Abstract
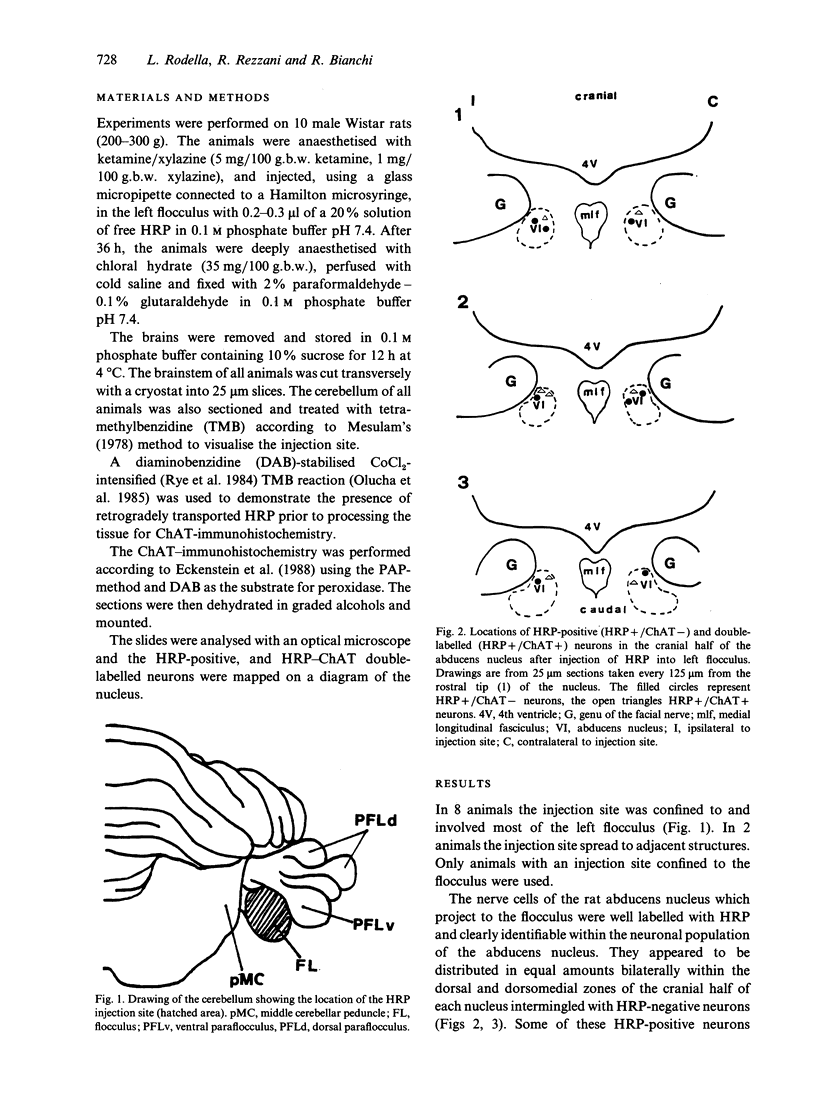
The neurons of the rat abducens nucleus that project to the flocculus of the cerebellum were studied by double labelling using the retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) immunohistochemistry. Double-labelled cells were present bilaterally in the dorsal and dorsomedial zones of the cranial pole of the nucleus. They represented about half of the total number of HRP-positive neurons. These findings show the existence of a bilateral projection from the abducens nucleus to the flocculus which uses acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter. This projection could be part of the system of the nerve circuits through which the cerebellum modulates visual activities.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker R., Highstein S. M. Physiological identification of interneurons and motoneurons in the abducens nucleus. Brain Res. 1975 Jun 27;91(2):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90551-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barmack N. H., Baughman R. W., Eckenstein F. P. Cholinergic innervation of the cerebellum of rat, rabbit, cat, and monkey as revealed by choline acetyltransferase activity and immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Mar 15;317(3):233–249. doi: 10.1002/cne.903170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barmack N. H., Baughman R. W., Eckenstein F. P., Shojaku H. Secondary vestibular cholinergic projection to the cerebellum of rabbit and rat as revealed by choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry, retrograde and orthograde tracers. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Mar 15;317(3):250–270. doi: 10.1002/cne.903170304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanks R. H., Precht W., Torigoe Y. Afferent projections to the cerebellar flocculus in the pigmented rat demonstrated by retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. Exp Brain Res. 1983;52(2):293–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00236639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodal A., Brodal P. Observations on the secondary vestibulocerebellar projections in the macaque monkey. Exp Brain Res. 1985;58(1):62–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00238954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büttner-Ennever J. A., Horn A. K., Schmidtke K. Cell groups of the medial longitudinal fasciculus and paramedian tracts. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1989;145(8-9):533–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büttner U., Boyle R., Markert G. Cerebellar control of eye movements. Prog Brain Res. 1986;64:225–233. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand J. Electrophysiological and morphological properties of rat abducens motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1989;76(1):141–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00253631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenstein F. P., Baughman R. W., Quinn J. An anatomical study of cholinergic innervation in rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience. 1988 May;25(2):457–474. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glicksman M. A. Localization of motoneurons controlling the extraocular muscles of the rat. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 21;188(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90556-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M. Direct and indirect preoculomotor pathways of the brainstem: an autoradiographic study of the pontine reticular formation in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Sep 1;175(1):37–78. doi: 10.1002/cne.901750105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highstein S. M., Karabelas A., Baker R., McCrea R. A. Comparison of the morphology of physiologically identified abducens motor and internuclear neurons in the cat: a light microscopic study employing the intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Jul 10;208(4):369–381. doi: 10.1002/cne.902080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotchabhakdi N., Walberg F. Cerebeller afferents from neurons in motor nuclei of cranial nerves demonstrated by retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 25;137(1):158–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labandeira Garcia J. L., Gomez Segade L. A., Suarez Nuñez J. M. Localisation of motoneurons supplying the extra-ocular muscles of the rat using horseradish peroxidase and fluorescent double labelling. J Anat. 1983 Sep;137(Pt 2):247–261. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labandeira-Garcia J. L., Guerra-Seijas M. J., Labandeira-Garcia J. A. The abducens motor and internuclear neurons in the rabbit: retrograde horseradish peroxidase and double fluorescent labeling. Brain Res. 1989 Sep 18;497(2):305–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Fuchs A. F., Scudder C. A., Chubb M. C. Afferents to the flocculus of the cerebellum in the rhesus macaque as revealed by retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1985 May 1;235(1):1–25. doi: 10.1002/cne.902350102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Kaneko C. R., Scudder C. A., Fuchs A. F. Afferents to the abducens nucleus in the monkey and cat. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Mar 15;245(3):379–400. doi: 10.1002/cne.902450307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisberger S. G., Fuchs A. F. Role of primate flocculus during rapid behavioral modification of vestibuloocular reflex. I. Purkinje cell activity during visually guided horizontal smooth-pursuit eye movements and passive head rotation. J Neurophysiol. 1978 May;41(3):733–763. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.3.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M. Tetramethyl benzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry: a non-carcinogenic blue reaction product with superior sensitivity for visualizing neural afferents and efferents. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Feb;26(2):106–117. doi: 10.1177/26.2.24068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. H., Garone M., Tashayyod D., Baker R. B. Innervation of extraocular muscles in the rabbit. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Dec 1;254(1):78–90. doi: 10.1002/cne.902540107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olucha F., Martínez-García F., López-García C. A new stabilizing agent for the tetramethyl benzidine (TMB) reaction product in the histochemical detection of horseradish peroxidase (HRP). J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Apr;13(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodella L., Rezzani R., Corsetti G., Simonetti C., Stacchiotti A., Ventura R. G. A light and electron microscope study of rat abducens nucleus neurons projecting to the cerebellar flocculus. J Anat. 1995 Apr;186(Pt 2):357–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodella L., Rezzani R., Corsetti G., Stacchiotti A., Ventura R. G. The rat abducens nucleus: a histo- and immunohistochemical study. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1994 Apr;70(4):69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rye D. B., Saper C. B., Wainer B. H. Stabilization of the tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) reaction product: application for retrograde and anterograde tracing, and combination with immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Nov;32(11):1145–1153. doi: 10.1177/32.11.6548485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. F., Baker R. Histochemical localization of acetylcholinesterase in relation to motor neurons and internuclear neurons of the cat abducens nucleus. J Neurocytol. 1986 Apr;15(2):137–154. doi: 10.1007/BF01611651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. F., Sterling P. An electron microscope study of motoneurones and interneurones in the cat abducens nucleus identified by retrograde intraaxonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Nov 1;176(1):65–85. doi: 10.1002/cne.901760105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiger H. J., Büttner-Ennever J. Relationship between motoneurons and internuclear neurons in the abducens nucleus: a double retrograde tracer study in the cat. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 9;148(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waespe W., Cohen B., Raphan T. Role of the flocculus and paraflocculus in optokinetic nystagmus and visual-vestibular interactions: effects of lesions. Exp Brain Res. 1983;50(1):9–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00238229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zee D. S., Yamazaki A., Butler P. H., Gücer G. Effects of ablation of flocculus and paraflocculus of eye movements in primate. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Oct;46(4):878–899. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.4.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]