Abstract
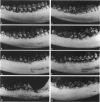
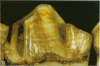
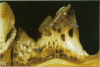
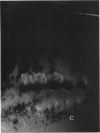
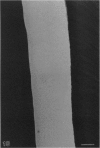
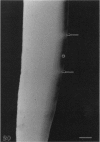
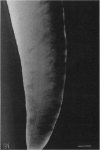
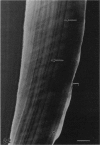
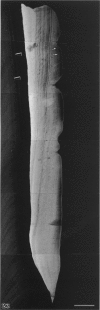
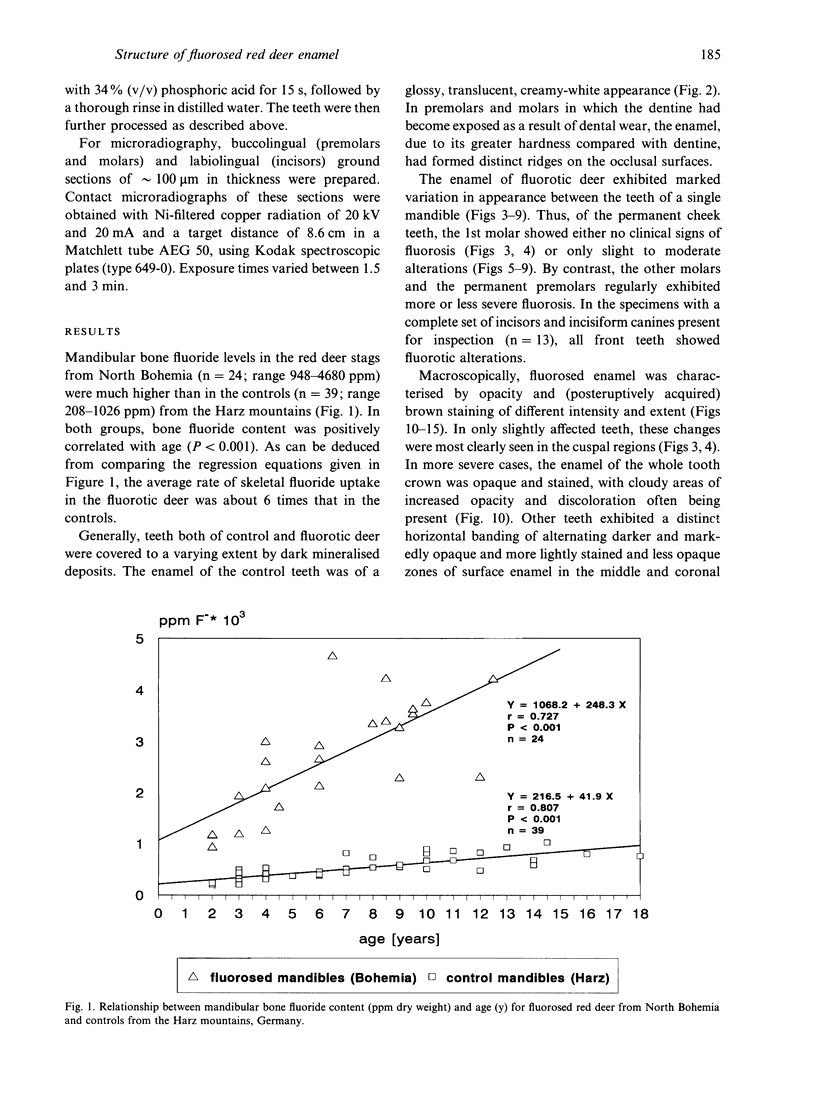
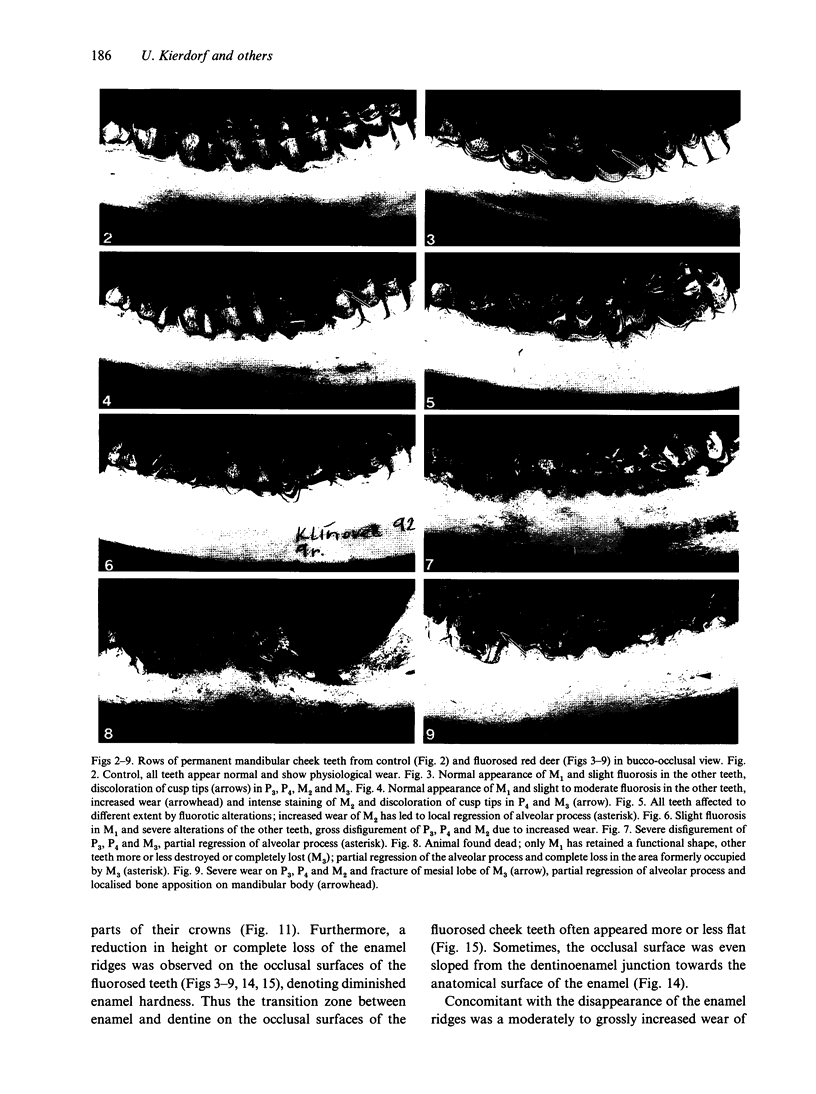
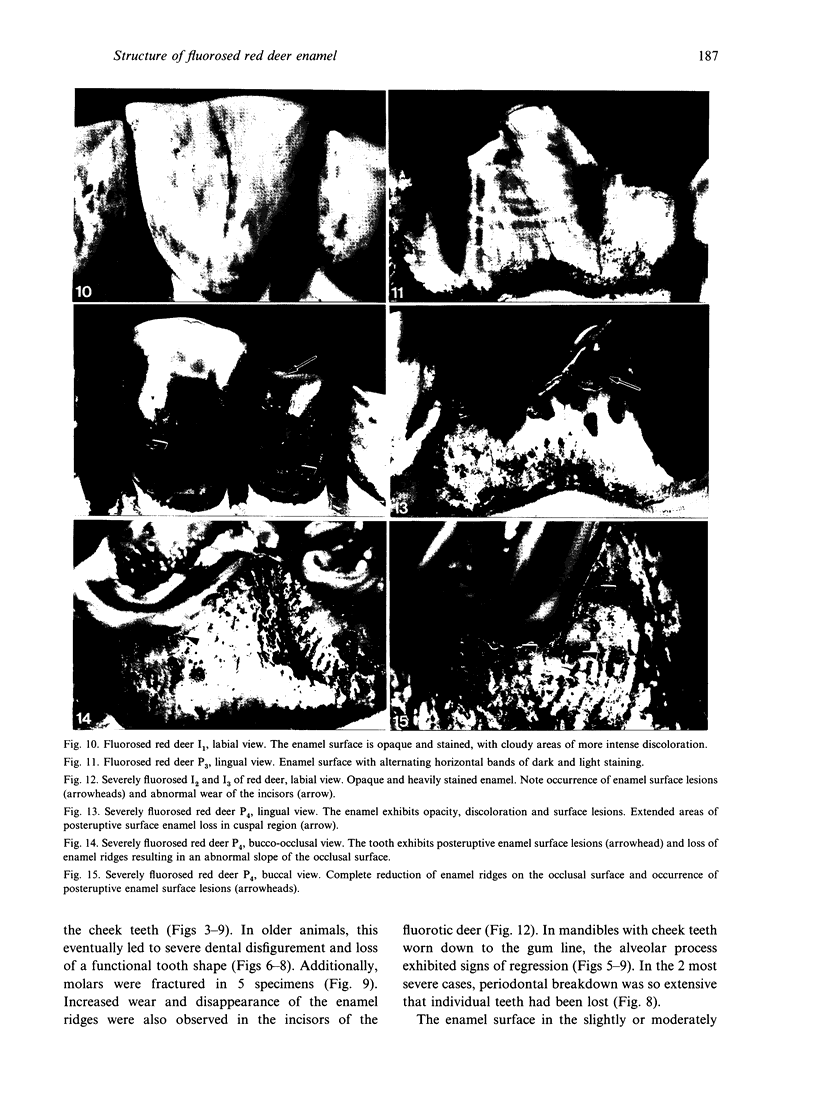
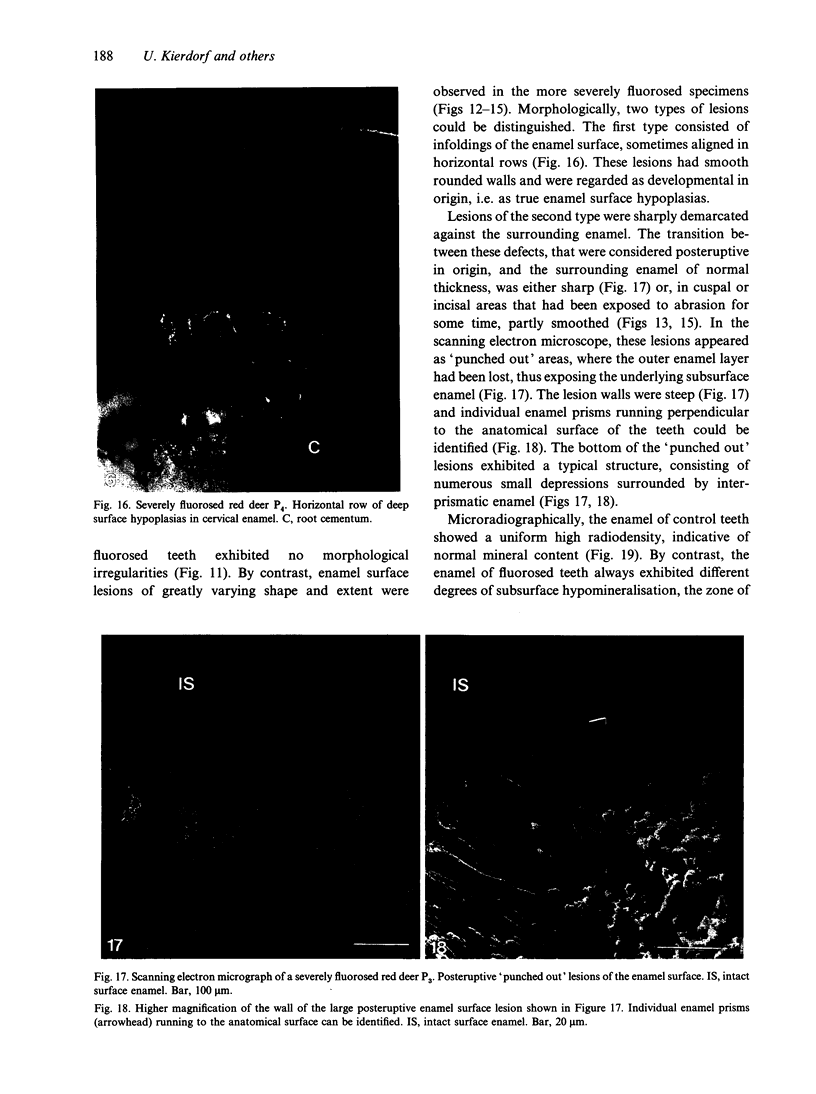
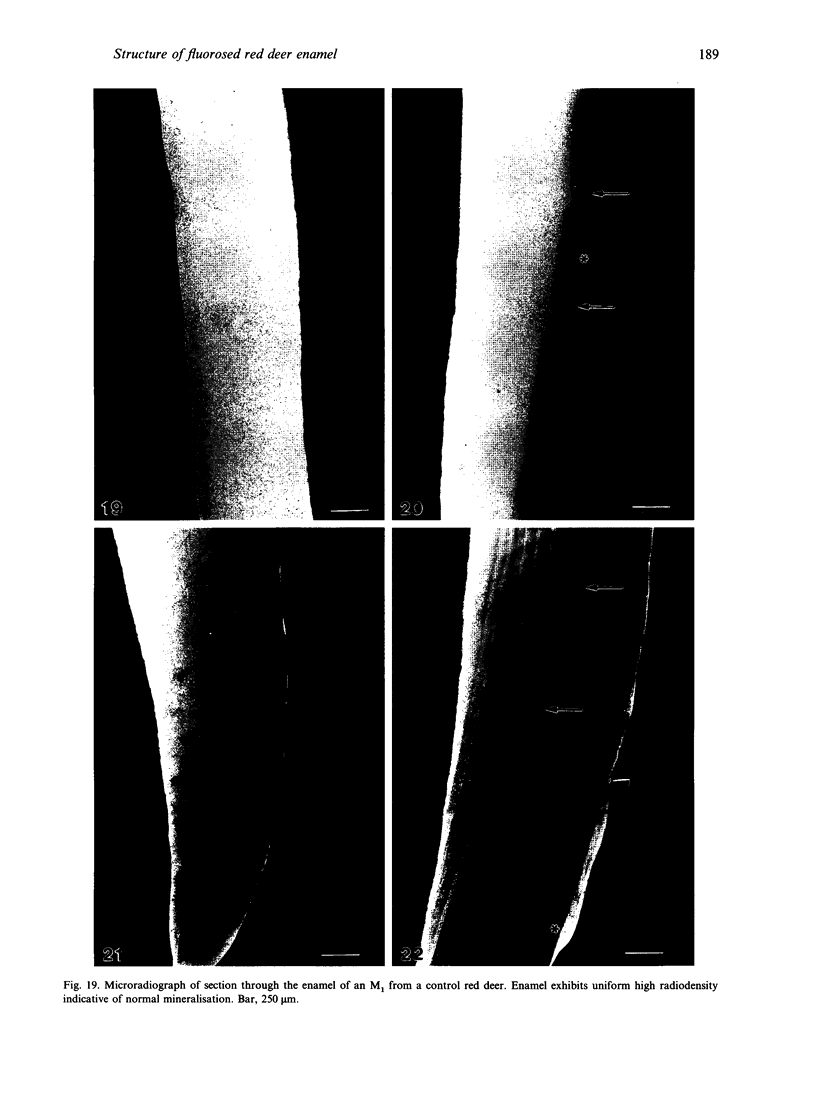
A macroscopic, microradiographic and scanning electron microscope study was performed on the structure of fluorosed dental enamel in red deer from a fluoride polluted region (North Bohemia, Czech Republic). As was revealed by analysis of mandibular bone fluoride content, the rate of skeletal fluoride accumulation in the fluorotic deer was about 6 times that in controls taken from a region not exposed to excessive fluoride deposition. In all fluorosed mandibles, the 1st molar was consistently less fluorotic than the other permanent teeth. This was related to the fact that crown formation in the M1 takes place prenatally and during the lactation period. Fluorosed teeth exhibited opaque and posteruptively stained enamel, reduction or loss of enamel ridges, moderately to grossly increased wear and, in more severe cases, also enamel surface lesions of partly posteruptive, partly developmental origin. Microradiographically, fluorosed enamel was characterised by subsurface hypomineralisation, interpreted as a result of fluoride interference with the process of enamel maturation. In addition, an accentuation of the incremental pattern due to the occurrence of alternating bands with highly varying mineral content was observed in severely fluorosed teeth, denoting fluoride disturbance during the secretory stage of amelogenesis. A corresponding enhancement of the incremental pattern was also seen in the dentine. The enamel along the more pronounced hypoplasias consisted of stacked, thin layers of crystals arranged in parallel, indicating that the ameloblasts in these locations had lost the distal (prism-forming) portions of their Tomes processes. The findings of the present study indicate that red deer are highly sensitive bioindicators of environmental pollution by fluorides.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boulton I. C., Cooke J. A., Johnson M. S. Fluoride accumulation and toxicity in wild small mammals. Environ Pollut. 1994;85(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0269-7491(94)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyde A. The development of enamel structure. Proc R Soc Med. 1967 Sep;60(9):923–928. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejerskov O., Larsen M. J., Richards A., Baelum V. Dental tissue effects of fluoride. Adv Dent Res. 1994 Jun;8(1):15–31. doi: 10.1177/08959374940080010601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejerskov O., Silverstone L. M., Melsen B., Moller I. J. Histological features of fluorosed human dental enamel. Caries Res. 1975;9(3):190–210. doi: 10.1159/000260157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejerskov O., Thylstrup A., Larsen M. J. Clinical and structural features and possible pathogenic mechanisms of dental fluorosis. Scand J Dent Res. 1977 Nov;85(7):510–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1977.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejerskov O., Yaeger J. A., Thylstrup A. Microradiography of the effect of acute and chronic administration of fluoride on human and rat dentine and enamel. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejerskov O., Yanagisawa T., Tohda H., Larsen M. J., Josephsen K., Mosha H. J. Posteruptive changes in human dental fluorosis--a histological and ultrastructural study. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1991;87(4):607–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierdorf H., Kierdorf U., Hommelsheim S. Scanning electron microscopic observations on the development and structure of tooth enamel in Cervidae (Mammalia: Ruminantia). Anat Histol Embryol. 1991 Sep;20(3):237–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0264.1991.tb00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierdorf U., Kierdorf H. A scanning electron microscopic study on surface lesions in fluorosed enamel of roe deer (Capreolus capreolus L.). Vet Pathol. 1989 May;26(3):209–215. doi: 10.1177/030098588902600304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierdorf U., Kierdorf H., Erdelen M., Machoy Z. Mandibular bone fluoride accumulation in wild red deer (Cervus elaphus L.) of known age. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol. 1995 Apr;110(4):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(94)00188-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierdorf U., Kierdorf H., Fejerskov O. Fluoride-induced developmental changes in enamel and dentine of European roe deer (Capreolus capreolus L.) as a result of environmental pollution. Arch Oral Biol. 1993 Dec;38(12):1071–1081. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(93)90169-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger B. J. Electron microscopy of enamel formed in the presence of fluoride and molybdenum. J Dent Res. 1969 Nov-Dec;48(6):1303–1307. doi: 10.1177/00220345690480063701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyaruu D. M., Tros G. H., Bronckers A. L., Wöltgens J. H. Micro-PIXE (proton-induced X-ray emission) study of the effects of fluoride on mineral distribution patterns in enamel and dentin in the developing hamster tooth germ. Scanning Microsc. 1990 Jun;4(2):315–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhaud G. E., Charles E., Loubière M. L., Kolf-Clauw M., Joubert C. Effects of fluoride on secretory and postsecretory phases of enamel formation in sheep molars. Am J Vet Res. 1992 Jul;53(7):1241–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsour P. A., Harbrow D. J., Warshawsky H. Effects of acute doses of sodium fluoride on the morphology and the detectable calcium associated with secretory ameloblasts in rat incisors. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Apr;37(4):463–471. doi: 10.1177/37.4.2926125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. P., Yu M. H. Fluorosis in black-tailed deer. J Wildl Dis. 1976 Jan;12(1):39–41. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-12.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund A. L., Ekstrand J. L., Hammarström L. Fluoride-induced cystic changes in the enamel organ of the rat molar. J Oral Pathol. 1986 Feb;15(2):87–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1986.tb00583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund A. L., Lindskog S. Scanning electron microscopy of fluoride-induced disturbances on the enamel surface of rat molars. Scand J Dent Res. 1986 Jun;94(3):185–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1986.tb01752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A., Kragstrup J., Josephsen K., Fejerskov O. Dental fluorosis developed in post-secretory enamel. J Dent Res. 1986 Dec;65(12):1406–1409. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650120501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer T. R., Kolstad D. L., Suttie J. W. Bovine dental fluorosis: histologic and physical characteristics. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Apr;39(4):587–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupe J. L., Olson A. E., Peterson H. B., Low J. B. Fluoride toxicosis in wild ungulates. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Dec 1;185(11):1295–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmelink J. W., Lange A. Ultrastructure of altered rat enamel beneath fluoride-induced cysts. J Oral Pathol. 1986 Mar;15(3):155–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1986.tb00598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckling G. W., Purdell-Lewis D. Macroscopic appearance, microhardness and microradiographic characteristics of experimentally produced fluorotic lesions in sheep enamel. Caries Res. 1982;16(3):227–234. doi: 10.1159/000260602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckling G., Thurley D. C. Histological, macroscopic and microhardness observations of fluoride-induced changes in the enamel organ and enamel of sheep incisor teeth. Arch Oral Biol. 1984;29(3):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(84)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckling G., Thurley D. C., Nelson D. G. The macroscopic and scanning electron-microscopic appearance and microhardness of the enamel, and the related histological changes in the enamel organ of erupting sheep incisors resulting from a prolonged low daily dose of fluoride. Arch Oral Biol. 1988;33(5):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(88)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. S., Dickie R., Clay A. B., Nielsen P., Mahan W. E., Baumann D. P., Hamilton R. J. Effects of fluoride emissions from a modern primary aluminum smelter on a local population of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). J Wildl Dis. 1987 Jan;23(1):135–143. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-23.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Carlson J. R., Faltin E. C. Effects of alternating periods of high- and low-fluoride ingestion on dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci. 1972 Jun;55(6):790–804. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(72)85574-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Hamilton R. J., Clay A. C., Tobin M. L., Moore W. G. Effects of fluoride ingestion on white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). J Wildl Dis. 1985 Jul;21(3):283–288. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-21.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thylstrup A., Fejerskov O. A scanning electron microscopic and microradiographic study of pits in fluorosed human enamel. Scand J Dent Res. 1979 Apr;87(2):105–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1979.tb00661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thylstrup A., Fejerskov O. Clinical appearance of dental fluorosis in permanent teeth in relation to histologic changes. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1978 Nov;6(6):315–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.1978.tb01173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thylstrup A. Posteruptive development of isolated and confluent pits in fluorosed enamel in a 6-year-old girl. Scand J Dent Res. 1983 Aug;91(4):243–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1983.tb00810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. C., Ackroyd S. Fluoride in mandibles and antlers of roe and red deer from different areas of England and Scotland. Environ Pollut. 1988;54(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0269-7491(88)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton R. E., Eisenmann D. R. Ultrastructural examination of various stages of amelogenesis in the rat following parenteral fluoride administration. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Feb;19(2):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshawsky H., Josephsen K., Thylstrup A., Fejerskov O. The development of enamel structure in rat incisors as compared to the teeth of monkey and man. Anat Rec. 1981 Aug;200(4):371–399. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092000402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]