Abstract
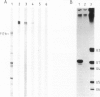
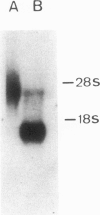
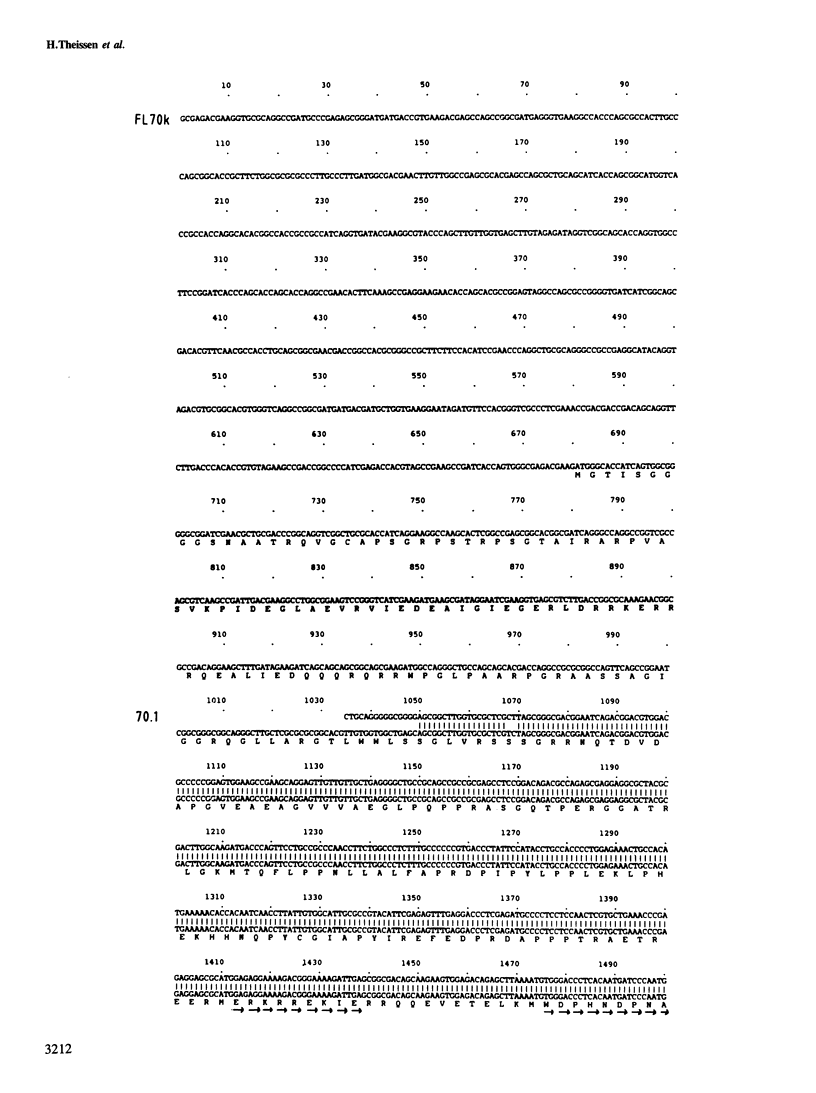
Anti-RNP sera were used to isolate a cDNA clone for the largest polypeptide of the U1 snRNP, a protein of mol. wt 70 kd designated 70K, from a human liver cDNA library constructed in the expression vector pEX1. The cro-beta-galactosidase-70K fusion protein reacted with various anti-RNP patient sera, a rabbit anti-70K antiserum, as well as with a monoclonal antibody specific for this protein. The sequences of four 70K peptides were determined and they match parts of the deduced amino acid sequence of the 1.3 kb insert of p70.1 indicating that it is a genuine 70K cDNA. Screening of a new cDNA library constructed from polysomal mRNA of HeLa cells with the p70.1 clone yielded an overlapping clone, FL70K, which was 2.7 kb long and covered the complete coding and 3'-untranslated sequence of the 70K protein in addition to 680 nucleotides upstream of the putative initiation codon, The predicted mol. wt of the encoded protein is approximately 70 kd. Amino acid analysis of the purified HeLa 70K protein yielded values close or identical to those deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the full-length cDNA. The 70K protein is rich in arginine (20%) and acidic amino acids (18%). Extremely hydrophilic regions containing mixed-charge amino acid clusters have been identified at the carboxyl-terminal half of the protein, which may function in RNA binding. A sequence comparison with two recently cloned RNA binding proteins revealed homology with one region in the U1 RNP 70K protein. This domain may also be responsible for RNA binding.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P. Evidence for a repeating domain in type I restriction enzymes. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1351–1355. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billings P. B., Hoch S. O. Isolation of intact Sm/RNP antigens from rabbit thymus. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretzel G. Uber Thynnin, das Protamin des Thunfisches. Die Aminosäuresequenz von Thynnin Z1. XIII. Mitteilung: über die Struktur der Protamine in der Untersuchungsreihe von E. Waldschmidt-Leitz und Mitarbeitern. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Mar;354(3):312–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringmann P., Reuter R., Rinke J., Appel B., Bald R., Lührmann R. 5'-terminal caps of snRNAs are accessible for reaction with 2,2,7-trimethylguanosine-specific antibody in intact snRNPs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2745–2747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringmann P., Rinke J., Appel B., Reuter R., Lührmann R. Purification of snRNPs U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 with 2,2,7-trimethylguanosine-specific antibody and definition of their constituent proteins reacting with anti-Sm and anti-(U1)RNP antisera. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1129–1135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Wilson S. H. Structure of rodent helix-destabilizing protein revealed by cDNA cloning. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3536–3543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Conner G. E., Reeves W. H., Blobel G., Kunkel H. G. Synthesis and assembly of human small nuclear ribonucleoproteins generated by cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6356–6360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., de Rooij D. J., Salden M. H., Verhagen A. P., van Eekelen C. A., van de Putte L. B., van Venrooij W. J. Antibodies against distinct nuclear matrix proteins are characteristic for mixed connective tissue disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger M., Pettersson I., Steitz J. A. Isolation of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins containing U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6 RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2604–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlaw C. S., Robberson B. L., Berget S. M. Fractionation and characterization of human small nuclear ribonucleoproteins containing U1 and U2 RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7181–7189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W., Appel B., Lührmann R. The 5' terminus of the RNA moiety of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles is required for the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Williams K. R., Szer W. Purification and domain structure of core hnRNP proteins A1 and A2 and their relationship to single-stranded DNA-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11266–11273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter L., Schopfer K., Wilhelm J. A., Nyffenegger T., Parisot R. F., De Robertis E. M. Molecular characterization of ribonucleoprotein antigens bound by antinuclear antibodies. A diagnostic evaluation. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1278–1283. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Mount S. M., Steitz J. A., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors is inhibited by antisera to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Bond M. W., Kornberg R. D. A single gene from yeast for both nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylate-binding proteins: domain structure and expression. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K. Solubilization and immune-detection of beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins carrying foreign antigenic determinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4077–4092. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrant R. W., Kim S. H. alpha-Helix-double helix interaction shown in the structure of a protamine-transfer RNA complex and a nucleoprotamine model. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):130–135. doi: 10.1038/271130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Billings P. B., Hoch S. O. Assays for the Sm and RNP autoantigens: the requirement for RNA and influence of the tissue source. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2751–2756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieben E. D., Madore S. J., Pederson T. Protein binding sites are conserved in U1 small nuclear RNA from insects and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1217–1220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]