Abstract
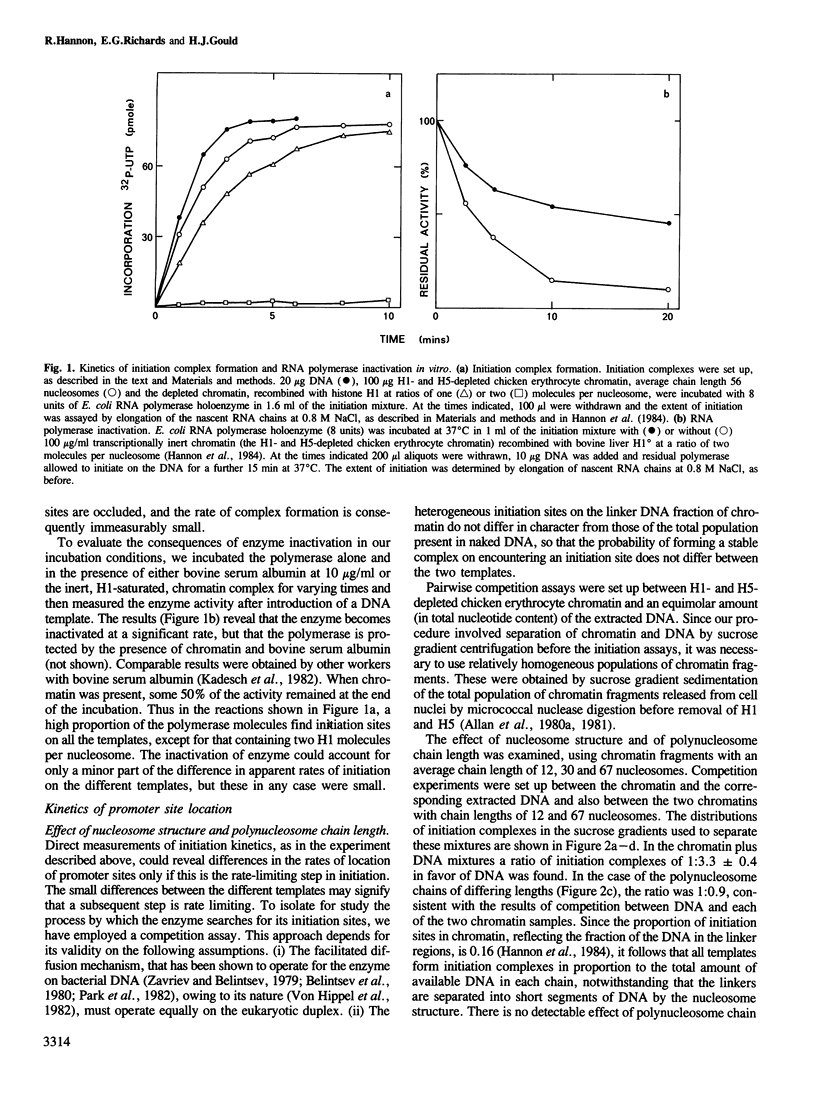
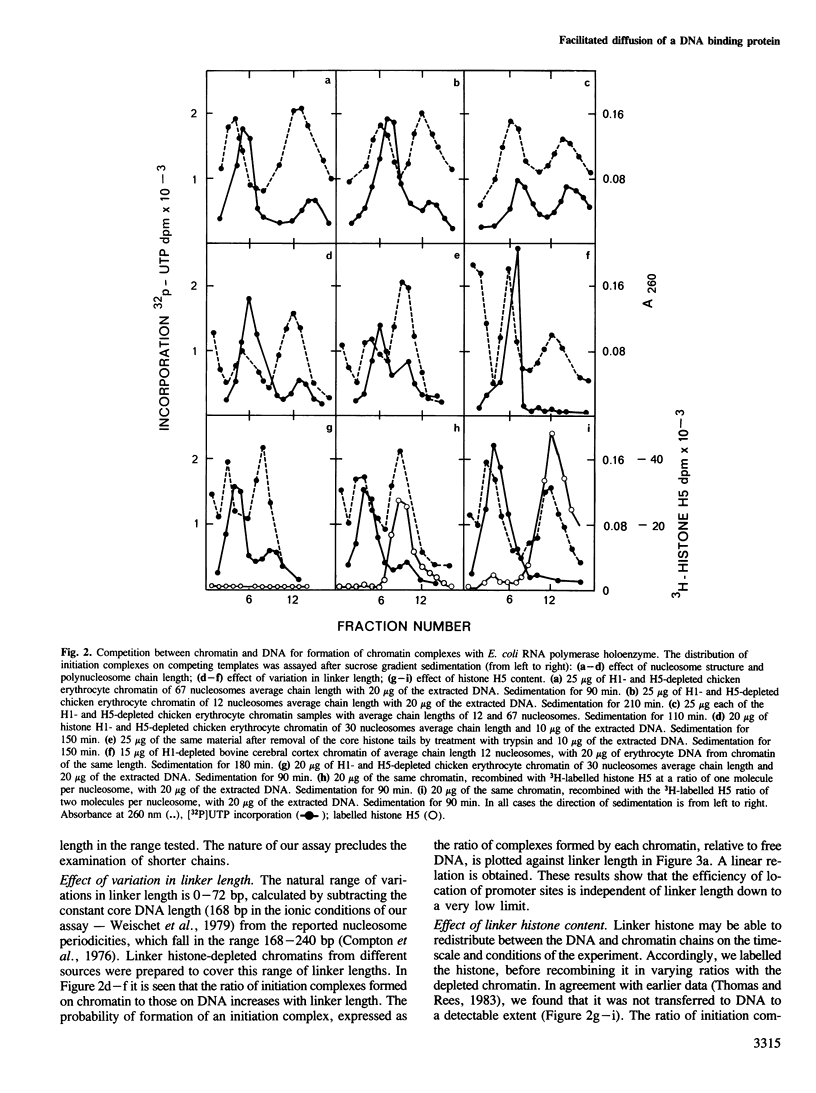
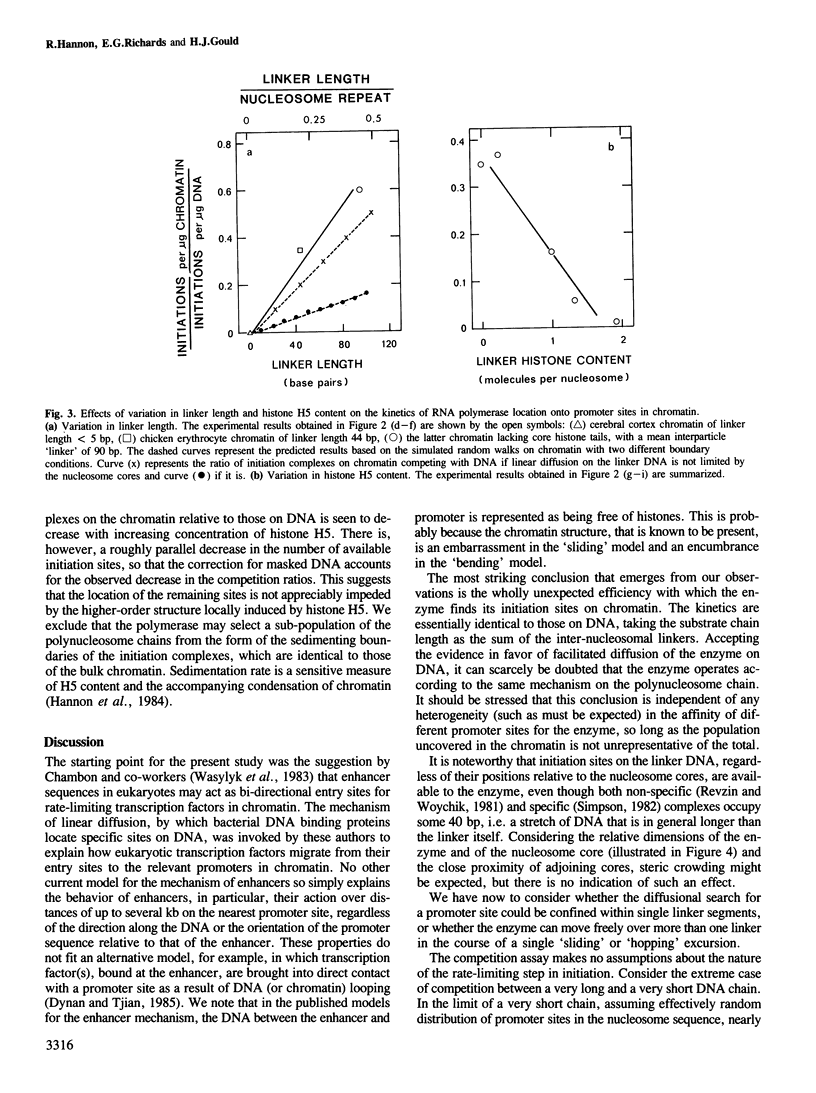
Facilitated diffusion accounts for the rapid rate of association of many bacterial DNA binding proteins with specific DNA sequences in vitro. In this mechanism the proteins bind at random to non-specific sites on the DAN and diffuse (by 'sliding' or 'hopping') along the DNA chain until they arrive at their specific functional sites. We have investigated whether such a mechanism can operate in chromatin by using a bacterial DNA binding protein, Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, that depends on linear diffusion to locate initiation sites on DNA. We have measured the competition between chromatin and its free DNA for the formation of initiation complexes. Only the short linker segments exposed by the removal of histone H1 are available for interaction with the polymerase, but the sparsely distributed promoter sites on the linker DNA of such a polynucleosome chain are located at the same rate as those on DNA. We conclude that the polymerase is free to migrate between the separate linker DNA segments of a polynucleosome chain to reach a promoter site. This chain thus permits the 'hopping' of proteins between neighboring linker segments in their search for a target site on the accessible DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J., Cowling G. J., Harborne N., Cattini P., Craigie R., Gould H. Regulation of the higher-order structure of chromatin by histones H1 and H5. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):279–288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J., Harborne N., Rau D. C., Gould H. Participation of core histone "tails" in the stabilization of the chromatin solenoid. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):285–297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J., Hartman P. G., Crane-Robinson C., Aviles F. X. The structure of histone H1 and its location in chromatin. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):675–679. doi: 10.1038/288675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J., Rau D. C., Harborne N., Gould H. Higher order structure in a short repeat length chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1320–1327. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J., Staynov D. Z., Gould H. Reversible dissociation of linker histone from chromatin with preservation of internucleosomal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):885–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belintsev B. N., Zavriev S. K., Shemyakin M. F. On the promoter complex formation rate of E. coli RNA polymerases with T7 phage DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., Winter R. B., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 1. Models and theory. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6929–6948. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Felsenfeld G. Transcription of chromatin in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;77(2):237–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Bellard M., Chambon P. Biochemical evidence of variability in the DNA repeat length in the chromatin of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez N., Wiggs J., Chamberlin M. J. A simple procedure for resolution of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme from core polymerase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon R., Bateman E., Allan J., Harborne N., Gould H. Control of RNA polymerase binding to chromatin by variations in linker histone composition. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack W. E., Terry B. J., Modrich P. Involvement of outside DNA sequences in the major kinetic path by which EcoRI endonuclease locates and leaves its recognition sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4010–4014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Rosenberg S., Chamberlin M. J. Binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme to bacteriophage T7 DNA. Measurements of binding at bacteriophage T7 promoter A1 using a template competition assay. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 15;155(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Rate-limiting steps in RNA chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5634–5638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. S., Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Molecular mechanism of promoter selection in gene transcription. II. Kinetic evidence for promoter search by a one-dimensional diffusion of RNA polymerase molecule along the DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6950–6956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilz I., Kratky O., Rabussay D. Studies on the conformation of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in solution by small-angle x-ray measurements. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):205–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revzin A., Woychik R. P. Quantitation of the interaction of EScherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme with double-helical DNA using a thermodynamically rigorous centrifugation method. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):250–256. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Rees C. Exchange of histones H1 and H5 between chromatin fragments. A preference of H5 for higher-order structures. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;134(1):109–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Thevenin G., Oudet P., Chambon P. Transcription of in vitro assembled chromatin by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):411–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weischet W. O., Allen J. R., Riedel G., Van Holde K. E. The effects of salt concentration and H-1 depletion on the digestion of calf thymus chromatin by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1843–1862. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson P., Felsenfeld G. Transcription of histone-covered T7 DNA by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5695–5705. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 3. The Escherichia coli lac repressor--operator interaction: kinetic measurements and conclusions. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6961–6977. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 2. The Escherichia coli repressor--operator interaction: equilibrium measurements. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6948–6960. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]