Abstract
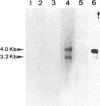
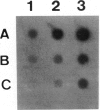
Villin, a Ca2+-regulated actin-binding protein is a major component of microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells and kidney proximal tubule cells. Villin expression during assembly of the brush border can be investigated using a human colon adenocarcinoma cell line HT29-18. This cell line is able to differentiate under nutritional control and develops an enterocyte-like phenotype. A cDNA library from a subclone HT29-18-C1 was constructed in an expression vector and a cDNA specific for human villin was isolated. This cDNA codes for the 110 carboxy-terminal residues of villin. Within that region, the 76 carboxy-terminal residues present 65% homology with the chicken villin 'head piece'. We show that two mRNA species 4.0 kb and 3.2 kb long hybridize with this cDNA probe in humans, whereas in rat and chicken only one mRNA species can be detected. The two villin mRNA species are co-expressed in normal human small and large intestinal mucosa and tumoral HT29-18 cells as well as in normal kidney. No villin mRNAs were detected in other normal or malignant epithelial cell types. Finally, we observed an accumulation of the two mRNA species coding for villin when HT29-18 cells become differentiated, suggesting that control of villin expression during terminal differentiation can occur at the transcription level or by RNA stabilization.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Osborn M., Wehland J., Weber K. Villin associates with specific microfilamentous structures as seen by immunofluorescence microscopy on tissue sections and cells microinjected with villin. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Sep;135(1):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coudrier E., Reggio H., Louvard D. Characterization of an integral membrane glycoprotein associated with the microfilaments of pig intestinal microvilli. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):469–475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. W., Powell L. D. Regulation of actin polymerization by villin, a 95,000 dalton cytoskeletal component of intestinal brush borders. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):739–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90550-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Geisler N., Kaulfus P., Weber K. Demonstration of at least two different actin-binding sites in villin, a calcium-regulated modulator of F-actin organization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8156–8161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Kaulfus P., Weber K. F actin assembly modulated by villin: Ca++-dependent nucleation and capping of the barbed end. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Weber K. Calcium control of microfilaments: uncoupling of the F-actin-severing and -bundling activity of villin by limited proteolysis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2810–2814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesterberg L. K., Weber K. Demonstration of three distinct calcium-binding sites in villin, a modulator of actin assembly. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):365–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesterberg L. K., Weber K. Ligand-induced conformational changes in villin, a calcium-controlled actin-modulating protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P., Jakes R., Walker J. E. A gelsolin-like Ca2+-dependent actin-binding domain in villin. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):248–250. doi: 10.1038/315248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S. Organization, chemistry, and assembly of the cytoskeletal apparatus of the intestinal brush border. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:209–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robine S., Huet C., Moll R., Sahuquillo-Merino C., Coudrier E., Zweibaum A., Louvard D. Can villin be used to identify malignant and undifferentiated normal digestive epithelial cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8488–8492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K. Solubilization and immune-detection of beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins carrying foreign antigenic determinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4077–4092. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Raibaud O. A convenient technique to compare the efficiency of promoters in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5919–5926. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]