a DNA probe encoding chicken vimentin. We show that the gene for this protein exists as a single copy in the haploid human genome and is transcribed into one mature RNA species of 2 kb. In vitro translation of poly(A)+ mRNA in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free system showed that vimentin is a major product of RNA from normal lymphocytes but not of RNA extracted from Burkitt cells. 2-kb vimentin mRNA can be detected with a DNA probe in normal lymphocytes and in fibroblasts, but not in cell lines derived from Burkitt's lymphoma (JI, JBL2, BJAB, DAUDI). The abundance of vimentin mRNA is correlated with the quantity of vimentin present in the cells, suggesting that the level of expression is regulated by the abundance of mRNA. The half-lives of vimentin mRNA were found identical in both fibroblasts and lymphocytes and belong to the class of stable mRNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso S., Minty A., Bourlet Y., Buckingham M. Comparison of three actin-coding sequences in the mouse; evolutionary relationships between the actin genes of warm-blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02100994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capetanaki Y. G., Ngai J., Flytzanis C. N., Lazarides E. Tissue-specific expression of two mRNA species transcribed from a single vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellagi K., Brouet J. C., Portier M. M., Lenoir G. M. Abnormal expression of vimentin intermediate filaments in human lymphoid cell lines with deletion or translocation of the distal end of chromosome 8. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Jul;73(1):95–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellagi K., Vainchenker W., Vinci G., Paulin D., Brouet J. C. Alteration of vimentin intermediate filament expression during differentiation of human hemopoietic cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1509–1514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodemont H. J., Soriano P., Quax W. J., Ramaekers F., Lenstra J. A., Groenen M. A., Bernardi G., Bloemendal H. The genes coding for the cytoskeletal proteins actin and vimentin in warm-blooded vertebrates. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Breitkreutz D., Lüder M., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Osborn M., Weber K. Simultaneous expression of two different types of intermediate sized filaments in mouse keratinocytes proliferating in vitro. Differentiation. 1979;14(1-2):35–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Amino acid sequence data on glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFA); implications for the subdivision of intermediate filaments into epithelial and non-epithelial members. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2059–2063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Lenoir G. Translocations involving Ig-locus-carrying chromosomes: a model for genetic transposition in carcinogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1982;37:381–387. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60887-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McTavish C. F., Nelson W. J., Traub P. Synthesis of vimentin in a reticulocyte cell-free system programmed by poly(A)-rich RNA from several cell lines and rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):211–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Meera Khan P., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The human desmin and vimentin genes are located on different chromosomes. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., van den Heuvel R., Egberts W. V., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. Intermediate filament cDNAs from BHK-21 cells: demonstration of distinct genes for desmin and vimentin in all vertebrate classes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5970–5974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. Message of myc in context. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):585–587. doi: 10.1038/309585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehner Z. E., Paterson B. M. Characterization of the chicken vimentin gene: single copy gene producing multiple mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):911–915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehner Z. E., Paterson B. M. Vimentin gene expression during myogenesis: two functional transcripts from a single copy gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8317–8332. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]