Abstract
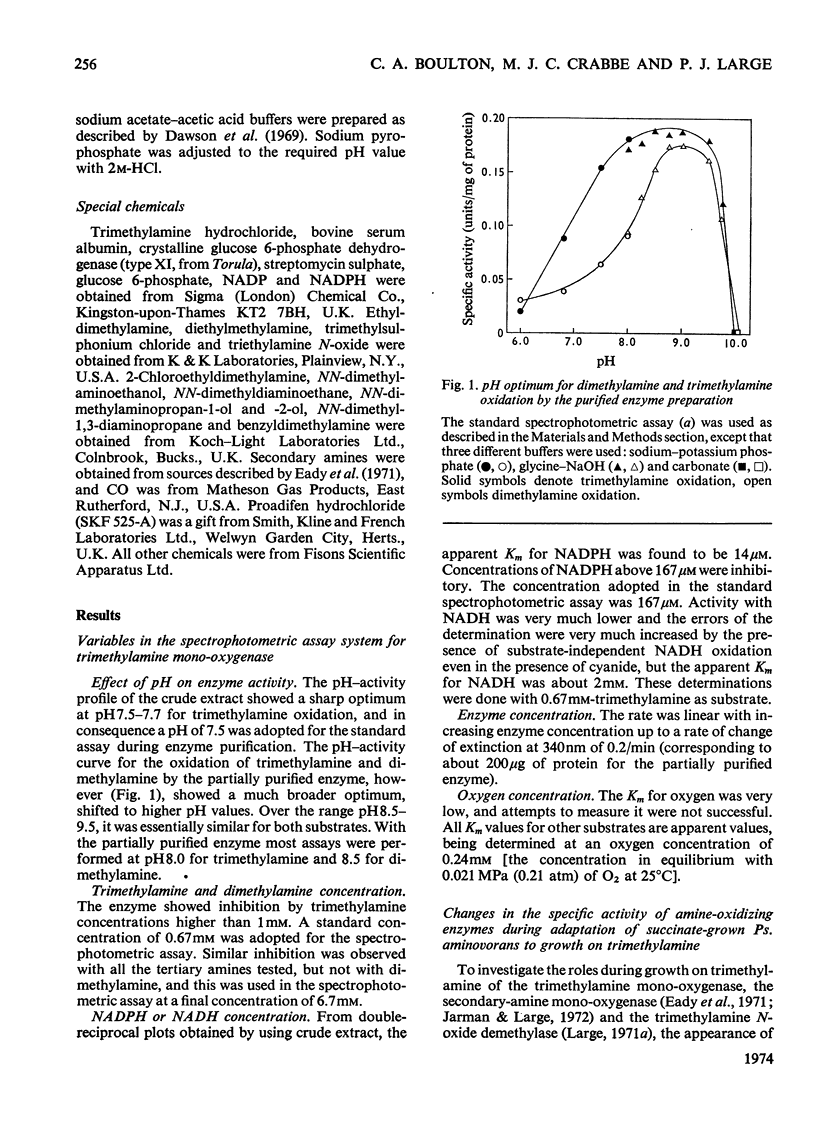
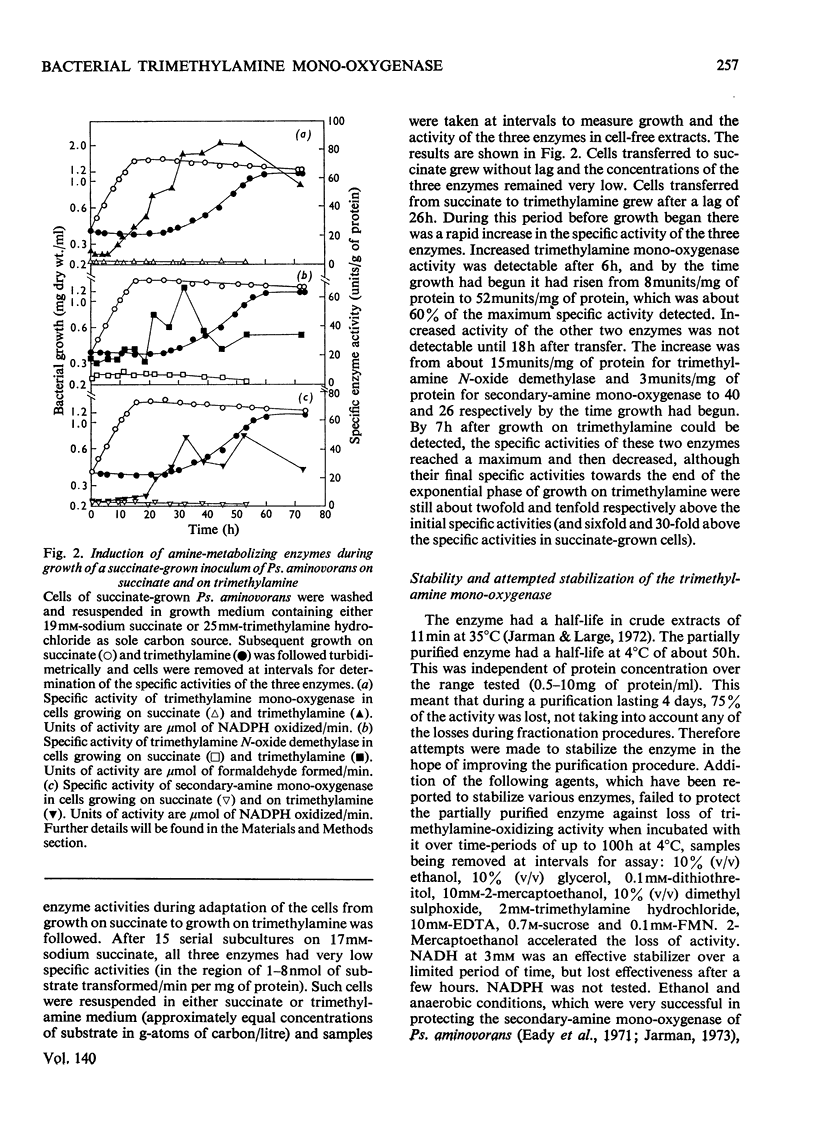
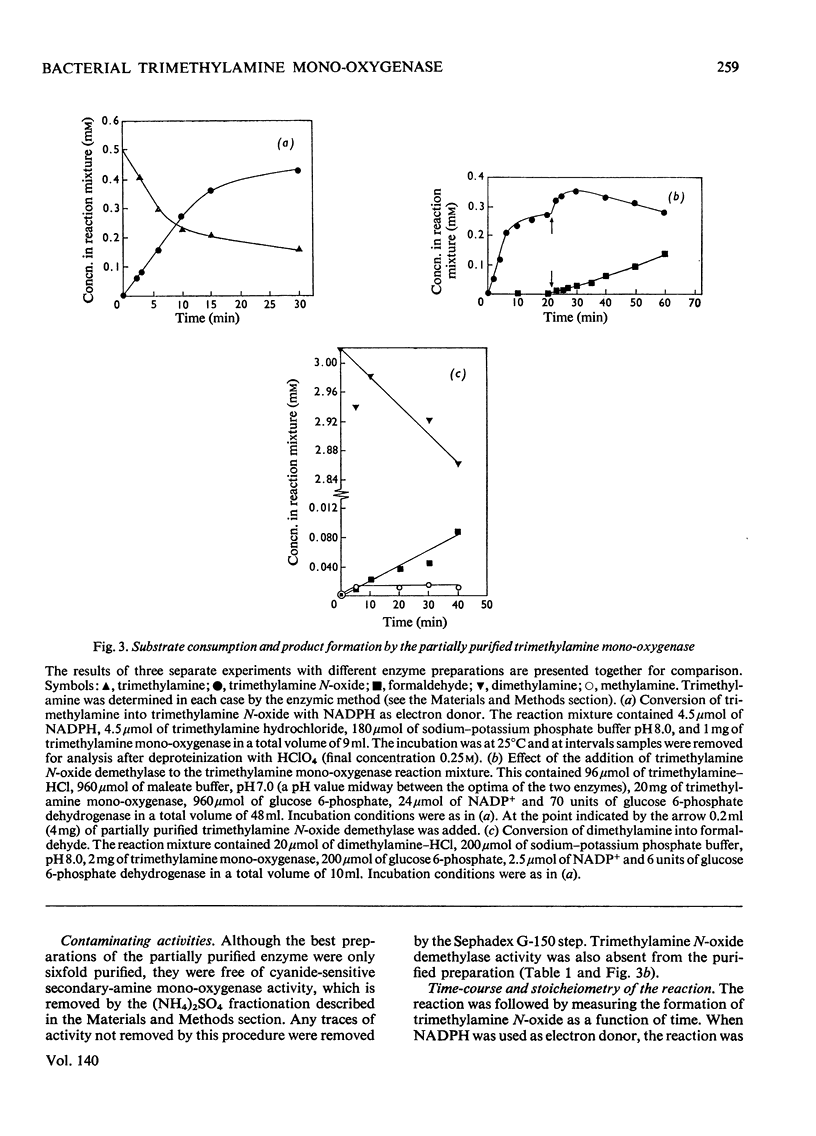
1. A mono-oxygenase, which oxidizes trimethylamine and other tertiary amines bearing methyl or ethyl groups, was partially purified sixfold from Pseudomonas aminovorans grown on trimethylamine as sole carbon source. 2. The preferred electron donor was NADPH. The enzyme had a pH optimum of 8.0–9.4 for trimethylamine oxidation, and 8.8–9.2 for dimethylamine oxidation. 3. The oxidation product of trimethylamine was shown to be trimethylamine N-oxide. Other tertiary amines were probably also converted into N-oxides. 4. The enzyme also oxidized secondary amines. 5. The oxidation of trimethylamine was only slightly inhibited by CO and not at all by KCN or proadifen hydrochloride (SKF 525-A), but was inhibited by trimethylsulphonium chloride, tetramethylammonium chloride, 2,4-dichloro-6-phenylphenoxyethylamine (Lilly 53325) and its NN-diethyl derivative (Lilly 18947). 6. The oxidation of dimethylamine showed a similar response to inhibitors and a parallel loss in activity on heating at 35°C. 7. The activities of the trimethylamine mono-oxygenase, trimethylamine N-oxide demethylase and the secondary-amine mono-oxygenase increased severalfold during adaptation of succinate-grown bacteria to growth on trimethylamine, and the trimethylamine mono-oxygenase was the first enzyme to show an increase in activity. It is concluded that all three enzymes are involved in growth on trimethylamine by this organism.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER J. R., CHAYKIN S. The biosynthesis of trimethylamine-N-oxide. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1309–1313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellion E., Hersh L. B. Methylamine metabolism in a pseudomonas species. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Nov;153(1):368–374. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90457-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau K. Chromatographic methods for the study of amines from biological material. Biochem J. 1961 Jul;80(1):193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj0800193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROMWELL B. T. The micro-estimation and origin of trimethylamine in Chenopodium vulvaria L. Biochem J. 1950 May;46(5):578–582. doi: 10.1042/bj0460578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Zatman L. J. Hexose phosphate synthese and tricarboxylic acid-cycle enzymes in bacterium 4B6, an obligate methylotroph. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1373–1376. doi: 10.1042/bj1281373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Zatman L. J. Trimethylamine metabolism in obligate and facultative methylotrophs. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):101–112. doi: 10.1042/bj1320101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps R. E., Noble A. S. The metabolism of nitrilotriacetate by a pseudomonad. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):1059–1068. doi: 10.1042/bj1361059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBIN D. T. The assay and characterization of amines by 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:783–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Jarman T. R., Large P. J. Microbial oxidation of amines. Partial purification of a mixed-function secondary-amine oxidase system from Pseudomonas aminovorans that contains an enzymically active cytochrome-P-420-type haemoprotein. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):449–459. doi: 10.1042/bj1250449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH P., CONTI S. F. BIOLOGY OF BUDDING BACTERIA. II. GROWTH AND NUTRITION OF HYPHOMICROBIUM SPP. Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Jun 26;48:358–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00405979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Peterson J. A., Thompson A. A. An N-methyl glutamate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas M.A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jul;145(1):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman T. R., Large P. J. Distribution of the enzymes oxidizing secondary and tertiary amines in Pseudomonas aminovorans grown on various substrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(1):205–208. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlubar F. F., McKee E. M., Ziegler D. M. Reduced pyridine nucleotide-dependent N-hydroxy amine oxidase and reductase activities of hepatic microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 May;156(1):46–57. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90339-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large P. J., Eady R. R., Murden D. J. An enzymic method for the micro estimation of methylamine, ethylamine, and n-propylamine. Anal Biochem. 1969 Dec;32(3):402–407. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(69)80007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large P. J. Non-oxidative demethylation of trimethylamine N-oxide by Pseudomonas aminovorans. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large P. J. The oxidative cleavage of alkyl-nitrogen bonds in micro-organisms. Xenobiotica. 1971 Jul-Oct;1(4):457–467. doi: 10.3109/00498257109041511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. H., Ziegler D. M. A quantitative micro method for the estimation of amine oxides. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):416–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0550416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiedje J. M., Mason B. B., Warren C. B., Malec E. J. Metabolism of nitrilotriacetate by cells of Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):811–818. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.811-818.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D. M., Mitchell C. H. Microsomal oxidase. IV. Properties of a mixed-function amine oxidase isolated from pig liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 May;150(1):116–125. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D. M., Poulsen L. L., McKee E. M. Interaction of primary amines with a mixed-function amine oxidase isolated from pig liver microsomes. Xenobiotica. 1971 Jul-Oct;1(4):523–531. doi: 10.3109/00498257109041521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


