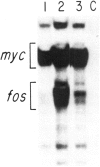Abstract
Expression of the myc and fos genes has been monitored in mouse primary keratinocytes after induction of terminal differentiation by calcium or tetradecanoylphorbol acetate (TPA). myc RNA levels in growing cells are very high and remain elevated even at late times after calcium-induced differentiation. Thus, keratinocytes provide the first example of normal primary cells with persistent c-myc expression irrespective of their proliferative or differentiated state. fos expression is also relatively unaffected by addition of calcium. In contrast to calcium, TPA-induced differentiation is accompanied by dramatic changes in proto-oncogene expression: marked c-fos induction and considerable although transient decrease in c-myc expression. These effects might be important for the keratinocyte response to TPA: TPA treatment of a keratinocyte cell line (RBK) resistant to this substance has no effect on c-myc expression and leads only to minimal c-fos induction. In these cells full fos induction can still be triggered by addition of fresh medium. Thus, the fos gene in normal keratinocytes is inducible through at least two independent mechanisms, only one of which has been lost during derivation of the TPA-resistant cell line.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Zullo J., Verma I. M., Stiles C. D. Expression of the c-fos gene and of an fos-related gene is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1080–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6093261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Morgan J. I. Superinduction of c-fos by nerve growth factor in the presence of peripherally active benzodiazepines. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.4035354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Nadal-Ginard B. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of c-myc during myogenesis: its mRNA remains inducible in differentiated cells and does not suppress the differentiated phenotype. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1412–1421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusenig N. E., Breitkreutz D., Dzarlieva R. T., Boukamp P., Bohnert A., Tilgen W. Growth and differentiation characteristics of transformed keratinocytes from mouse and human skin in vitro and in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):168s–175s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12541032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny A. E., Morgan D., Spangler E. F., Yuspa S. H. Correlation of initiating potency of skin carcinogens with potency to induce resistance to terminal differentiation in cultured mouse keratinocytes. Cancer Res. 1985 May;45(5):2219–2225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Schubert D., Verma I. M. Induction of the proto-oncogene fos by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7330–7334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesz-Martin M. F., Koehler B., Hennings H., Yuspa S. H. Quantitative assay for carcinogen altered differentiation in mouse epidermal cells. Carcinogenesis. 1980;1(12):995–1006. doi: 10.1093/carcin/1.12.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Henning-Chubb C., Huberman E., Verma I. M. c-fos expression is neither sufficient nor obligatory for differentiation of monomyelocytes to macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
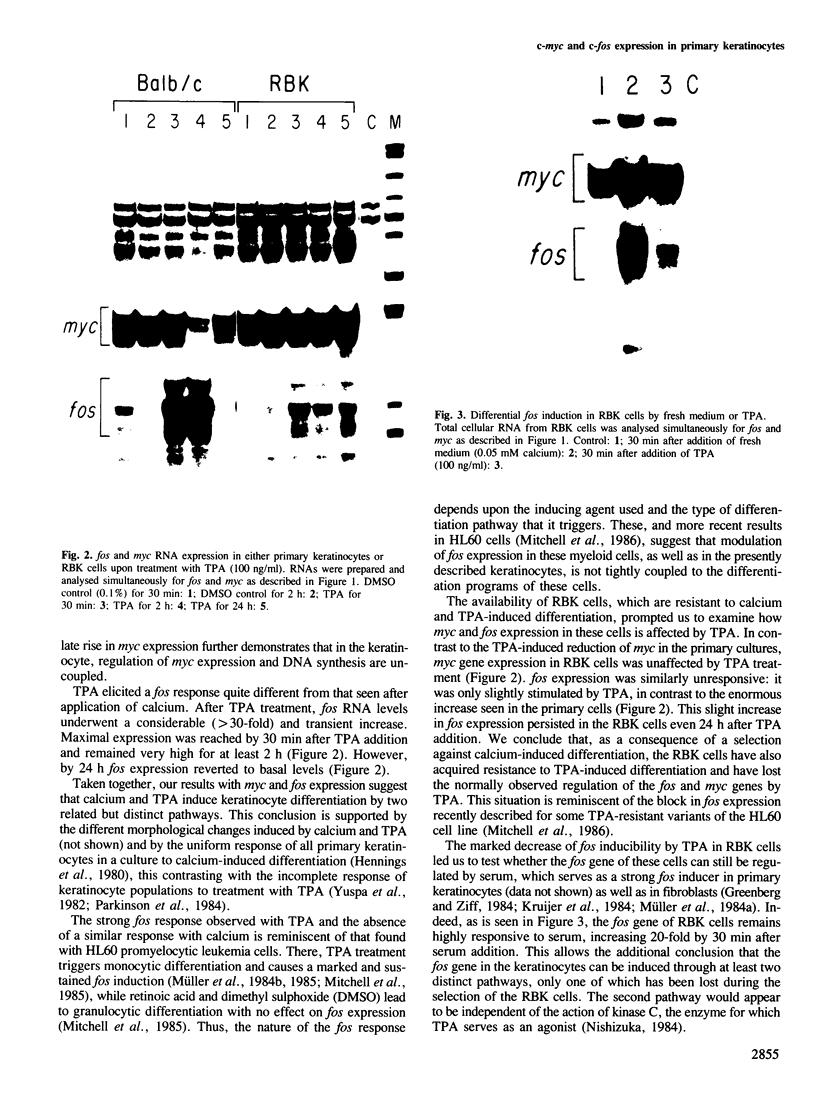
- Mitchell R. L., Zokas L., Schreiber R. D., Verma I. M. Rapid induction of the expression of proto-oncogene fos during human monocytic differentiation. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Curran T., Müller D., Guilbert L. Induction of c-fos during myelomonocytic differentiation and macrophage proliferation. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):546–548. doi: 10.1038/314546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Müller D., Guilbert L. Differential expression of c-fos in hematopoietic cells: correlation with differentiation of monomyelocytic cells in vitro. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1887–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson E. K., Pera M. F., Emmerson A., Gorman P. A. Differential effects of complete and second-stage tumour promoters in normal but not transformed human and mouse keratinocytes. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Aug;5(8):1071–1077. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.8.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Differentiation of the epidermal keratinocyte in cell culture: formation of the cornified envelope. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):511–521. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toftgard R., Roop D. R., Yuspa S. H. Proto-oncogene expression during two-stage carcinogenesis in mouse skin. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Apr;6(4):655–657. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Curran T., Müller R., Verma I. M. Analysis of FBJ-MuSV provirus and c-fos (mouse) gene reveals that viral and cellular fos gene products have different carboxy termini. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1241–1255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Wong-Staal F., Gelmann E. P., Dalla-Favera R., Papas T. S., Lautenberger J. A., Eva A., Reddy E. P., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Expression of cellular homologues of retroviral onc genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2490–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Ben T., Hennings H., Lichti U. Divergent responses in epidermal basal cells exposed to the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2344–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Harris C. C. Altered differentiation of mouse epidermal cells treated with retinyl acetate in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1974 May;86(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90653-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Kulesz-Martin M., Ben T., Hennings H. Transformation of epidermal cells in culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):162s–168s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Morgan D. L. Mouse skin cells resistant to terminal differentiation associated with initiation of carcinogenesis. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):72–74. doi: 10.1038/293072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]