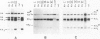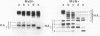Abstract
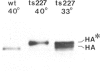
Mutants ts1 and ts227 of fowl plague virus have a temperature-sensitive defect in the transport of the hemagglutinin from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. The primary structure of the hemagglutinin of the mutants and of a number of revertants derived from them has been analysed by nucleotide sequencing. The transport block of the hemagglutinin of ts227 can be attributed to a single amino acid exchange. It involves the replacement of aspartic acid at position 457 by asparagine thereby introducing a new glycosylation site which appears to be located in a cryptic position in the lower part of the hemagglutinin stalk. Attachment of carbohydrate to this site is temperature-dependent. At permissive temperature only a small fraction of the monomers (approximately 30%) is glycosylated in this position, whereas at nonpermissive temperature this is the case with all subunits. The data suggest that under the latter conditions the new oligosaccharide interferes by steric hindrance with the trimerization of the hemagglutinin. The hemagglutinin of ts1 has an essential amino acid exchange at position 275 where serine is replaced by glycine. This substitution may increase the flexibility of the molecule in the hinge region between the globular domain and the stalk. The exchange of a conserved glutamic acid residue at position 398 that is involved in the interaction between different monomers contributes also to the structural instability of the ts1 hemagglutinin. These observations support the notion that the transport of the hemagglutinin from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus depends on trimer assembly.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias C., Bell J. R., Lenches E. M., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Sequence analysis of two mutants of Sindbis virus defective in the intracellular transport of their glycoproteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):87–102. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Analyses of the antigenicity of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH optimum for virus-mediated membrane fusion. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1657–1662. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. S., Downie J. C., Hay A. J., Knossow M., Skehel J. J., Wang M. L., Wiley D. C. Fusion mutants of the influenza virus hemagglutinin glycoprotein. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle C., Roth M. G., Sambrook J., Gething M. J. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of the influenza virus hemagglutinin affect different stages of intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):704–714. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallione C. J., Rose J. K. A single amino acid substitution in a hydrophobic domain causes temperature-sensitive cell-surface transport of a mutant viral glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):374–382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.374-382.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Kuroda K., Schuy W., Naruse H., Scholtissek C., Klenk H. D. Haemagglutinin transport mutants. Vaccine. 1985 Sep;3(3 Suppl):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Klein U., Waheed A., Strecker G., von Figura K. Phosphorylated oligosaccharides in lysosomal enzymes: identification of alpha-N-acetylglucosamine(1)phospho(6)mannose diester groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7074–7078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil W., Geyer R., Dabrowski J., Dabrowski U., Niemann H., Stirm S., Klenk H. D. Carbohydrates of influenza virus. Structural elucidation of the individual glycans of the FPV hemagglutinin by two-dimensional 1H n.m.r. and methylation analysis. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2711–2720. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil W., Niemann H., Schwarz R. T., Klenk H. D. Carbohydrates of influenza virus. V. Oligosaccharides attached to individual glycosylation sites of the hemagglutinin of fowl plague virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmeyer J., Klenk H. D. A mutant of influenza virus with a temperature-sensitive defect in the posttranslational processing of the hemagglutinin. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):134–145. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse H., Scholtissek C., Klenk H. D. Temperature-sensitive mutants of fowl plague virus defective in the intracellular transport of the hemagglutinin. Virus Res. 1986 Aug;5(2-3):293–305. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. G., Barber C., Carey N. H., Hallewell R. A., Threlfall G., Emtage J. S. Complete nucleotide sequence of an influenza virus haemagglutinin gene from cloned DNA. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):471–477. doi: 10.1038/282471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P. A., Datema R., Schwarz R. T. N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin, a novel inhibitor of glycoprotein processing, and its effect on fowl plague virus maturation. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Orlich M., Klenk H. D., Wang M. L., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Studies on the adaptation of influenza viruses to MDCK cells. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3329–3332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Bowles A. L. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of fowl plague virus. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):576–587. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90457-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Kruczinna R., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Characteristics of an influenza mutant temperature-sensitive for viral RNA synthesis. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Schwarz R. T., Keil W., Klenk H. D. A mutant of fowl plague virus (influenza A) with an altered glycosylation pattern in its hemagglutinin. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabas I., Kornfeld S. Biosynthetic intermediates of beta-glucuronidase contain high mannose oligosaccharides with blocked phosphate residues. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6633–6639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]