Abstract
In the amphibian oocyte, most of the non-chromatin-bound histones are not free but form complexes with specific karyophilic proteins, the most prominent being nucleoplasmin and 'protein N1/N2'. Using antibodies against polypeptide N1 and N2 (Mr approximately 105,000 and approximately 110,000) we have isolated, from a Xenopus laevis ovary lambda gt11 expression library, several full length cDNA clones encoding one of the two closely related polypeptides N1 and N2 (these could not be distinguished by hybridization techniques). The amino acid sequence deduced from one of these clones (N1/N2, lambda 106.2) defines a polypeptide of mol. wt 64,774. The remarkably high difference between the value of Mr approximately 110,000 estimated from SDS-PAGE mobility and the true mol. wt has been found for (i) the cell protein, (ii) the polypeptide synthesized in vitro by transcription and translation and (iii) the fusion protein with beta-galactosidase expressed in Escherichia coli, indicating that the protein runs anomalously on SDS-PAGE. The amino and carboxy termini of the purified protein N1/N2 have been confirmed by direct amino acid sequencing of CNBr fragments. The amino acid sequence displays two glutamic acid-rich domains, which are probably involved in the interaction with the histones, and a putative nuclear targeting signal with high homology to that of the SV40 large T-antigen which is located near the carboxy terminus.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballantine J. E., Woodland H. R., Sturgess E. A. Changes in protein synthesis during the development of Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1979 Jun;51:137–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne-Andrea C., Harper F., Sobczak J., De Recondo A. M. Rat liver HMG1: a physiological nucleosome assembly factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1193–1199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M. Protein migration into nuclei. II. Frog oocyte nuclei accumulate a class of microinjected oocyte nuclear proteins and exclude a class of microinjected oocyte cytoplasmic proteins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):431–437. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Voss S. D., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. Structural analysis of murine genes containing homoeo box sequences and their expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):713–718. doi: 10.1038/314713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Franke W. W. Karyophilic proteins: polypeptides synthesized in vitro accumulate in the nucleus on microinjection into the cytoplasm of amphibian oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5302–5306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Longthorne R. F., Gurdon J. B. Intracellular migration of nuclear proteins in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):254–256. doi: 10.1038/272254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Sharnick S. V., Laskey R. A. A polypeptide domain that specifies migration of nucleoplasmin into the nucleus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer C., Hausen P. Two-dimensional gel analysis of the fate of oocyte nuclear proteins in the development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1983 Dec;100(2):412–425. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Honda B. M., Laskey R. A., Thomas J. O. Assembly of nucleosomes: the reaction involving X. laevis nucleoplasmin. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90474-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldherr C. M., Cohen R. J., Ogburn J. A. Evidence for mediated protein uptake by amphibian oocyte nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1486–1490. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz J. K., Franke W. W. Cloning of cDNA and amino acid sequence of a cytokeratin expressed in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6475–6479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Fischer S., Plessmann U., Weber K. Neurofilament architecture combines structural principles of intermediate filaments with carboxy-terminal extensions increasing in size between triplet proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1295–1302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D. S., Gariépy J., Schoolnik G., Kornberg R. D. Synthetic peptides as nuclear localization signals. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):641–644. doi: 10.1038/322641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Hereford L., Herskowitz I. Targeting of E. coli beta-galactosidase to the nucleus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorcano J. L., Magin T. M., Franke W. W. Cell type-specific expression of bovine keratin genes as demonstrated by the use of complementary DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 15;176(1):21–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90380-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann E., Geisler N., Weber K. SDS-PAGE strongly overestimates the molecular masses of the neurofilament proteins. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81373-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
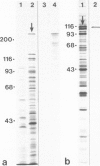
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Fortkamp E., Krohne G., Zentgraf H., Franke W. W. Co-existence of two different types of soluble histone complexes in nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1166–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Franke W. W. Soluble acidic complexes containing histones H3 and H4 in nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):799–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W. A major soluble acidic protein located in nuclei of diverse vertebrate species. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Sep;129(1):167–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90341-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W. Immunological identification and localization of the predominant nuclear protein of the amphibian oocyte nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1034–1038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G. Immunological identification of the karyophilic, histone-binding proteins N1 and N2 in somatic cells and oocytes of diverse amphibia. Exp Cell Res. 1985 May;158(1):205–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Induction of nuclear transport with a synthetic peptide homologous to the SV40 T antigen transport signal. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Honda B. M., Mills A. D., Finch J. T. Nucleosomes are assembled by an acidic protein which binds histones and transfers them to DNA. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):416–420. doi: 10.1038/275416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. Genetics, evolution, and expression of the 68,000-mol-wt neurofilament protein: isolation of a cloned cDNA probe. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):843–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magin T. M., Jorcano J. L., Franke W. W. Translational products of mRNAs coding for non-epidermal cytokeratins. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1387–1392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills A. D., Laskey R. A., Black P., De Robertis E. M. An acidic protein which assembles nucleosomes in vitro is the most abundant protein in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90148-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L. Diffusive and nondiffusive proteins in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 2):188s–195s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.188s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponstingl H., Krauhs E., Little M., Kempf T., Hofer-Warbinek R., Ade W. Amino acid sequence of alpha- and beta-tubulins from pig brain: heterogeneity and regional similarity to muscle proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):191–197. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Roberts B. L., Smith A. E. Nuclear location signals in polyoma virus large-T. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano V., Hatzfeld M., Magin T. M., Zimbelmann R., Franke W. W., Maier G., Ponstingl H. Cytokeratin expression in simple epithelia. I. Identification of mRNA coding for human cytokeratin no. 18 by a cDNA clone. Differentiation. 1986;30(3):244–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A., Whitlock J. P., Jr, Bina M. Acidic polypeptides can assemble both histones and chromatin in vitro at physiological ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5000–5004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedlich D., Dreyer C., Hausen P. Occurrence of a species-specific nuclear antigen in the germ line of Xenopus and its expression from paternal genes in hybrid frogs. Dev Biol. 1985 Mar;108(1):220–234. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Moir A. J., Waterfield M. D. The expression of multiple forms of troponin T in chicken-fast-skeletal muscle may result from differential splicing of a single gene. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]