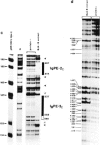
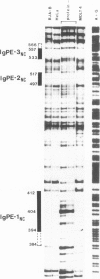
Abstract
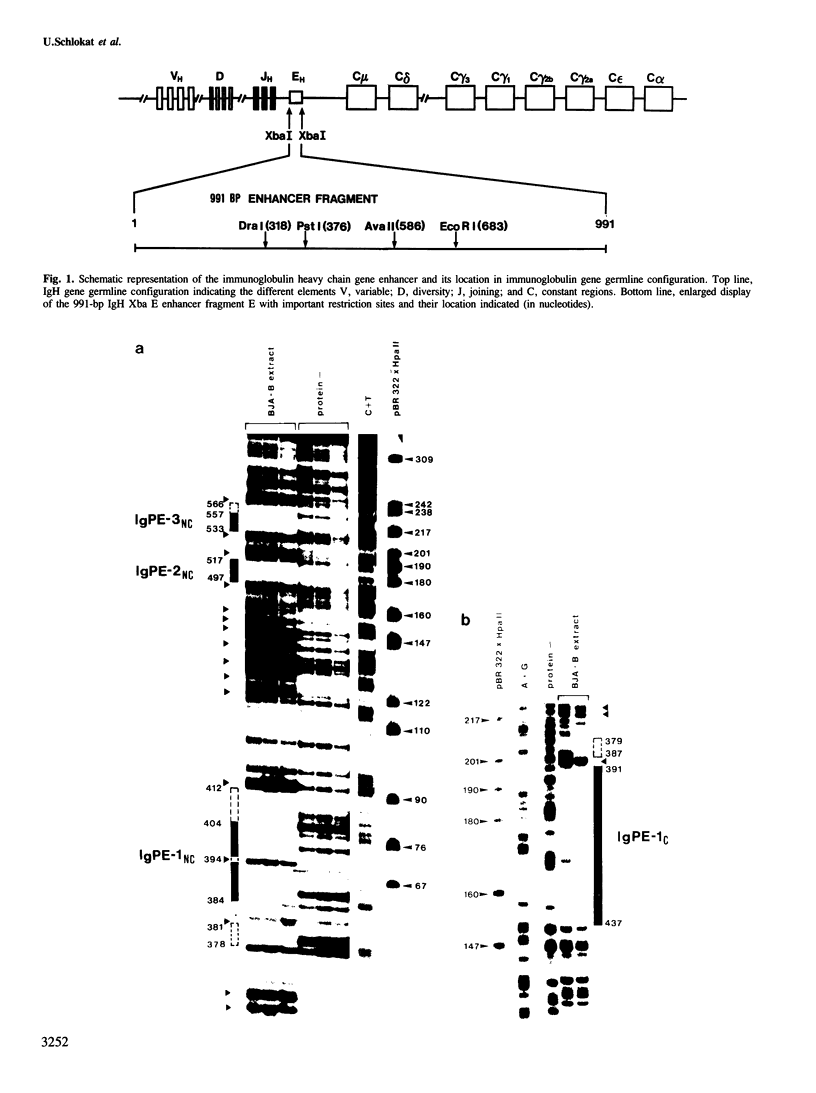
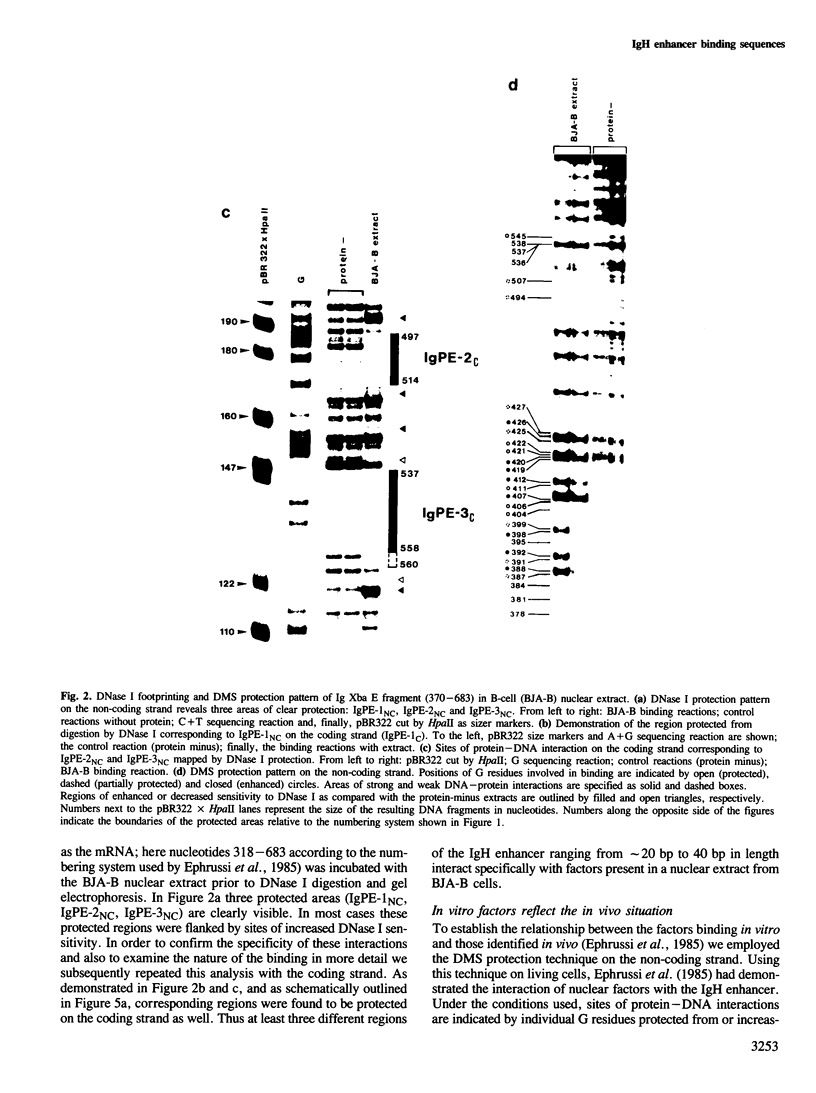
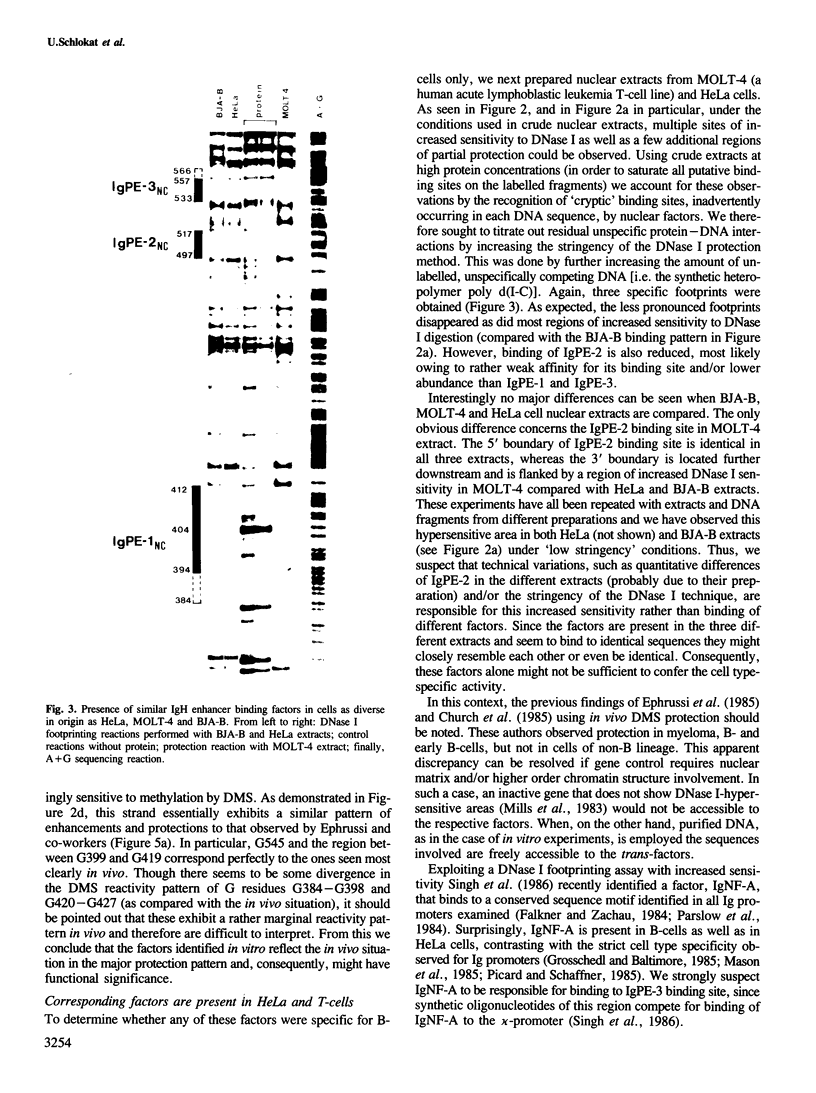
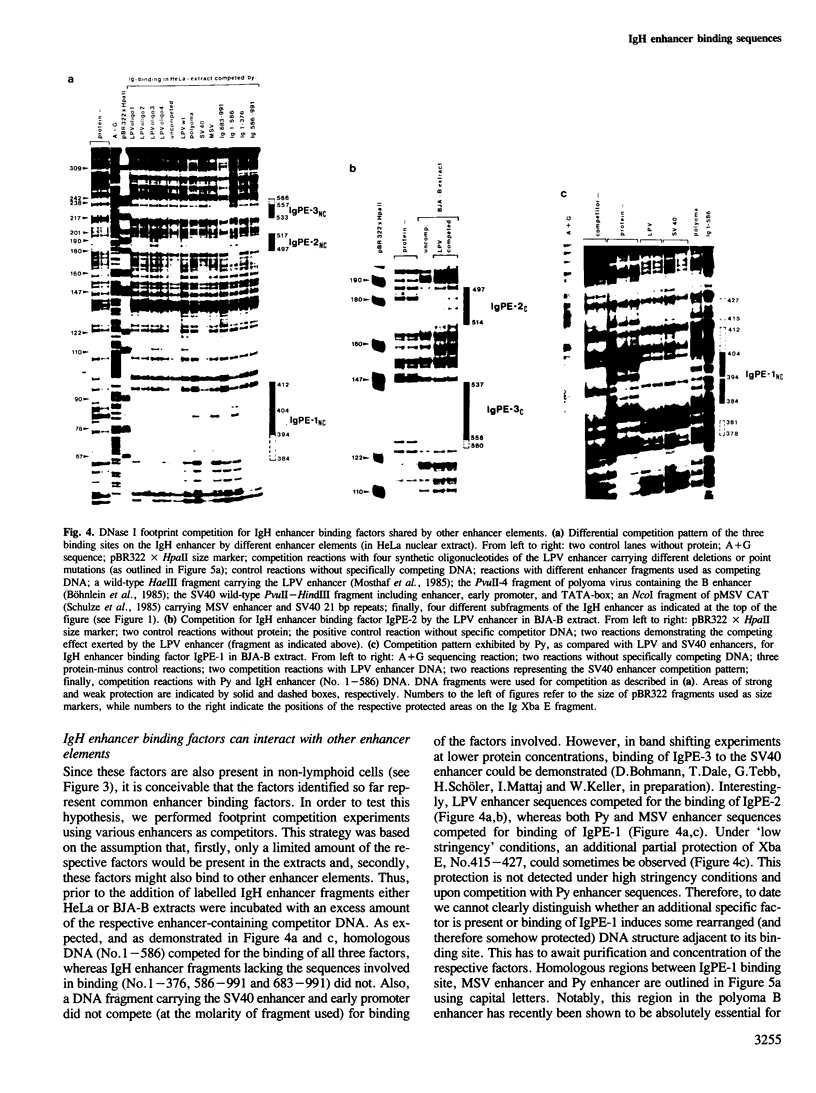
The mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) enhancer represents a cis essential control element that confers lymphoid-specific expression. Based on in vivo and in vitro competition experiments, as well as on in vivo dimethylsulfate (DMS) protection experiments, it has been inferred that cellular factors interact in trans with IgH enhancer sequences. In addition, transcription is stimulated in vitro by up to one order of magnitude in the presence of IgH enhancer sequences on an appropriate template. Thus, at least some of these factors have to be present in nuclear extracts. To examine the factors interacting with this lymphoid-specific enhancer in more detail we compared the binding pattern of nuclear factors present in B-cell, T-cell and HeLa cell extracts. We demonstrate here, using the DNase I and DMS protection methods, the specific interaction of three different nuclear factors with the central PstI--EcoRI fragment of the IgH enhancer. This fragment has previously been suggested to retain the major enhancing activity. Surprisingly, no or only minor differences were discovered when the footprints obtained with B-cell extracts were compared with those obtained with HeLa cell and T-cell extracts. Intriguingly, two factors binding specifically to different sequences of the IgH enhancer are shared by polyoma as well as Moloney sarcoma virus (MSV) and lymphotropic papova virus (LPV) enhancer, respectively. All three of these enhancer elements exhibit altered cell type specificities. This indicates the utilization of similar or identical factors for transcriptional enhancement in different cell types. A cassette model consisting of different factor binding sites will be discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. Functional analysis of the regulatory region of polyoma mutant F9-1 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4789–4809. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Gruss P. Interaction of distinct nuclear proteins with sequences controlling the expression of polyomavirus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1401–1411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Clarke J. The SV40 enhancer is composed of multiple functional elements that can compensate for one another. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gluzman Y. Duplications of a mutated simian virus 40 enhancer restore its activity. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):711–714. doi: 10.1038/313711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. Transcription cell type specificity is conferred by an immunoglobulin VH gene promoter that includes a functional consensus sequence. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Fisher L. M., Kuroda R., Ford A. M., Gould H. J. DNase I hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of human mu immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):809–812. doi: 10.1038/306809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosthaf L., Pawlita M., Gruss P. A viral enhancer element specifically active in human haematopoietic cells. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):597–600. doi: 10.1038/315597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. Cell-type preference of immunoglobulin kappa and lambda gene promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2831–2838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Kryszke M. H., Yaniv M. Specific interaction of cellular factors with the B enhancer of polyoma virus. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2675–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze F., Boehnlein E., Gruss P. Mutational analyses of the Moloney murine sarcoma virus enhancer. DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):193–202. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Cell type-specific transcriptional enhancement in vitro requires the presence of trans-acting factors. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain B-lymphocyte enhancer efficiently stimulates transcription in non-lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):553–560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Sassone-Corsi P., Grundström T., Zenke M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from the SV40 early promoter by the enhancer involves a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3129–3133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Zenke M., Schatz C., Wintzerith M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Takahashi K., Chambon P. Specific protein binding to the simian virus 40 enhancer in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2098–2105. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]