Abstract
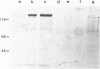
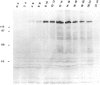
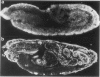
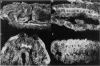
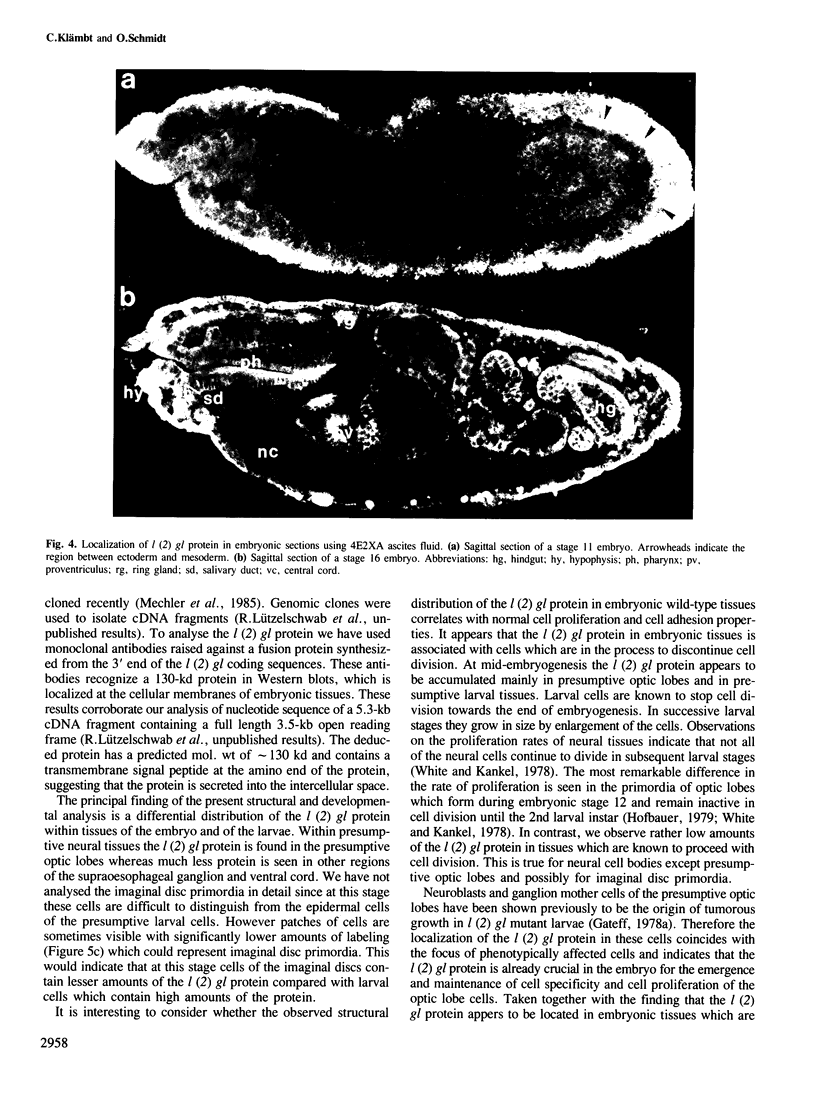
Recessive mutations in the Drosophila tumor gene lethal (2) giant larvae affect the growth and tissue specificity of determined cells in imaginal discs and presumptive optic centers of the brain. To analyse the function of the l (2) gl gene during development, we have raised monoclonal antibodies against the l (2) gl protein. These antibodies detect a 130-kd protein in wild-type tissue which is absent in homozygous mutant tissues. The protein is detected in increasing amounts up to mid-embryonic stages. Antibody binding to embryo sections and indirect immunofluorescence labeling indicate that the protein is localized at the cellular membranes or in the intercellular matrix of the embryonic cells. The primordia of all larval tissues are labeled in the embryo. Much less labeling is found in the neural primordia of the central nervous system, except that within the supraoesophageal ganglion the regions of the presumptive optic centers are distinctly labeled. Moreover, the axon bundles of the ventral cord are labeled in the embryo, apparently a reflection of the accumulation of cell membranes here. After embryogenesis the l (2) gl protein is found at a low level until the end of the 3rd larval instar, when it is preferentially seen in the brain and imaginal discs. The protein distribution in embryonic and larval tissues correlates with already known proliferation patterns, which could indicate that the l (2) gl protein is involved in proliferation arrest of cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dequin R., Saumweber H., Sedat J. W. Proteins shifting from the cytoplasm into the nuclei during early embryogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):37–48. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROB H. Entwicklungsphysiologische Untersuchungen an den Speicheldrüsen, dem Darmtraktus und den Imaginalscheiben einer Letralrasse (lgl) von Drosophila melanogaster. Z Indukt Abstamm Vererbungsl. 1952 Sep;84(4):320–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gateff E. Malignant neoplasms of genetic origin in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1978 Jun 30;200(4349):1448–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.96525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gateff E., Schneiderman H. A. Neoplasms in mutant and cultured wild-tupe tissues of Drosophila. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1969 Jul;31:365–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadorn E. An Accelerating Effect of Normal "Ring-Glands" on Puparium-Formation in Lethal Larvae of Drosophila Melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1937 Sep;23(9):478–484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.23.9.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechler B. M., McGinnis W., Gehring W. J. Molecular cloning of lethal(2)giant larvae, a recessive oncogene of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1551–1557. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03816.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Sedat J. Localization of antigenic determinants in whole Drosophila embryos. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K., Kankel D. R. Patterns of cell division and cell movement in the formation of the imaginal nervous system in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1978 Aug;65(2):296–321. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. A., Wilcox M. Protein products of the bithorax complex in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90202-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]