Abstract
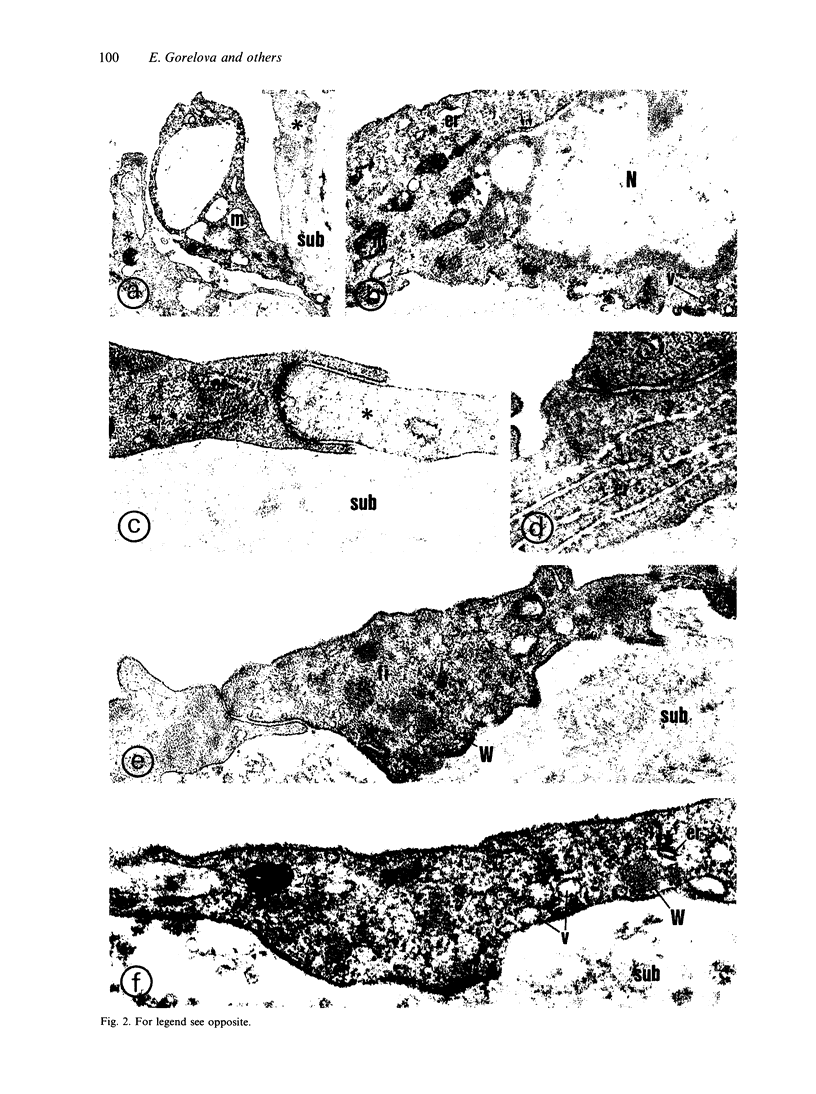
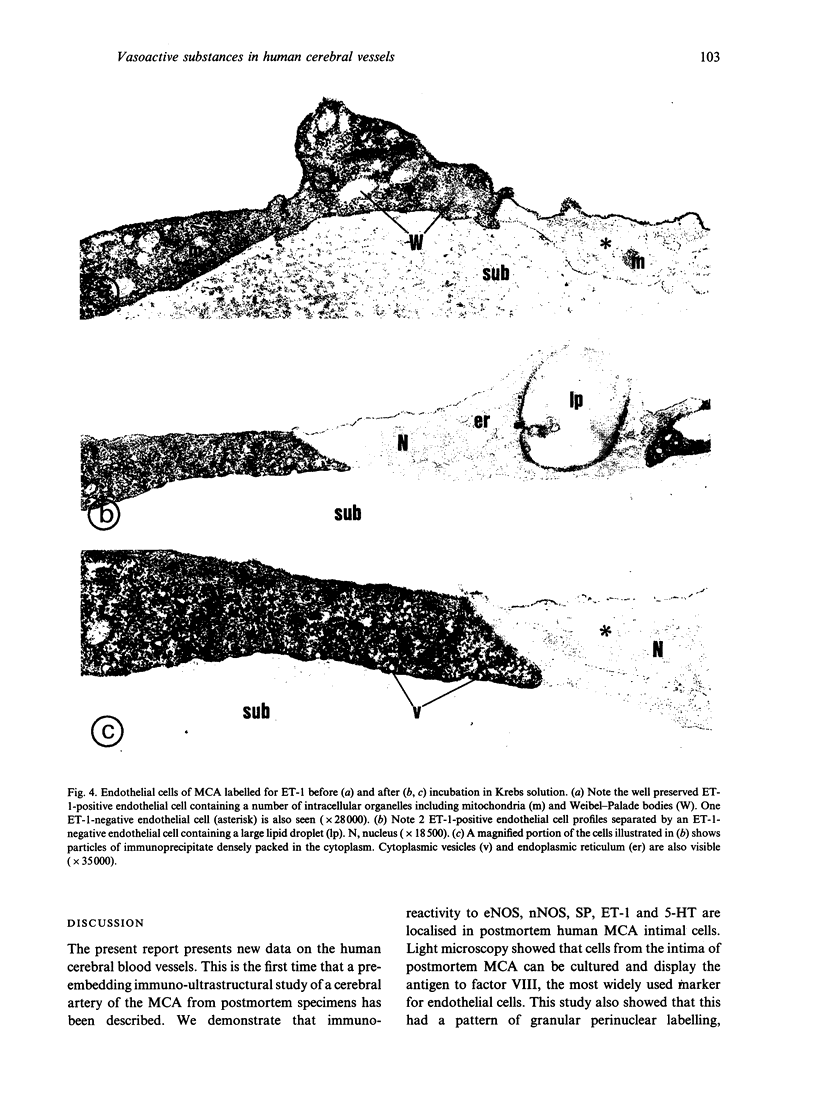
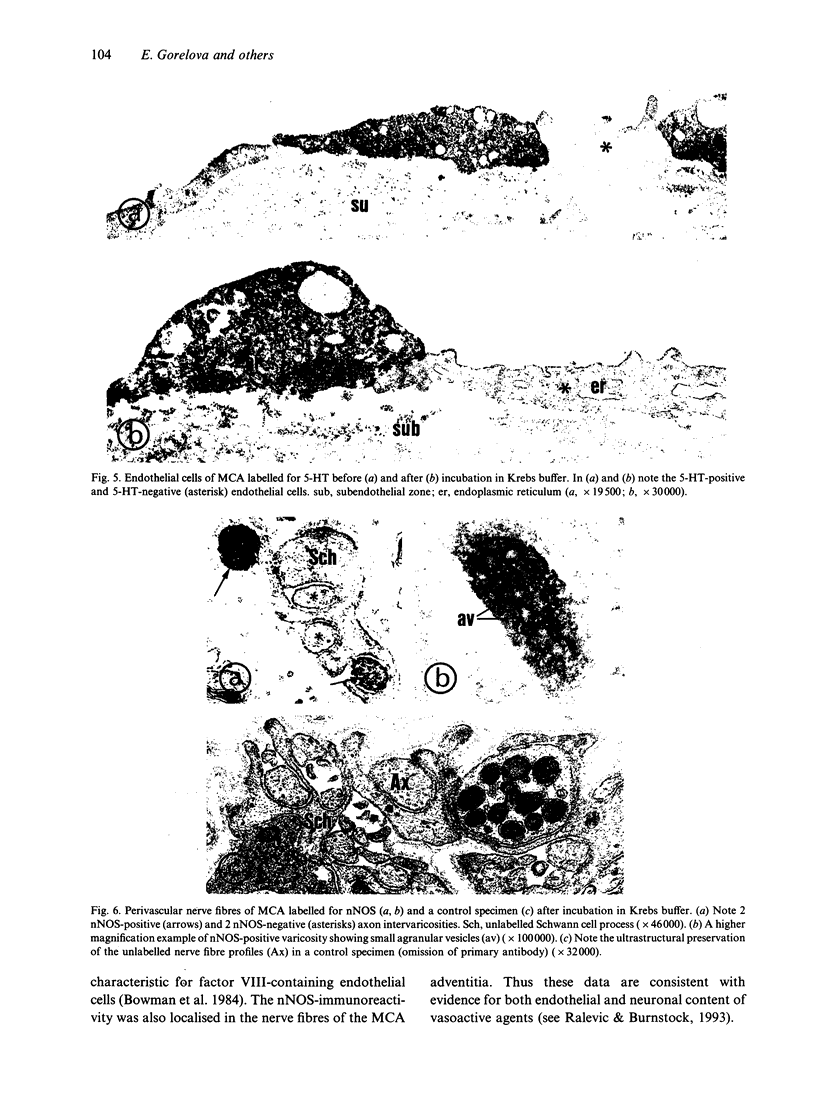
This pre-embedding electron-immunocytochemical study investigated the localisation of endothelial (type III) and neuronal (type I) isoforms of nitric oxide synthase, substance P, endothelin-1 and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the human middle cerebral artery taken up to 40 h postmortem. To ¿recover' from the anoxic period some of the vessels were incubated in oxygenated Krebs solution prior to the immunoprocedure. At this long postmortem time, immunoreactivity to type III and type I nitric oxide synthase, substance P, endothelin-1 and 5-hydroxytryptamine was found in a subpopulation of intact cells present in the vessel intima; immunoreactivity to type I nitric oxide synthase was also observed in a subpopulation of adventitial perivascular nerve fibres. Cultures of the cells from the intima of the postmortem vessels showed that the cells were proliferating and positive immunoreactivity to factor VII identified them as endothelial cells. The results therefore indicate that even after up to 40 h postmortem, endothelium of human middle cerebral artery is immunoreactive for a number of vasoactive agents and perivascular nerve fibres show nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodin P., Milner P., Winter R., Burnstock G. Chronic hypoxia changes the ratio of endothelin to ATP release from rat aortic endothelial cells exposed to high flow. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Feb 22;247(1319):131–135. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizzolara A. L., Crowe R., Burnstock G. Evidence for the involvement of both ATP and nitric oxide in non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory neurotransmission in the rabbit portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):606–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Local mechanisms of blood flow control by perivascular nerves and endothelium. J Hypertens Suppl. 1990 Dec;8(7):S95–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh J. F., Mione M. C., Burnstock G. Use of enhanced silver staining combined with electron microscopical immunolabelling to demonstrate the colocalization of neuropeptide Y and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in cerebrovascular nerves. Neuroscience. 1990;39(3):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90260-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhital K. K., Gerli R., Lincoln J., Milner P., Tanganelli P., Weber G., Fruschelli C., Burnstock G. Increased density of perivascular nerves to the major cerebral vessels of the spontaneously hypertensive rat: differential changes in noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y during development. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 15;444(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90910-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikranian K., Trosheva M., Nikolov S., Bodin P. Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in the human umbilical cord vessels. An immunohistochemical study. Acta Histochem. 1994 Jun;96(2):145–153. doi: 10.1016/S0065-1281(11)80170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinerman J. L., Dawson T. M., Schell M. J., Snowman A., Snyder S. H. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase localized to hippocampal pyramidal cells: implications for synaptic plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4214–4218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer F. R., Alexander B., Milner P., Bodin P., Burnstock G. Effect of changes in rate of vascular perfusion on release of substances into the effluent from the brain of the rabbit. Brain Res. 1993 Dec 10;630(1-2):88–94. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Ekman R., Jansen I., McCulloch J., Uddman R. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and cerebral blood vessels: distribution and vasomotor effects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987 Dec;7(6):720–728. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Ekman R., Ottosson A. Demonstration of perivascular peptides and changes in concentration with age in man. Gerontology. 1986;32 (Suppl 1):50–52. doi: 10.1159/000212828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faraci F. M., Brian J. E., Jr Nitric oxide and the cerebral circulation. Stroke. 1994 Mar;25(3):692–703. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.3.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson C. C., Richardson J. B. A simple technique for the utilization of postmortem tracheal and bronchial tissues for ultrastructural studies. Hum Pathol. 1978 Jul;9(4):463–470. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaw A. J., Aberdeen J., Humphrey P. P., Wadsworth R. M., Burnstock G. Relaxation of sheep cerebral arteries by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and neurogenic stimulation: inhibition by L-NG-monomethyl arginine in endothelium-denuded vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):567–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbins I. L., Brayden J. E., Bevan J. A. Perivascular nerves with immunoreactivity to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in cephalic arteries of the cat: distribution, possible origins and functional implications. Neuroscience. 1984 Dec;13(4):1327–1346. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiroe M., Hirata Y., Marumo F., Nagata M., Toyozaki T., Hasumi M., Ohta Y., Horie T., Sekiguchi M. Immunohistochemical localization of endothelin in human vascular endothelial cells. Peptides. 1989 Nov-Dec;10(6):1281–1282. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Byrns R. E., Buga G. M., Wood K. S. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor from pulmonary artery and vein possesses pharmacologic and chemical properties identical to those of nitric oxide radical. Circ Res. 1987 Dec;61(6):866–879. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.6.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jójárt I., Joó F., Siklós L., László F. A. Immunoelectronhistochemical evidence for innervation of brain microvessels by vasopressin-immunoreactive neurons in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Oct 12;51(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90561-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnik M. D., Moskowitz M. A. Identification of immunoreactive substance P in human and other mammalian endothelial cells. Peptides. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):957–962. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Chen L. Y., Liszczak T. M., King J. C., Moskowitz M. A. Immunoelectron microscopic study of substance P-containing fibers in feline cerebral arteries. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 26;369(1-2):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch A., Belai A., Burnstock G. An ultrastructural study of NADPH-diaphorase and nitric oxide synthase in the perivascular nerves and vascular endothelium of the rat basilar artery. J Neurocytol. 1994 Jan;23(1):49–59. doi: 10.1007/BF01189816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch A., Bodin P., Burnstock G. Colocalization of endothelin, vasopressin and serotonin in cultured endothelial cells of rabbit aorta. Peptides. 1991 Sep-Oct;12(5):1095–1103. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(91)90065-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch A., Burnstock G. Ultrastructural localisation of serotonin and substance P in vascular endothelial cells of rat femoral and mesenteric arteries. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1988;178(2):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF02463647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch A., Burnstock G. Ultrastructural localization of nitric oxide synthase and endothelin in coronary and pulmonary arteries of newborn rats. Cell Tissue Res. 1995 Mar;279(3):475–483. doi: 10.1007/BF00318161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch A., Domer F. R., Alexander B., Burnstock G. Electron-immunocytochemistry of peptides in endothelial cells of rabbit cerebral vessels following perfusion with a perfluorocarbon emulsion. Brain Res. 1993 May 21;611(2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90522-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Shiosaka S., Matsumoto M., Yoneda S., Kimura K., Abe H., Hayakawa T., Inoue H., Tohyama M. Overall distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing nerves on the wall of cerebral arteries: an immunohistochemical study using whole-mounts. Neuroscience. 1983 Sep;10(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Li G. K., Busconi L. Phosphorylation and subcellular translocation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6252–6256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner P., Bodin P., Loesch A., Burnstock G. Rapid release of endothelin and ATP from isolated aortic endothelial cells exposed to increased flow. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92141-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mione M. C., Dhital K. K., Amenta F., Burnstock G. An increase in the expression of neuropeptidergic vasodilator, but not vasoconstrictor, cerebrovascular nerves in aging rats. Brain Res. 1988 Sep 13;460(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki K., Moskowitz M. A., Maynard K. I., Koketsu N., Dawson T. M., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Possible origins and distribution of immunoreactive nitric oxide synthase-containing nerve fibers in cerebral arteries. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993 Jan;13(1):70–79. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnavelas J. G., Kelly W., Burnstock G. Ultrastructural localization of choline acetyltransferase in vascular endothelial cells in rat brain. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):724–725. doi: 10.1038/316724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. S., Nakane M., Buttery L. D., Martinez A., Springall D., Polak J. M., Förstermann U., Murad F. Characterization and localization of endothelial nitric oxide synthase using specific monoclonal antibodies. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 1):C1379–C1387. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.5.C1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand M. J. Nitrergic transmission: nitric oxide as a mediator of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neuro-effector transmission. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1992 Mar;19(3):147–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1992.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Wu J. Y., Lee T. J. Evidence for the presence of cholinergic nerves in cerebral arteries: an immunohistochemical demonstration of choline acetyltransferase. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985 Jun;5(2):327–334. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1985.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Gagne G. D., Nakane M., Pollock J. S., Miller M. F., Murad F. Mapping of neural nitric oxide synthase in the rat suggests frequent co-localization with NADPH diaphorase but not with soluble guanylyl cyclase, and novel paraneural functions for nitrinergic signal transduction. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Oct;40(10):1439–1456. doi: 10.1177/40.10.1382087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sexton A. J., Loesch A., Turmaine M., Miah S., Burnstock G. Nitric oxide and human umbilical vessels: pharmacological and immunohistochemical studies. Placenta. 1995 Apr;16(3):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0143-4004(95)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stones R. W., Loesch A., Beard R. W., Burnstock G. Substance P: endothelial localization and pharmacology in the human ovarian vein. Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Feb;85(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0029-7844(94)00368-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Hardebo J. E., Owman C. Origins and pathways of cerebrovascular vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-positive nerves in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Oct;8(5):697–712. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., McMaster D., Lederis K., Rorstad O. P. Characterization of the relaxant effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and PHI on isolated brain arteries. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 19;322(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N., Ayajiki K., Okamura T. Cerebroarterial relaxations mediated by nitric oxide derived from endothelium and vasodilator nerve. J Vasc Res. 1993 Mar-Apr;30(2):61–67. doi: 10.1159/000158976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N. Mediation by nitric oxide of neurally-induced human cerebral artery relaxation. Experientia. 1993 Jan 15;49(1):51–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01928789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoutte P. M., Rubanyi G. M., Miller V. M., Houston D. S. Modulation of vascular smooth muscle contraction by the endothelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:307–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]