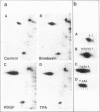
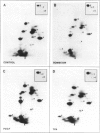
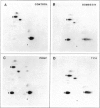
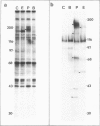
Abstract
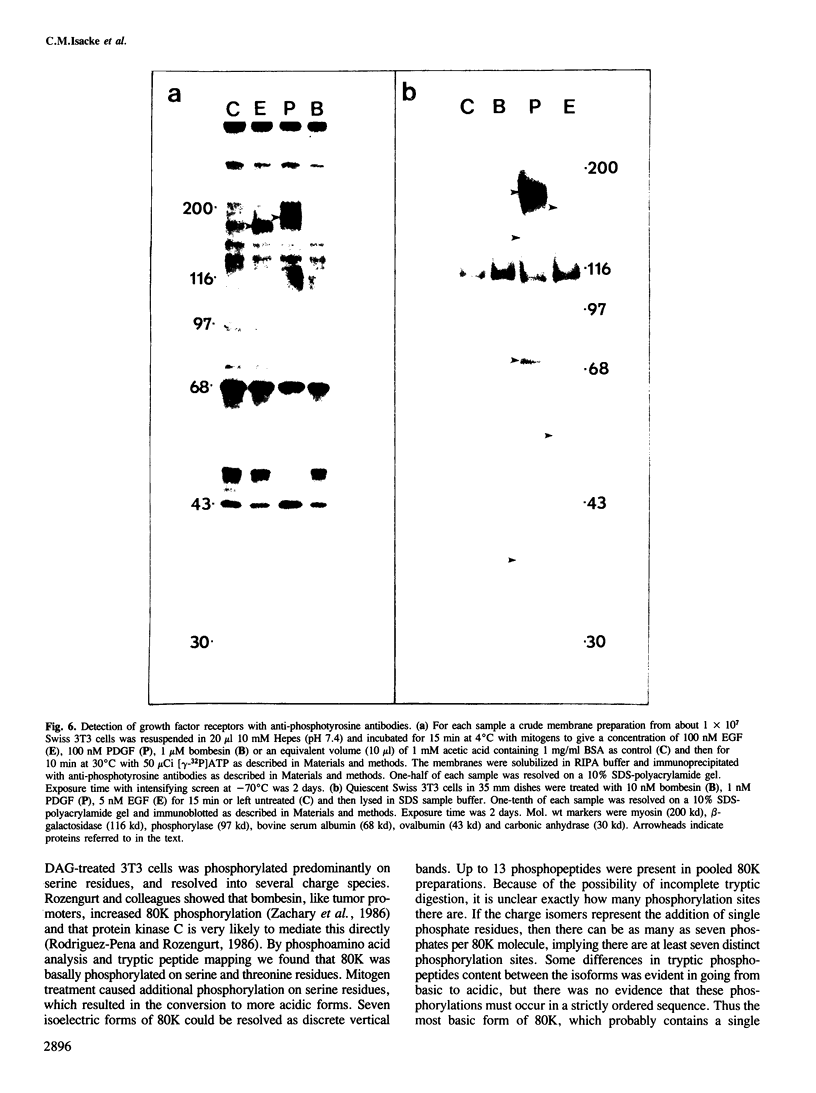
Bombesin and the related mammalian peptides, such as gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP), are potent mitogens for some fibroblast cell lines. Here we have examined the bombesin- and GRP-mediated changes in the phosphorylation of proteins in Swiss 3T3 cells and compared these to the events observed after platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF) and tumor promoter treatment. In agreement with previous reports, bombesin, GRP and PDGF, but not EGF, increased the activity of protein kinase C. This was assayed by an inhibition of [125I]EGF binding, stimulation in phosphorylation of pp60c-src on serine 12 and stimulation in phosphorylation of a group of 80 kd proteins. The different phosphorylated forms of the 80 kd proteins were examined by tryptic peptide mapping and shown to contain multiple phosphorylation sites. An investigation of the tyrosine phosphorylation events following mitogen treatment revealed a significant difference between PDGF and the bombesin peptides. PDGF treatment caused a marked increase in total cellular phosphotyrosine levels, and tyrosine phosphorylation both of known substrates and its own receptor. In contrast, bombesin and GRP treatments resulted in only a weak or undetectable increase in tyrosine phosphorylation of total cellular protein or known substrates. In this respect bombesin and GRP were more similar to EGF. The fact that the bombesin peptides do not induce a phosphorylation response identical with either PDGF or EGF suggests that there is not a single common signal pathway which is activated by all these mitogens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anastasi A., Erspamer V., Bucci M. Isolation and structure of bombesin and alytesin, 2 analogous active peptides from the skin of the European amphibians Bombina and Alytes. Experientia. 1971 Feb 15;27(2):166–167. doi: 10.1007/BF02145873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashendel C. L. The phorbol ester receptor: a phospholipid-regulated protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 9;822(2):219–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R., Martinez R., Weber M. J., Blackshear P. J., Beatty S., Lim R., Herschman H. R. Protein phosphorylation in a tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-nonproliferative variant of 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2231–2237. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Wen L., Glynn B. P., Witters L. A. Protein kinase C-stimulated phosphorylation in vitro of a Mr 80,000 protein phosphorylated in response to phorbol esters and growth factors in intact fibroblasts. Distinction from protein kinase C and prominence in brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1459–1469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Witters L. A., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Quamo S. N. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13304–13315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blay J., Irvine R. F., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. Reduction of epidermal growth factor receptor affinity by heterologous ligands: evidence for a mechanism involving the breakdown of phosphoinositides and the activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to surface receptors by tumor promotors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Märki W., Rivier J. Is gastrin releasing peptide mammalian bombesin? Life Sci. 1980 Jul 14;27(2):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90453-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Rozengurt E. Binding of phorbol esters to high-affinity sites on murine fibroblastic cells elicits a mitogenic response. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jul;112(1):42–50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Rozengurt E. Homologous and heterologous mitogenic desensitization of Swiss 3T3 cells to phorbol esters and vasopressin: role of receptor and postreceptor steps. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Feb;118(2):133–142. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Raines E., Ross R., Hunter T. Similar effects of platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor on the phosphorylation of tyrosine in cellular proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90426-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Changes in protein phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):165–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Major substrate for growth factor-activated protein-tyrosine kinases is a low-abundance protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3304–3309. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Regulation of cell growth and transformation by tyrosine-specific protein kinases: the search for important cellular substrate proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:125–161. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69075-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Diverse mitogenic agents induce the phosphorylation of two related 42,000-dalton proteins on tyrosine in quiescent chick cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corps A. N., Rees L. H., Brown K. D. A peptide that inhibits the mitogenic stimulation of Swiss 3T3 cells by bombesin or vasopressin. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):781–784. doi: 10.1042/bj2310781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuttitta F., Carney D. N., Mulshine J., Moody T. W., Fedorko J., Fischler A., Minna J. D. Bombesin-like peptides can function as autocrine growth factors in human small-cell lung cancer. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):823–826. doi: 10.1038/316823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erisman M. D., Linnoila R. I., Hernandez O., DiAugustine R. P., Lazarus L. H. Human lung small-cell carcinoma contains bombesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2379–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry M. J., Gebhardt A., Parker P. J., Foulkes J. G. Phosphatidylinositol turnover and transformation of cells by Abelson murine leukaemia virus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3173–3178. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis and computer analysis of proteins synthesized by clonal cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7961–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. E., Chaffin K. E., Shoyab M., Purchio A. F. Novel serine phosphorylation of pp60c-src in intact cells after tumor promoter treatment. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):735–738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Phorbol ester and diacylglycerol induce protein phosphorylation at tyrosine. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):487–490. doi: 10.1038/306487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Woodgett J. R., Cooper J. A., Buss J. E., Shalloway D., Hunter T. Protein kinase C phosphorylates pp60src at a novel site. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., King W. C., Nist C., Mitchell C. D., Ross R. Early changes in phosphatidylinositol and arachidonic acid metabolism in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12329–12335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacke C. M., Trowbridge I. S., Hunter T. Modulation of p36 phosphorylation in human cells: studies using anti-p36 monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2745–2751. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. J., Jörnvall H., Nilsson G., Vagne M., Ghatei M., Bloom S. R., Mutt V. Characterization of a gastrin releasing peptide from porcine non-antral gastric tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody T. W., Carney D. N., Cuttitta F., Quattrocchi K., Minna J. D. High affinity receptors for bombesin/GRP-like peptides on human small cell lung cancer. Life Sci. 1985 Jul 15;37(2):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90413-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody T. W., Pert C. B., Gazdar A. F., Carney D. N., Minna J. D. High levels of intracellular bombesin characterize human small-cell lung carcinoma. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1246–1248. doi: 10.1126/science.6272398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines E. W., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. I. High yield purification and evidence for multiple forms. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5154–5160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R., Bishop J. M. The product of the protooncogene c-src is modified during the cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier C., Rivier J., Vale W. The effect of bombesin and related peptides on prolactin and growth hormone secretion in the rat. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):519–522. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier J. E., Brown M. R. Bombesin, bombesin analogues, and related peptides: effects on thermoregulation. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1766–1771. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Phosphorylation of an acidic mol. wt. 80 000 cellular protein in a cell-free system and intact Swiss 3T3 cells: a specific marker of protein kinase C activity. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):77–83. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Serum, like phorbol esters, rapidly activates protein kinase C in intact quiescent fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):71–76. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Rodriguez-Pena M., Smith K. A. Phorbol esters, phospholipase C, and growth factors rapidly stimulate the phosphorylation of a Mr 80,000 protein in intact quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7244–7248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Sinnett-Smith J. Bombesin stimulation of DNA synthesis and cell division in cultures of Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Beemon K., Hunter T. Comparison of the expression of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus in vitro and in vivo. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):957–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.957-971.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Diacylglycerol treatment rapidly decreases the affinity of the epidermal growth factor receptors of Swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jul;124(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swope S. L., Schonbrunn A. Bombesin stimulates insulin secretion by a pancreatic islet cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1822–1826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber S., Zuckerman J. E., Bostwick D. G., Bensch K. G., Sikic B. I., Raffin T. A. Gastrin releasing peptide is a selective mitogen for small cell lung carcinoma in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):306–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI111690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westendorf J. M., Schonbrunn A. Bombesin stimulates prolactin and growth hormone release by pituitary cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1982 Feb;110(2):352–358. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-2-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westendorf J. M., Schonbrunn A. Characterization of bombesin receptors in a rat pituitary cell line. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7527–7535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey J. C., Lechner J. F., Harris C. C. Bombesin and the C-terminal tetradecapeptide of gastrin-releasing peptide are growth factors for normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jul;153(1):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Rozengurt E. High-affinity receptors for peptides of the bombesin family in Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7616–7620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Early events elicited by bombesin and structurally related peptides in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. I. Activation of protein kinase C and inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2211–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zippel R., Sturani E., Toschi L., Naldini L., Alberghina L., Comoglio P. M. In vivo phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor studied by immunoblot analysis with phosphotyrosine antibodies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 19;881(1):54–61. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]