Abstract
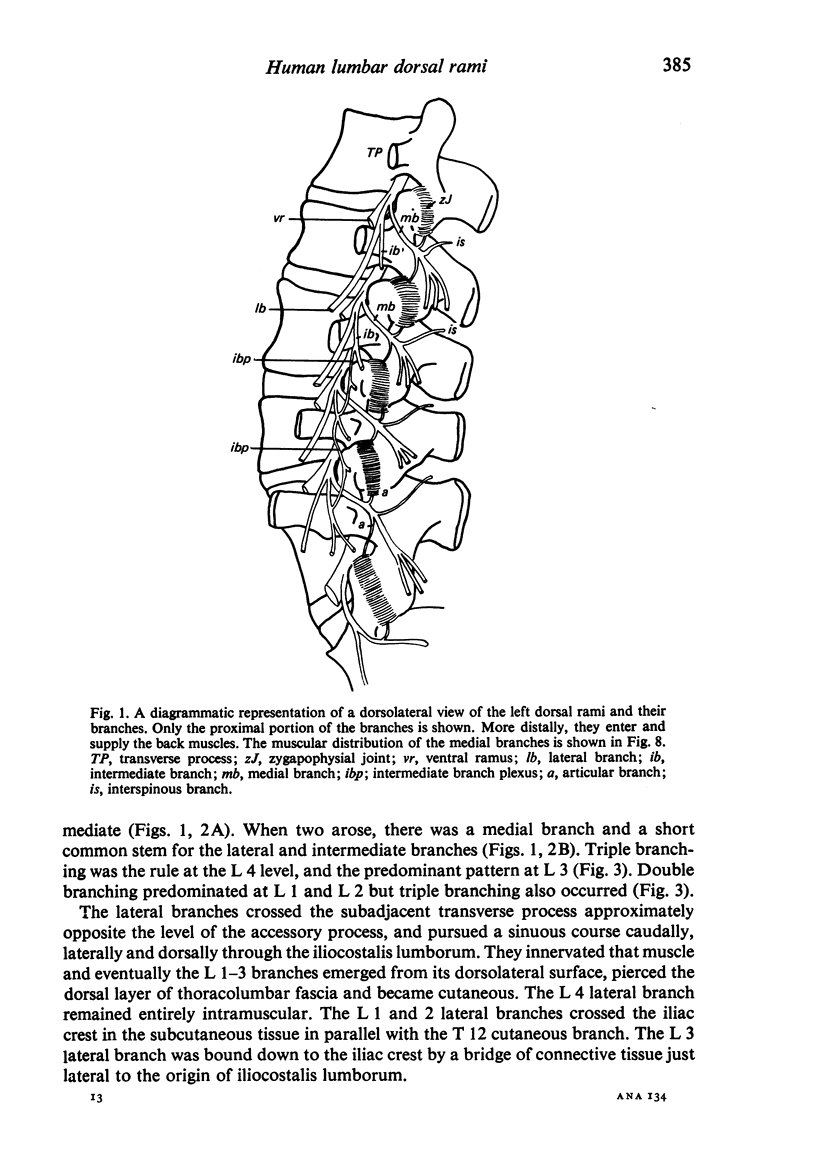
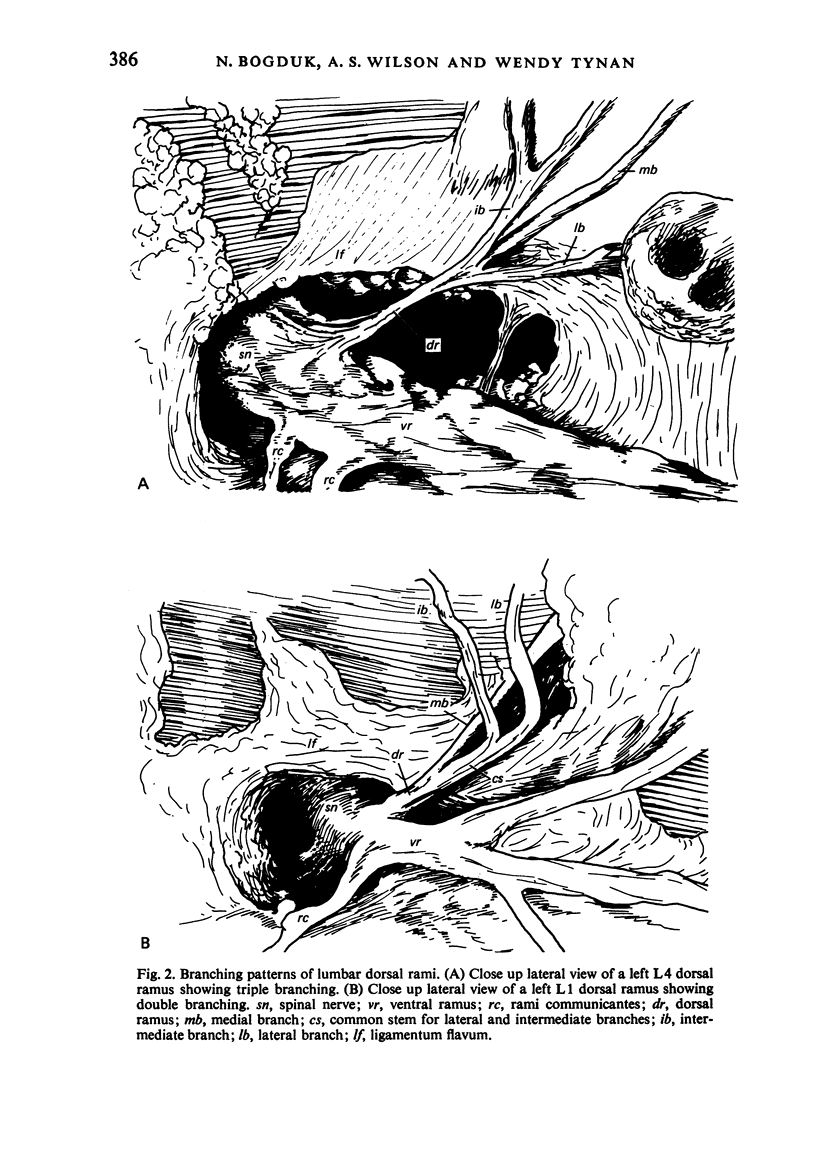
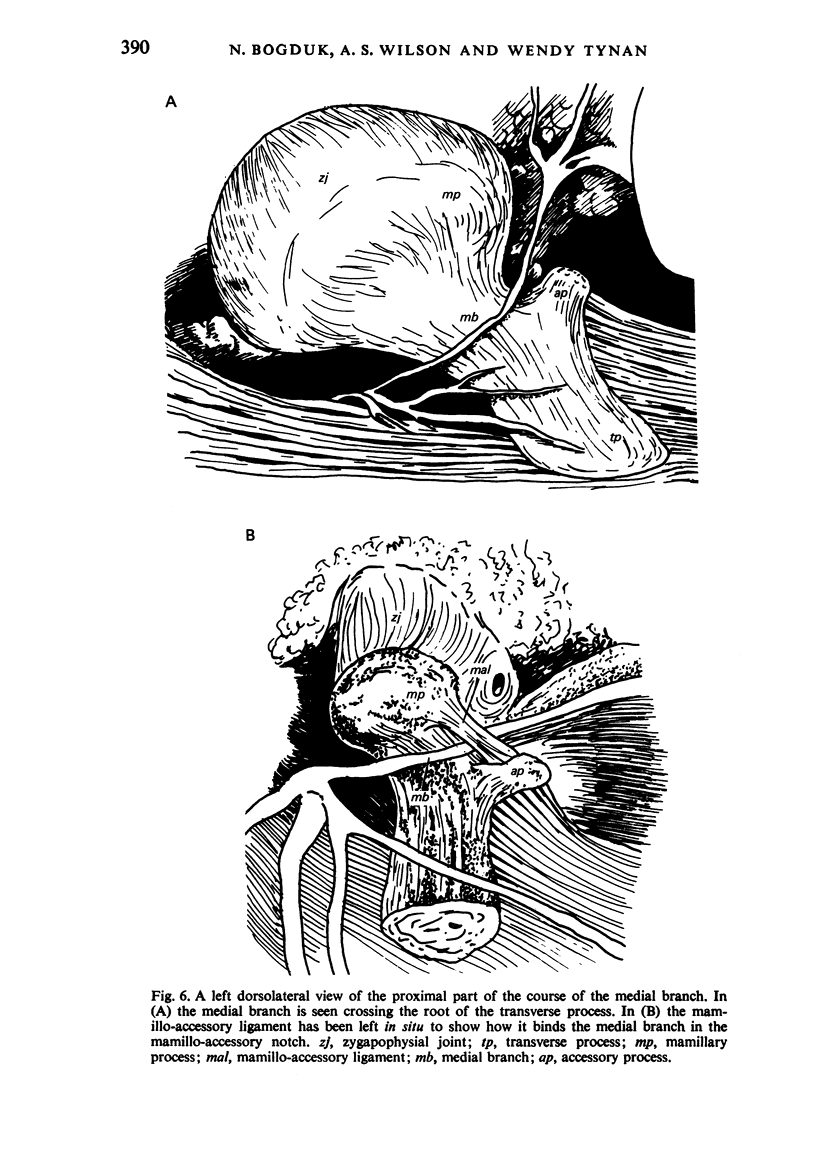
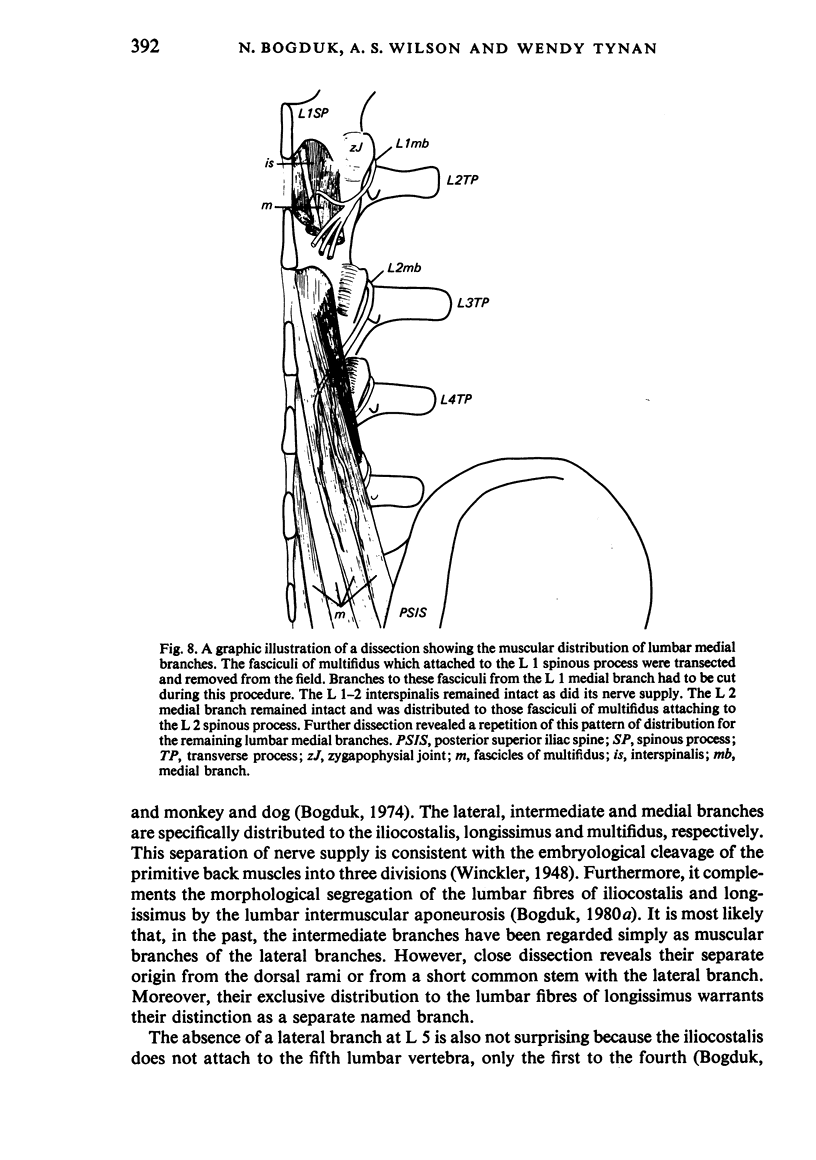
The L 1-4 dorsal rami tend to form three branches, medial, lateral, and intermediate, which are distributed, respectively, to multifidus, iliocostalis, and longissimus. The intertransversarii mediales are innervated by a branch of the dorsal ramus near the origin of the medial branch. The L 4 dorsal ramus regularly forms three branches while the L 1-3 levels the lateral and intermediate branches may, alternatively, arise from a short common stem. The L 5 dorsal ramus is much longer than the others and forms only a medial and an intermediate branch. Each lumbar medial branch innervates two adjacent zygapophysial joints and ramifies in multifidus, supplying only those fascicles which arise from the spinous process with the same segmental number as the nerve. The comparative anatomy of the lumbar dorsal rami is discussed and the applied anatomy with respect to 'rhizolysis', 'facet denervation' and diagnostic paraspinal electromyography is described.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogduk N. A reappraisal of the anatomy of the human lumbar erector spinae. J Anat. 1980 Oct;131(Pt 3):525–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N., Colman R. R., Winer C. E. An anatomical assessment of the "percutaneous rhizolysis" procedure. Med J Aust. 1977 Mar 19;1(12):397–399. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb130762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N., Long D. M. Percutaneous lumbar medial branch neurotomy: a modification of facet denervation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1980 Mar-Apr;5(2):193–200. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198003000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N., Long D. M. The anatomy of the so-called "articular nerves" and their relationship to facet denervation in the treatment of low-back pain. J Neurosurg. 1979 Aug;51(2):172–177. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.2.0172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N. Lumbar lateral branch neuralgia: a complication of rhizolysis. Med J Aust. 1981 Mar 7;1(5):242–243. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1981.tb135513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N. Proceedings: The lumbosacral dorsal rami of the monkey and dog. J Anat. 1974 Nov;118(Pt 2):393–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N. The anatomy of the lumbar intervertebral disc syndrome. Med J Aust. 1976 Jun 5;1(23):878–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N. The dorsal lumbar muscles of the cat. Anat Anz. 1980;148(1):55–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N. The lumbosacral dorsal rami of the cat. J Anat. 1976 Dec;122(Pt 3):653–662. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley K. C. The anatomy of backache. Aust N Z J Surg. 1974 Jul;44(3):227–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1974.tb04409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson H. Morphology and contraction properties of cat lumbar back muscles. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Jun;103(2):180–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier B. B. Treatment for lumbar sciatic pain in posterior articular lumbar joint syndrome. Anaesthesia. 1979 Feb;34(2):202–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1979.tb06280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar M. A., Ghadially J. A. Innervation of the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976 Mar-Apr;(115):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. L., Rizzoli H. V. Identification of radiologic coordinates for the posterior articular nerve of Luschka in the lumbar spine. Surg Neurol. 1973 Nov;1(6):343–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston J. R. A study of subcutaneous rhizolysis in the treatment of chronic backache. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1975 Sep;25(158):692–697. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H M. The Cutaneous Branches of the Posterior Primary Divisions of the Spinal Nerves, and their Distribution in the Skin. J Anat Physiol. 1908 Oct;43(Pt 1):80–92.5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIN T., MOFFETT B., VIDIK A. The morphology of the lumbar synovial interveertebral joints. Acta Morphol Neerl Scand. 1962;4:299–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maigne R., Le Corre F., Judet H. Lombalgies basses d'origine dorso-lombaire: traitement chirugical par excision des capsules articulaires postérieures. Rapport préliminaire. Nouv Presse Med. 1978 Feb 18;7(7):565–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudenhoven R. C. Articular rhizotomy. Surg Neurol. 1974 Jul;2(4):275–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudenhoven R. C. The role of laminectomy, facet rhizotomy, and epidural steroids. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1979 Mar-Apr;4(2):145–147. doi: 10.1097/00007632-197903000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEDERSEN H. E., BLUNCK C. F., GARDNER E. The anatomy of lumbosacral posterior rami and meningeal branches of spinal nerve (sinu-vertebral nerves); with an experimental study of their functions. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1956 Apr;38-A(2):377–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees W. S. Multiple bilateral percutaneous rhizolysis. Med J Aust. 1975 Apr 26;1(17):536–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILWELL D. L., Jr The nerve supply of the vertebral column and its associated structures in the monkey. Anat Rec. 1956 Jun;125(2):139–169. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091250202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toakley J. G. Subcutaneous lumbar "rhizolysis"--an assessment of 200 cases. Med J Aust. 1973 Sep 8;2(10):490–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


