Abstract
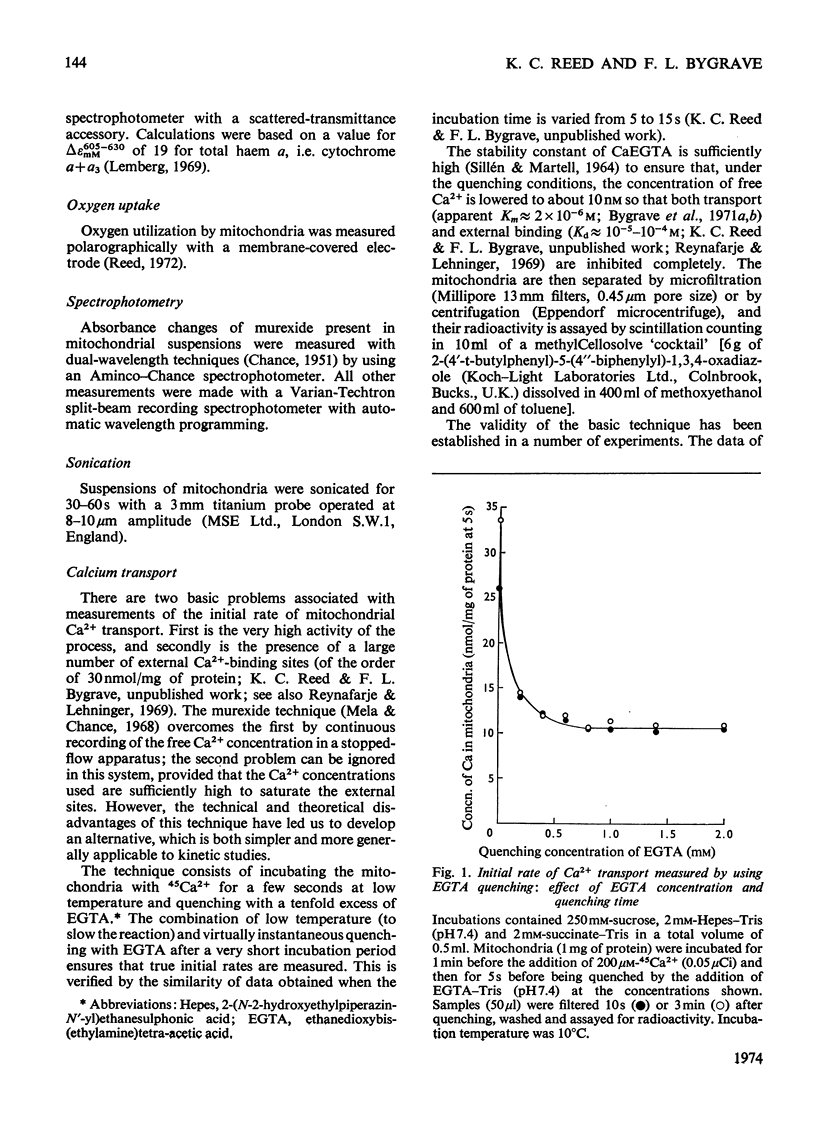
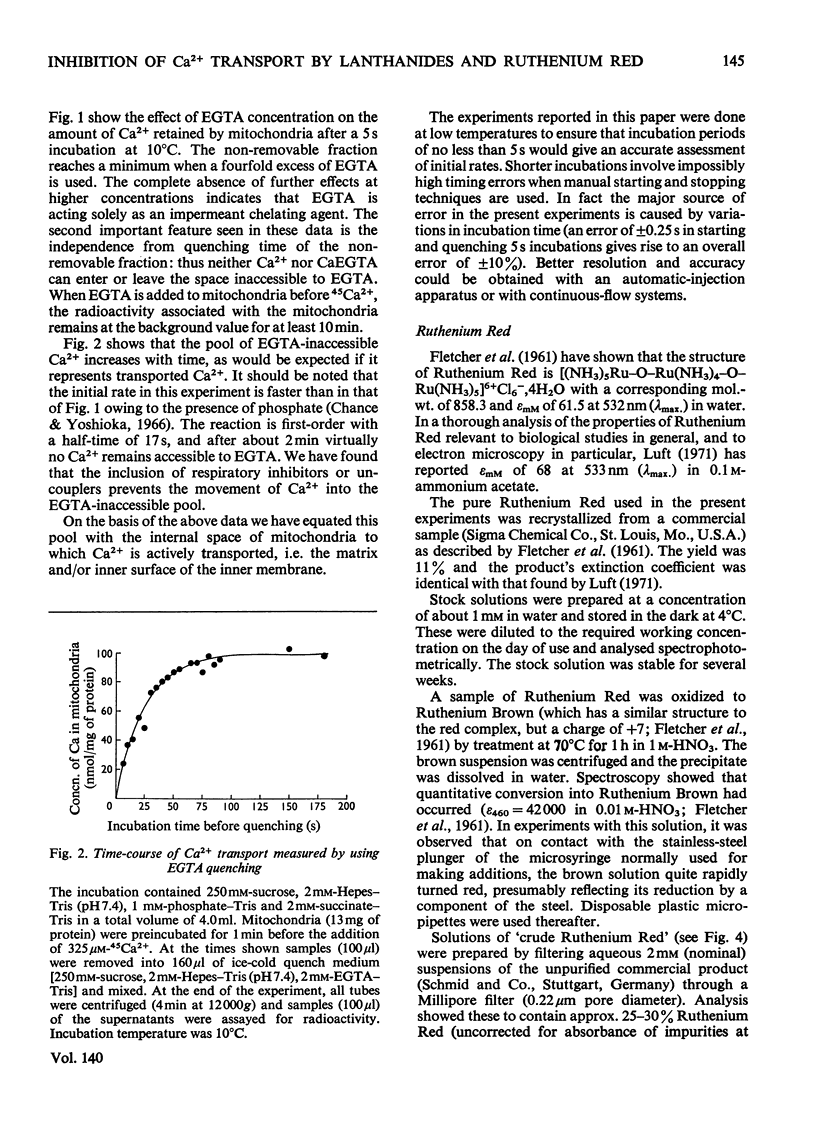
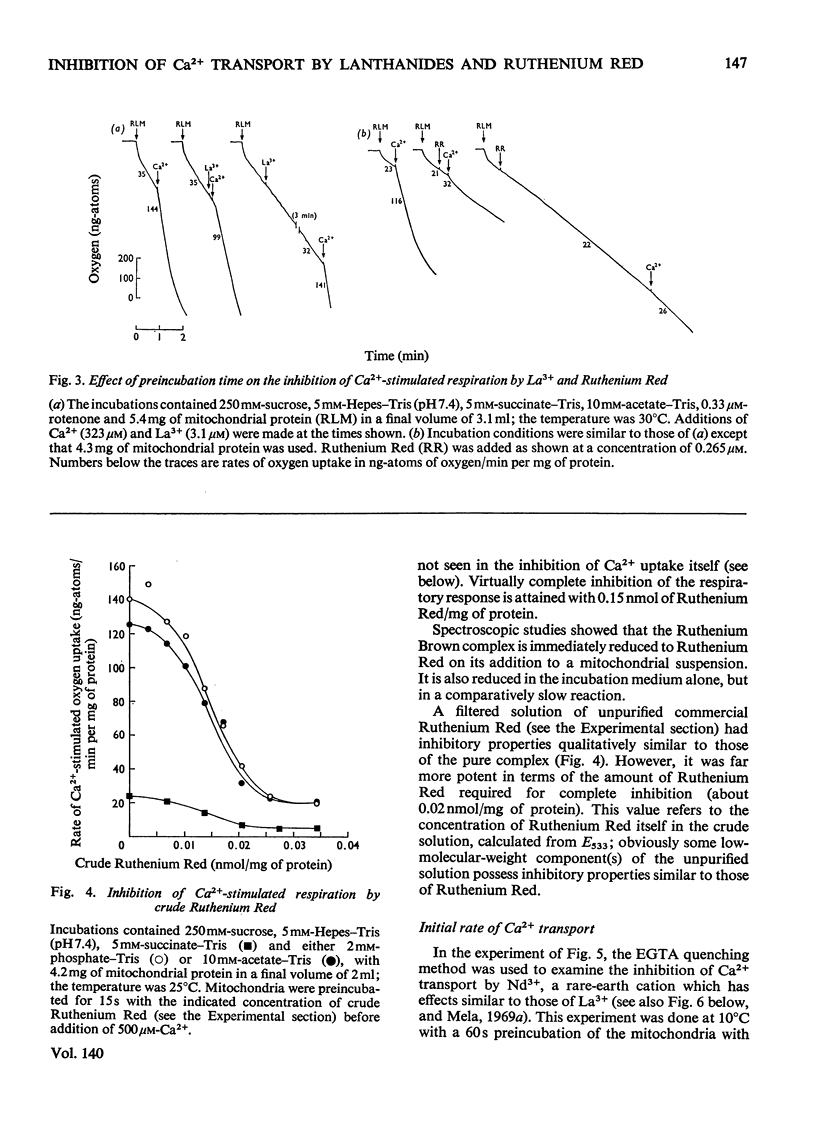
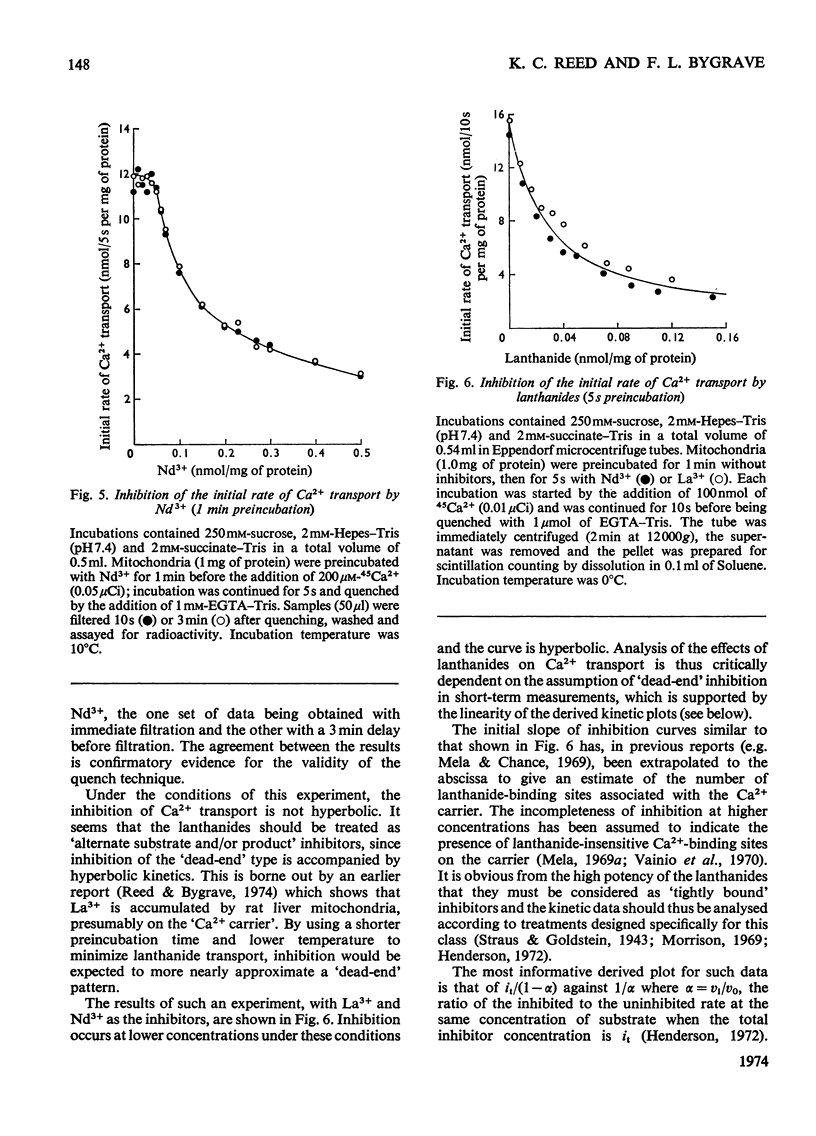
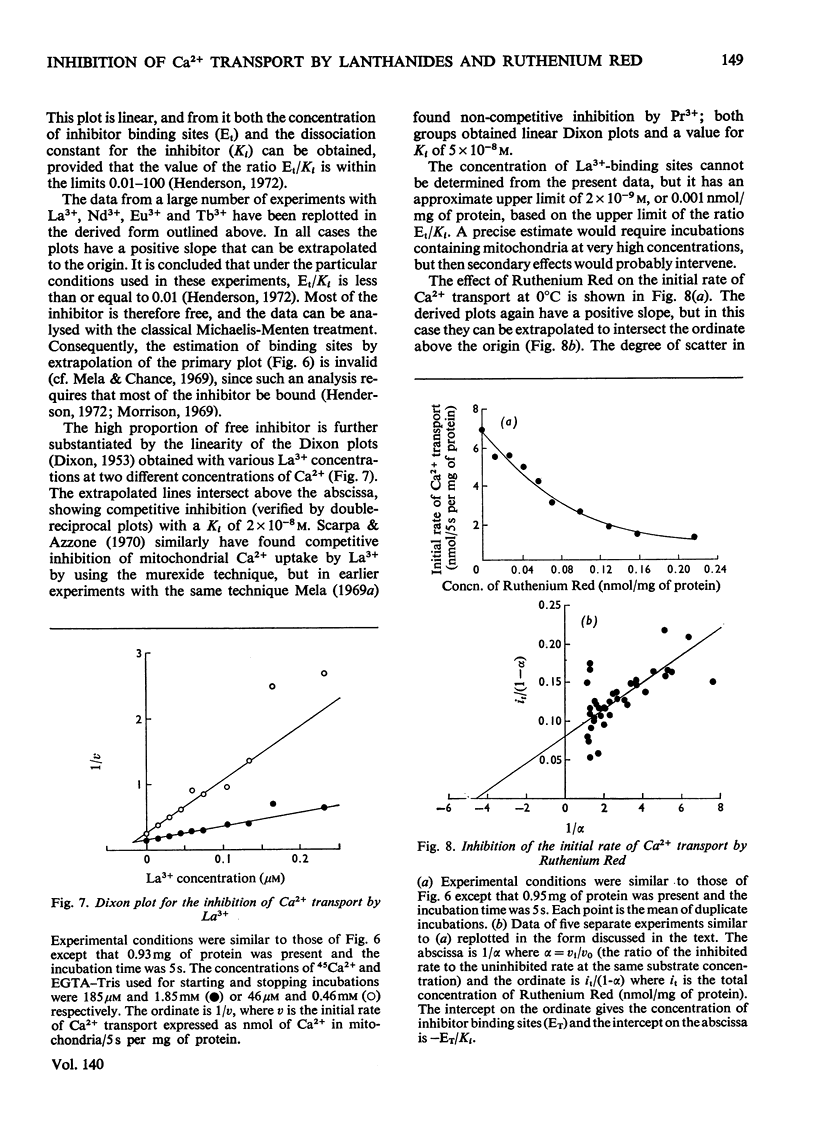
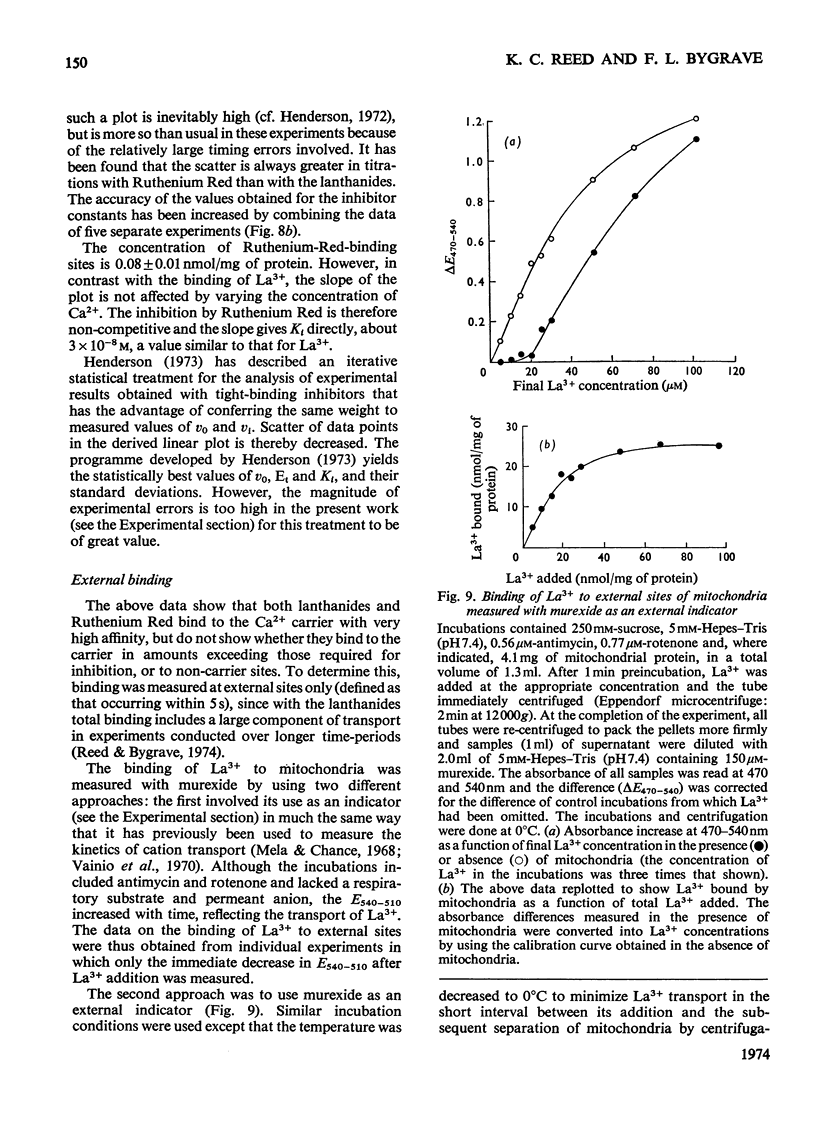
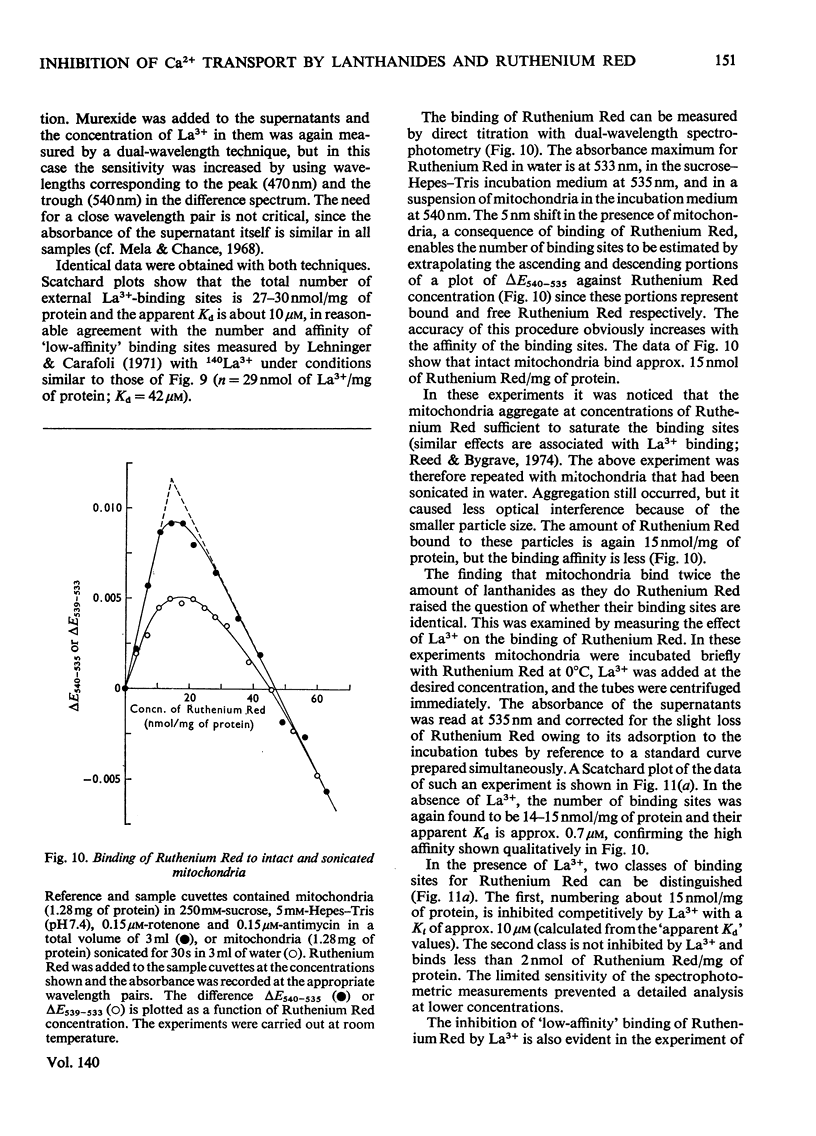
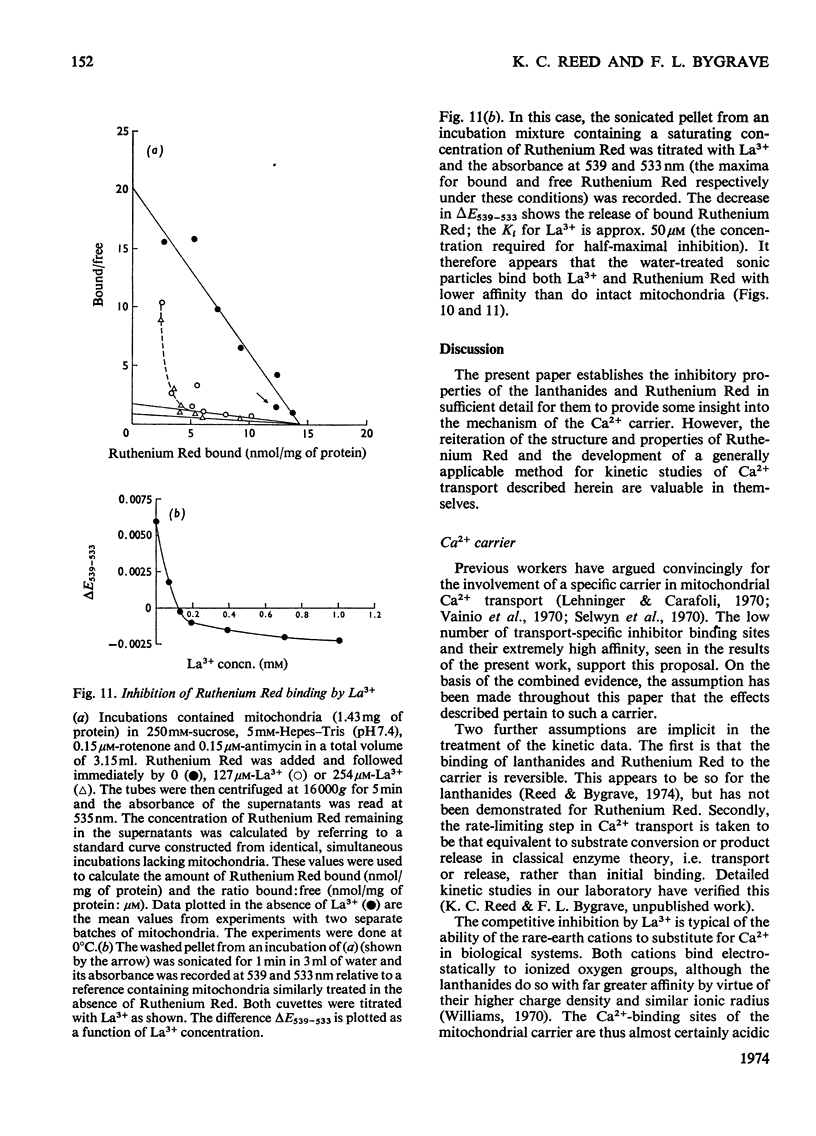
An EGTA (ethanedioxybis(ethylamine)tetra-acetic acid)-quench technique was developed for measuring initial rates of 45Ca2+ transport by rat liver mitochondria. This method was used in conjunction with studies of Ca2+-stimulated respiration to examine the mechanisms of inhibition of Ca2+ transport by the lanthanides and Ruthenium Red. Ruthenium Red inhibits Ca2+ transport non-competitively with Ki 3×10−8m; there are 0.08nmol of carrier-specific binding sites/mg of protein. The inhibition by La3+ is competitive (Ki=2×10−8m); the concentration of lanthanide-sensitive sites is less than 0.001nmol/mg of protein. A further difference between their modes of action is that lanthanide inhibition diminishes with time whereas that by Ruthenium Red does not. Binding studies showed that both classes of inhibitor bind to a relatively large number of external sites (probably identical with the `low-affinity' Ca2+-binding sites). La3+ competes with Ruthenium Red for most of these sites, but a small fraction of the bound Ruthenium Red (less than 2nmol/mg of protein) is not displaced by La3+. The results are discussed briefly in relation to possible models for a Ca2+ carrier.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bygrave F. L., Reed K. C., Spencer T. Cooperative interactions in energy-dependent accumulation of Ca2+ by isolated rat liver mitochondria. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):89–89. doi: 10.1038/newbio230089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. THE ENERGY-LINKED REACTION OF CALCIUM WITH MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2729–2748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Lehninger A. L. A survey of the interaction of calcium ions with mitochondria from different tissues and species. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):681–690. doi: 10.1042/bj1220681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Mela L. Calcium and manganese interactions in mitochondrial ion accumulation. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3220–3223. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Yoshioka T. External ca2+ concentrations associated with membrane alkalinization in mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3224–3229. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. A linear equation that describes the steady-state kinetics of enzymes and subcellular particles interacting with tightly bound inhibitors. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):321–333. doi: 10.1042/bj1270321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. Steady-state enzyme kinetics with high-affinity substrates or inhibitors. A statistical treatment of dose-response curves. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):101–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1350101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg M., Falkner G., Erdelt H., Grebe K. On the relation between adenine nucleotide carrier sites and atractyloside binding in mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L., Carafoli E., Rossi C. S. Energy-linked ion movements in mitochondrial systems. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:259–320. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L., Carafoli E. The interaction of La 3+ with mitochondria in relation to respiration-coupled Ca 2+ transport. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Apr;143(2):506–515. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemberg M. R. Cytochrome oxidase. Physiol Rev. 1969 Jan;49(1):48–121. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mela L., Chance B. Calcium carrier and the "high affinity calcium binding site" in mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 22;35(4):556–559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mela L., Chance B. Spectrophotometric measurements of the kinetics of Ca2+ and Mn2+ accumulation in mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4059–4063. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mela L. Inhibition and activation of calcium transport in mitochondria. Effect of lanthanides and local anesthetic drugs. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2481–2486. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mela L. Interactions of La3+ and local anesthetic drugs with mitochondrial Ca++ and Mn++ uptake. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Feb;123(2):286–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mela L. Reaction of lanthanides with mitochondrial membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 31;147(19):824–828. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb41290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L. Specific inhibition of mitochondrial Ca++ transport by ruthenium red. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 22;42(2):298–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. F. Kinetics of the reversible inhibition of enzyme-catalysed reactions by tight-binding inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;185(2):269–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C. An oxygen polarograph designed for undergraduate use. Anal Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(1):206–212. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90500-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Bygrave F. L. Accumulation of lanthanum by rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;138(2):239–252. doi: 10.1042/bj1380239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. High affinity and low affinity binding of Ca++ by rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):584–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi C. S., Vasington F. D., Carafoli E. The effect of ruthenium red on the uptake and release of Ca 2+ by mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):846–852. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91322-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi C., Azzi A., Azzone G. F. Ion transport in liver mitochondria. I. Metabolism-independent Ca++ binding and H+ release. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):951–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Azzi A. Cation binding to submitochondrial particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Azzone G. F. Effects of phospholipids in liver mitochondria. Osmotic properties and binding of cations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 28;173(1):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Azzone G. F. The mechanism of ion translocation in mitochondria. 4. Coupling of K+ efflux with Ca2+ uptake. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(2):328–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn M. J., Dawson A. P., Dunnett S. J. Calcium transport in mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1970 Sep 18;10(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80402-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio H., Mela L., Chance B. Energy dependent bivalent cation translocation in rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(2):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasington F. D., Gazzotti P., Tiozzo R., Carafoli E. The effect of ruthenium red on Ca 2+ transport and respiration in rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 21;256(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann M. J., Erdelt H., Klingenberg M. Adenine nucleotide translocation of mitochondria. Identification of carrier sites. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Oct;16(2):313–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. N., Jr A comparative study of cytochrome ratios in mitochondria from organs of the rat, chicken, and guinea pig. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 20;162(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


