Abstract
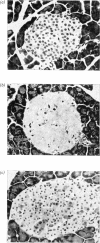
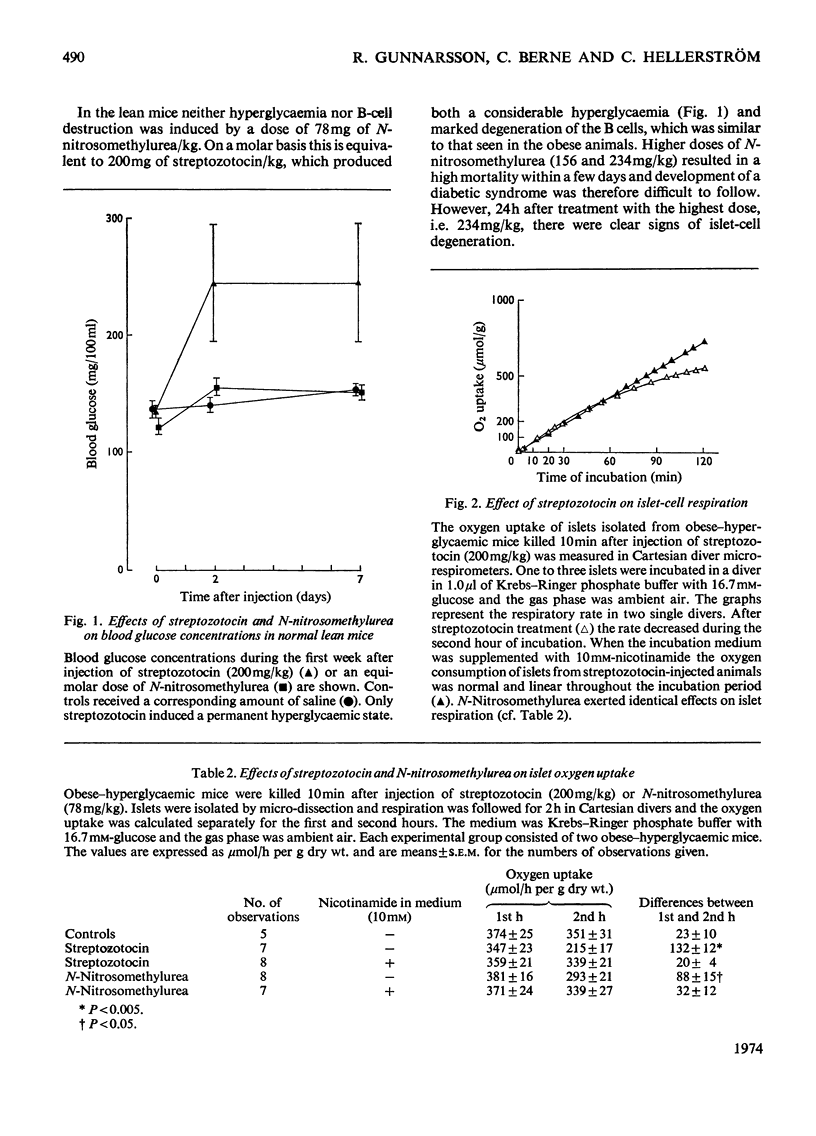
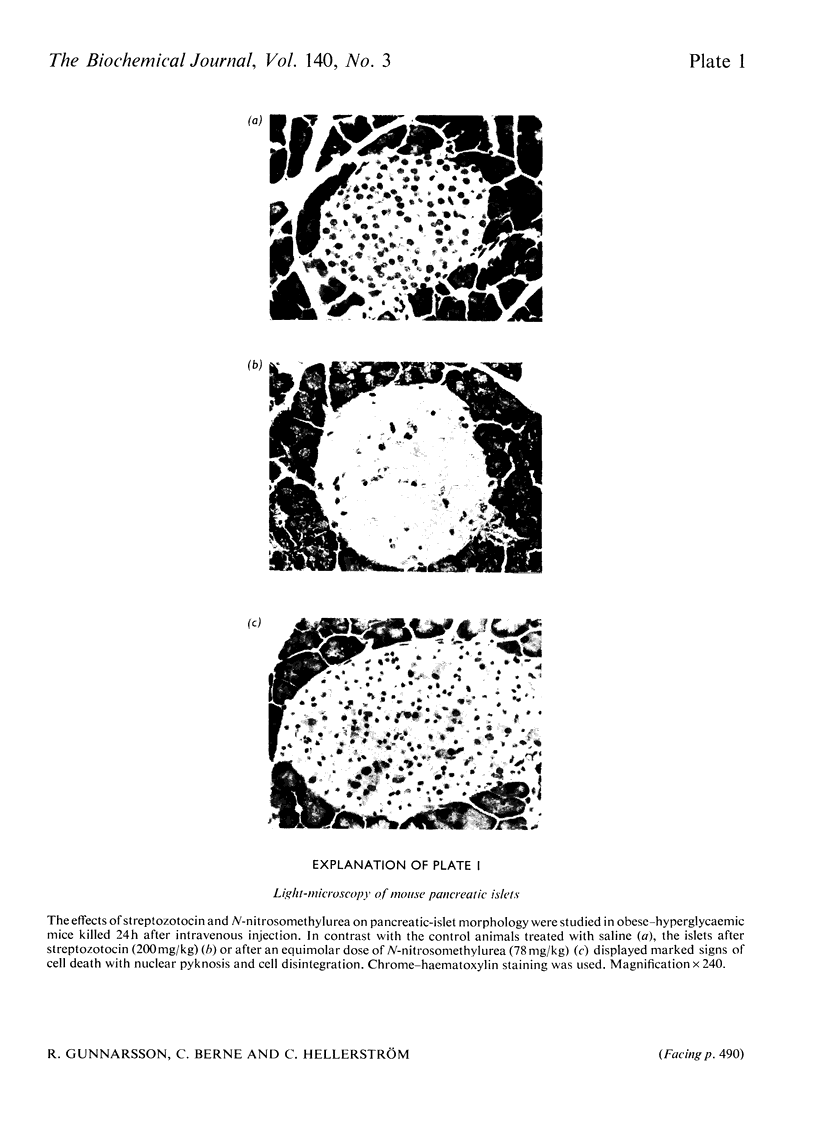
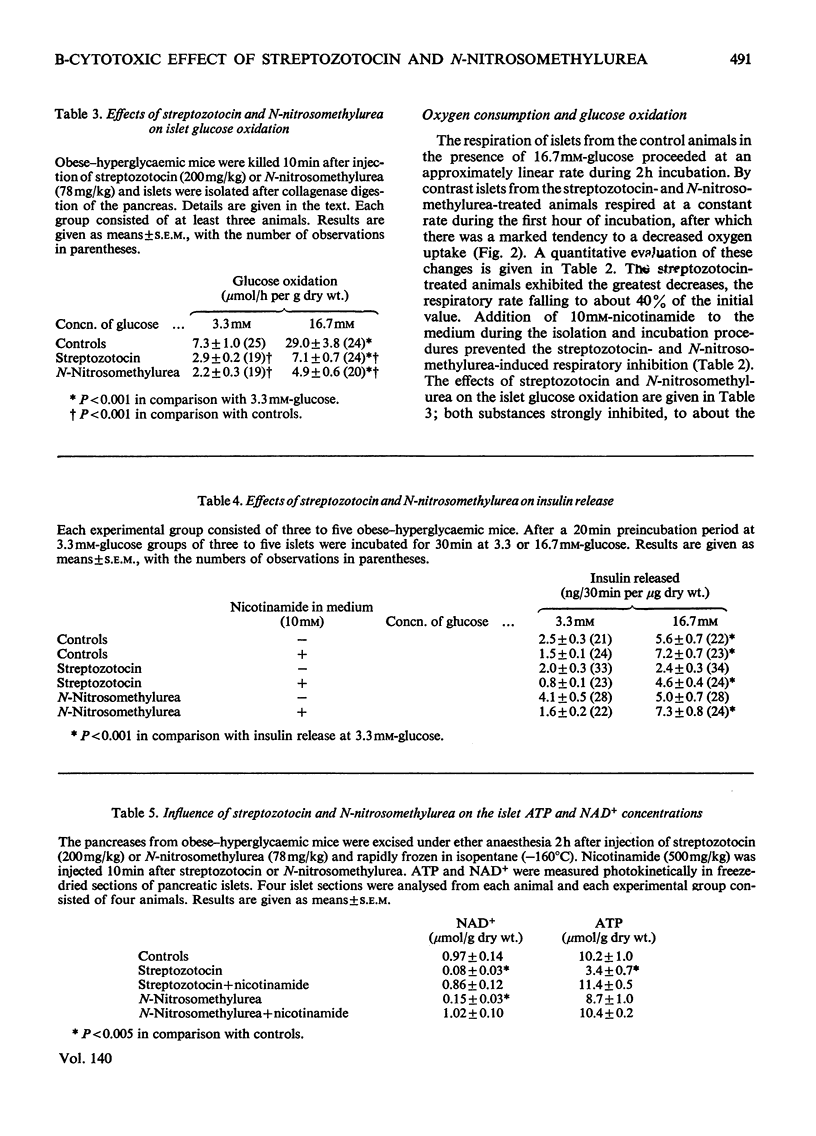
The effects on the pancreatic B cell of streptozotocin and its aglucone derivative N-nitrosomethylurea were investigated in obese–hyperglycaemic mice and their lean littermates. Both streptozotocin and N-nitrosomethylurea were found to be B-cytotoxic although N-nitrosomethylurea produced less islet damage. Both substances decreased the concentrations of NAD+ in the islet cells to about 10% of the control values within 2h after injection. This NAD+ depletion was prevented by injection of nicotinamide 10min after the administration of streptozotocin or N-nitrosomethylurea. In islets taken from animals 10min after injection of streptozotocin or N-nitrosomethylurea there was no stimulatory effect of glucose on the respiration or insulin release and the oxidation of glucose was markedly decreased. Addition of nicotinamide (10mm) to the incubated islets restored glucose stimulation of both the oxygen consumption and insulin release. It is concluded that islet NAD+ depletion is probably important for the B-cytotoxin action of N-nitrosomethylurea and streptozotocin. The glucose residue in the streptozotocin molecule may potentiate the B-cytotoxic action of this drug in mice.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENCOSME S. A. Studies on the methods of staining the islet cells of the pancreas. AMA Arch Pathol. 1952 Jan;53(1):87–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berne C., Gunnarsson R., Hellerström C., Wilander E. Letter: Diabetogenic nitrosamines? Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):173–174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92474-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brolin S. E., Berne C., Isacsson U. Photokinetic assay of NADH and NADPH in microdissected tissue samples. Anal Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(1):50–55. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90484-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brolin S. E., Borglund E., Tegner L., Wettermark G. Photokinetic micro assay based on dehydrogenase reactions and bacterial luciferase. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jul;42(1):124–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosky G., Logothetopoulos J. Streptozotocin diabetes in the mouse and guinea pig. Diabetes. 1969 Sep;18(9):606–611. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.9.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTOPHE J., DAGENAIS Y., MAYER J. Increased circulating insulin-like activity in obese-hyperglycaemic mice. Nature. 1959 Jul 4;184:61–62. doi: 10.1038/184061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosby N. T., Foreman J. K., Palframan J. F., Sawyer R. EWstimation of steam-volatile N-nitrosamines in foods at the 1 micro g-kg level. Nature. 1972 Aug 11;238(5363):342–343. doi: 10.1038/238342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRUCKREY H., IVANKOVIC S., PREUSSMANN R. SELEKTIVE ERZEUGUNG MALIGNER TUMOREN IM GEHIRN UND RUECKENMARK VON RATTEN DURCH N-METHYL-N-NITROSOHARNSTOFF. Z Krebsforsch. 1965 Feb 3;66:389–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. The bioelectrical properties of pancreatic islet cells: effects of diabetogenic agents. Diabetologia. 1972 Jul;8(3):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01212257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deery D. J., Taylor K. W. Effect of phenylpyruvate on enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis in rat brain. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;134(2):557–563. doi: 10.1042/bj1340557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulin W. E., Wyse B. M. Reversal of streptozotocin diabetes with nicotinamide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Mar;130(3):992–994. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulin W. E., Wyse B. M. Studies on the ability of compounds to block the diabetogenic activity of streptozotocin. Diabetes. 1969 Jul;18(7):459–466. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.7.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEPTS W., CHRISTOPHE J., MAYER J. Pancreatic islets in mice with the obese-hyperglycemic syndrome: lack of effect of carbutamide. Diabetes. 1960 Jan-Feb;9:63–69. doi: 10.2337/diab.9.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson R., Hellerström C. Acute effects of alloxan on the metabolism and insulin secretion of the pancreatic B-cell. Horm Metab Res. 1973 Nov;5(6):404–409. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLMAN B. The occurrence of argyrophil cells in the islets of Langerhans of American obese-hyperglycaemic mice. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1961 Apr;36:596–602. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0360596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerström C. Effects of carbohydrates on the oxygen consumption of isolated pancreatic islets of mice. Endocrinology. 1967 Jul;81(1):105–112. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-1-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr R. R., Jahnke J. K., Argoudelis A. D. The structure of streptozotocin. J Am Chem Soc. 1967 Aug 30;89(18):4808–4809. doi: 10.1021/ja00994a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinz M., Katsilambros N., Maier V., Schatz H., Pfeiffer E. F. Significance of streptozotocin induced nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide (NAD) degradation in mouse pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1973 Mar 1;30(2):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80656-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C. K., Hashim S. A. Pyridine nucleotide depletion in pancreatic islets associated with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetes. 1972 Jul;21(7):789–793. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.7.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Taylor K. W. Potassium ions and the secretion of insulin by islets of Langerhans incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(1):17–24. doi: 10.1042/bj1080017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEEN H., FIELD J. B., PASTAN I. H. A simple method for in vitro metabolic studies using small volumes of tissue and medium. Metabolism. 1963 Feb;12:143–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., CORI C. F. Studies of tissue permeability. V. The penetration and phosphorylation of 2-deoxyglucose in the rat diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):171–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H. The quantitative histochemistry of the brain; histological sampling. J Histochem Cytochem. 1953 Nov;1(6):420–428. doi: 10.1177/1.6.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER J., RUSSELL R. E., BATES M. W., DICKIE M. M. Metabolic, nutritional and endocrine studies of the hereditary obesity-diabetes syndrome of mice and mechanism of its development. Metabolism. 1953 Jan;2(1):9–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rerup C. C. Drugs producing diabetes through damage of the insulin secreting cells. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Dec;22(4):485–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein P. S., Cooney D. A., McMenamin M. G., Anderson T. Streptozotocin diabetes--further studies on the mechanism of depression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide concentrations in mouse pancreatic islets and liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Oct 15;22(20):2625–2631. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein P. S., Cooney D. A., Vernon M. L. The use of nicotinamide to modify the toxicity of streptozotocin diabetes without loss of antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 1967 Dec;27(12):2324–2332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein P. S., Loftus S. Streptozotocin: depression of mouse liver pyridine nucleotides. Cancer Res. 1968 Aug;28(8):1501–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder P. J., Kashket S., O'Sullivan J. B. Pentose cycle in isolated islets during glucose-stimulated insulin release. Am J Physiol. 1970 Oct;219(4):876–880. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.4.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffacher W., Burr I., Gutzeit A., Beaven D., Veleminsky J., Renold A. E. Streptozotocin diabetes: time course of irreversible B-cell damage; further observations on prevention by nicotinamide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):194–200. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swann P. F. The rate of breakdown of methyl methanesulphonate, dimethyl sulphate and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea in the rat. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):49–52. doi: 10.1042/bj1100049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyse B. M., Dulin W. E. The effects of streptozotocin on glucose oxidation by isolated islets of Langerhans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jan;136(1):70–72. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Beidler L. M. Glucose and alloxan interactions in the pancreatic islets. Am J Physiol. 1973 Apr;224(4):963–966. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.4.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]