Abstract
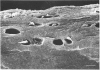
In order to elucidate the structure near the articular surface, frozen unfixed hydrated articular cartilage with subchondral bone from the pig knee was examined using a cryoscanning electron microscope (cryo-SEM). This method is considered to reduce the introduction of artefacts due to fixation and drying. An amorphous layer, without a collagen-fibril network or chondrocytes, covered most of the surface of the cartilage. This layer was termed the surface amorphous layer. It showed various appearances, which were classified into 4 groups. The average thickness of the layer did not differ among the 8 anatomical regions from which the specimens were taken. The thickness of the layer was found to correlate with the type of appearance of the layer. The 4 appearances associated with thicknesses in descending order are: 'streaked', 'foliate', 'spotted', and 'vestigial'. The surface layer observed in the cryo-SEM was thicker than that observed by a conventional SEM. This difference may be attributable to dehydration of the specimen used in specimen preparation for the latter technique. The layer was also observed in articular cartilage taken from human and rabbit knees. The layer was found to be unstable and to have very variable features. Its thickness and appearance may be influenced by various factors such as dehydration, fluid absorption or mechanical stress.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akizuki S., Mow V. C., Müller F., Pita J. C., Howell D. S., Manicourt D. H. Tensile properties of human knee joint cartilage: I. Influence of ionic conditions, weight bearing, and fibrillation on the tensile modulus. J Orthop Res. 1986;4(4):379–392. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100040401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aspden R. M., Hukins D. W. The lamina splendens of articular cartilage is an artefact of phase contrast microscopy. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Nov 30;206(1162):109–113. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balazs E. A., Bloom G. A., Swann D. A. Fine structure and glycosaminoglycan content of the surface layer of articular cartilage. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1813–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bald W. B., Robards A. W. A device for the rapid freezing of biological specimens under precisely controlled and reproducible conditions. J Microsc. 1978 Jan;112(1):3–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1978.tb01150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst R., Bayliss M. T., Maroudas A., Coysh H. L., Freeman M. A., Revell P. A., Ali S. Y. The composition of normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage from human knee joints. With special reference to unicompartmental replacement and osteotomy of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984 Jan;66(1):95–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullough P. G., Yawitz P. S., Tafra L., Boskey A. L. Topographical variations in the morphology and biochemistry of adult canine tibial plateau articular cartilage. J Orthop Res. 1985;3(1):1–16. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100030101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Rudd E. Cell patterns in the surface of rabbit articular cartilage revealed by the backscatter mode of scanning electron microscopy. J Orthop Res. 1991 Mar;9(2):275–283. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100090216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M. The organization of collagen in cryofractured rabbit articular cartilage: a scanning electron microscopic study. J Orthop Res. 1985;3(1):17–29. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100030102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M. Variation of collagen fiber alignment in a joint surface: a scanning electron microscope study of the tibial plateau in dog, rabbit, and man. J Orthop Res. 1991 Mar;9(2):246–257. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100090213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. C. Articular cartilage: a review and scanning electron microscope study. 1. The interterritorial fibrillar architecture. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1971 Nov;53(4):732–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. V., BARNETT C. H., COCHRANE W., PALFREY A. J. Electron microscopy of articular cartilage in the young adult rabbit. Ann Rheum Dis. 1962 Mar;21:11–22. doi: 10.1136/ard.21.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey G. P., Bullivant S. A copper block method for freezing non-cryoprotected tissue to produce ice-crystal-free regions for electron microscopy. I. Evaluation using freeze-substitution. J Microsc. 1976 Apr;106(3):251–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1976.tb02405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. L., O'Connor P., Oates K. Low temperature scanning electron microscopy of dog and guinea-pig hyaline articular cartilage. J Anat. 1981 Mar;132(Pt 2):267–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. L. The influence of microscopic technology on knowledge of cartilage surface structure. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jul;31(4):235–258. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.4.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. L., Woodward D. Scanning electron microscopy and replica studies of articular surfaces of guinea-pig synovial joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Jul;28(4):379–391. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.4.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadially F. N., Yong N. K., Lalonde J. M. A transmission electron microscopic comparison of the articular surface of cartilage processed attached to bone and detached from bone. J Anat. 1982 Dec;135(Pt 4):685–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helminen H. J., Jurvelin J., Tammi M., Pelttari A., Svartbäck C. M., Kiviranta I., Sämänen A. M., Paukkonen K. Prolonged ethanol replacement by CO2 increases splits on articular cartilage surface after critical point drying. J Microsc. 1985 Mar;137(Pt 3):305–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1985.tb02587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery A. K., Blunn G. W., Archer C. W., Bentley G. Three-dimensional collagen architecture in bovine articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991 Sep;73(5):795–801. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.73B5.1894669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane J. M., Weiss C. Review of articular cartilage collagen research. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):553–562. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipshitz H., Etheredge R., 3rd, Glimcher M. J. Changes in the hexosamine content and swelling ratio of articular cartilage as functions of depth from the surface. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976 Dec;58(8):1149–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEACHIM G., GHADIALLY F. N., COLLINS D. H. REGRESSIVE CHANGES IN THE SUPERFICIAL LAYER OF HUMAN ARTICULAR CARTILAGE. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Jan;24:23–30. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCONAILL M. A. The movements of bones and joints; the mechanical structure of articulating cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1951 May;33B(2):251–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroudas A., Muir H., Wingham J. The correlation of fixed negative charge with glycosaminoglycan content of human articular cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 6;177(3):492–500. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90311-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orford C. R., Gardner D. L. Ultrastructural histochemistry of the surface lamina of normal articular cartilage. Histochem J. 1985 Feb;17(2):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF01003221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saubermann A. J., Echlin P. The preparation, examination and analysis of frozen hydrated tissue sections by scanning transmission electron microscopy and x-ray microanalysis. J Microsc. 1975 Nov;105(2):155–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1975.tb04048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu R. Effects of enzymatic digestions on the negative charge of articular cartilage surfaces. J Rheumatol. 1985 Oct;12(5):833–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu R., Leibovich S. J. The negative charge of articular cartilage surfaces. An electron microscopic study using cationized ferritin. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982 Mar;64(3):388–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toller P. A. Ultrastructure of the condylar articular surface in severe mandibular pain-dysfunction syndrome. Int J Oral Surg. 1977 Dec;6(6):297–312. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9785(77)80023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss C., Rosenberg L., Helfet A. J. An ultrastructural study of normal young adult human articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968 Jun;50(4):663–674. doi: 10.2106/00004623-196850040-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bont L. G., Boering G., Havinga P., Liem R. S. Spatial arrangement of collagen fibrils in the articular cartilage of the mandibular condyle: a light microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1984 May;42(5):306–313. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(84)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]