Abstract
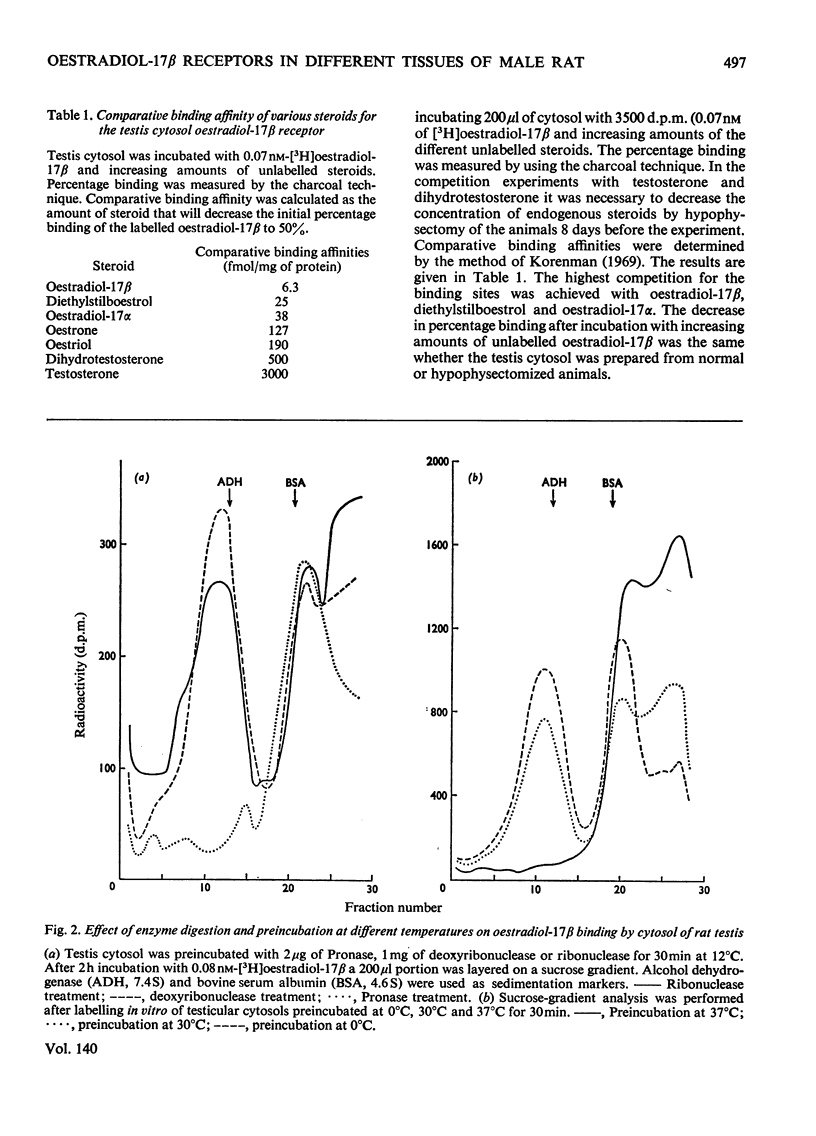
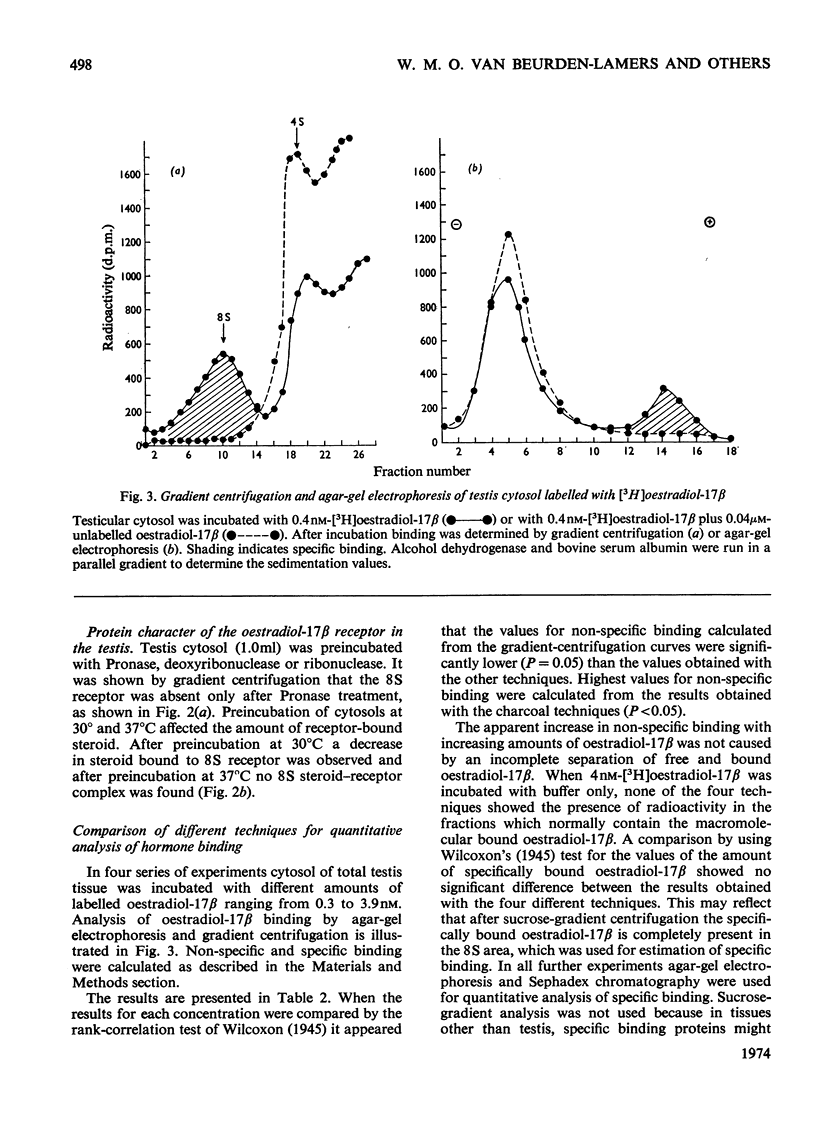
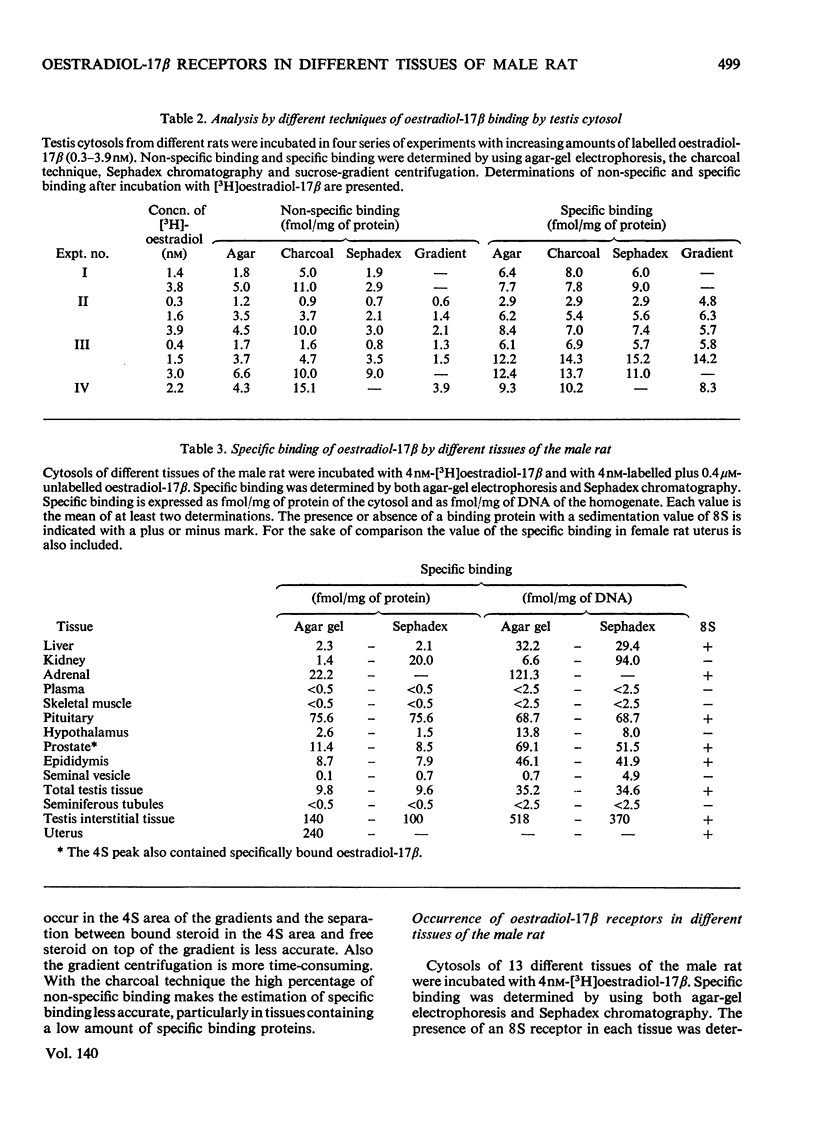
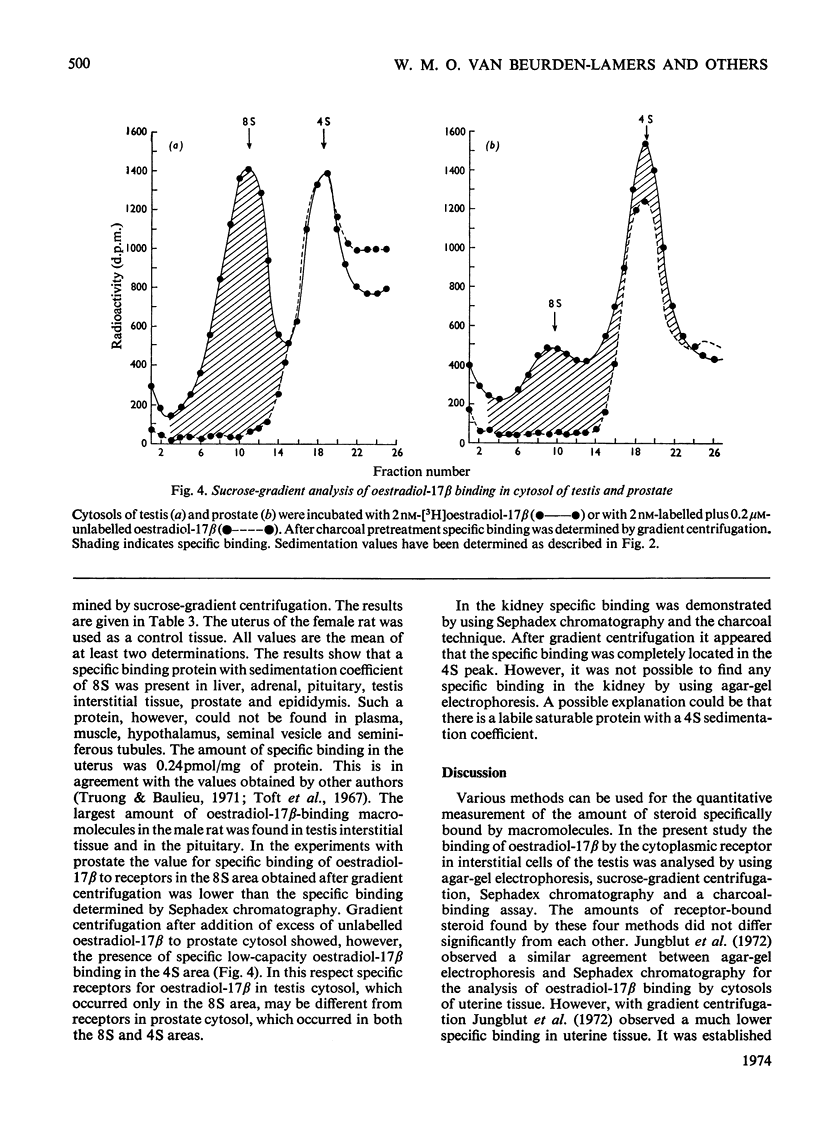
The specificity of the binding of oestradiol-17β by cytoplasmic fractions of several tissues of the male rat was investigated. 1. Agar-gel electrophoresis, Sephadex chromatography, adsorption by dextran-coated charcoal and sucrose-gradient centrifugation were used to estimate the binding capacity and specificity. The four different methods all gave similar results for the capacity of the specific oestradiol-17β-binding macromolecules in the testis. 2. The presence of a specific saturable binding protein with a sedimentation coefficient of 8S was demonstrated in liver, adrenal, pituitary, prostate, epididymis and testis interstitial tissue. The highest concentration of oestradiol-17β-binding macromolecules was found in testis interstitial tissue (0.12pmol/mg of protein) and in the pituitary (0.075pmol/mg of protein). 3. The oestradiol-17β receptor in the testis cytosol showed the characteristics of a protein with respect to Pronase treatment and temperature sensitivity. In competition experiments with different steroids the receptor showed a high affinity for oestradiol-17β, a moderate affinity for diethylstilboestrol and oestradiol-17α and a low affinity for oestrone, oestriol, testosterone and 5α-dihydrotestosterone (17β-hydroxy-5α-androstan-3-one). 4. The wide distribution of oestradiol-17β receptors in the male rat is in apparent contradiction to the current concept of the specificity of steroid-hormone action. Further research is required to investigate a possible physiological meaning of the presence of specific receptors in the different tissues.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attramadal A. Cellular localization of 3H-oestradiol in the hypothalamus. An autoradiographic study in male and female rats. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;104(4):572–581. doi: 10.1007/BF00335379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaquier J. A., Calandra R. S. Intranuclear receptor for androgens in rat epididymis. Endocrinology. 1973 Jul;93(1):51–60. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann A. O., Mulder E., Lamers-Stahlhofen G. J., Mechielsen M. J., van der Molen H. J. An oestradiol receptor in rat testis interstitial tissue. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 1;26(1):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN A. K., MASON N. R. COMPARATIVE ABILITY OF SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES AND INTERSTITIAL TISSUE OF RAT TESTES TO SYNTHESIZE ANDROGENS FROM PROGESTERONE-4-14C IN VITRO. Endocrinology. 1965 Apr;76:646–656. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-4-646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chobanian A., Brecher P. I., Lille R. D., Wotiz H. H. Metabolism of sex hormones in the aortic wall. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):701–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. H., Campbell P. S., Peck E. J., Jr Receptor-estrogen complex in the nuclear fraction of the pituitary and hypothalamus of male and female immature rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1972;10(4):218–228. doi: 10.1159/000122091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., DeSombre E. R. Mechanism of action of the female sex hormones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:203–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungblut P. W., Hughes S. F., Görlich L., Gowers U., Wagner R. K. Simultaneous occurrence of individual estrogen- and androgen receptors in female and male target organs. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Dec;352(12):1603–1610. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.2.1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungblut P. W., Hughes S., Hughes A., Wagner R. K. Evaluation of various methods for the assay of cytoplasmic oestrogen receptors in extracts of calf uteri and human breast cancers. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 May;70(1):185–195. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenman S. G. Comparative binding affinity of estrogens and its relation to estrogenic potency. Steroids. 1969 Feb;13(2):163–177. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(69)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa R., Stupnicka E., Kniewald Z., Martini L. The transformation of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone by the brain and the anterior pituitary. J Steroid Biochem. 1972 Apr;3(3):385–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(72)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowles T. F., Ashkanazy B., Mix E., Jr, Sheppard H. Hypothalamic and hypophyseal estradiol-binding complexes. Endocrinology. 1971 Aug;89(2):484–491. doi: 10.1210/endo-89-2-484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder E., Brinkmann A. O., Lamers-Stahlhofen G. J., van der Molen H. J. Binding of oestradiol by the nuclear fraction of rat testis interstitial tissue. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 1;31(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80090-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Haines M. E. Regulation of protein synthesis in chick oviduct. IV, Role of testosterone. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2107–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. N., Talwar G. P. Uptake of (6,7-3H) estradiol-17 beta by the hypothalamus, pituitary and other organs of rats in different conditions of hormonal status. Indian J Biochem. 1969 Jun;6(2):71–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf W. E. Nuclear concentration of 3H-estradiol in target tissues. Dry-mount autoradiography of vagina, oviduct, ovary, testis, mammary tumor, liver and adrenal. Endocrinology. 1969 Jul;85(1):31–37. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft D., Gorski J. A receptor molecule for estrogens: isolation from the rat uterus and preliminary characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1574–1581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft D., Shyamala G., Gorski J. A receptor molecule for estrogens: studies using a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1740–1743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truong H., Baulieu E. E. Interaction of uterus cytosol receptor with estradiol. Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 20;237(1):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuohimaa P., Johansson R. Decreased estradiol binding in the uterus and anterior hypothalamus of androgenized female rats. Endocrinology. 1971 May;88(5):1159–1164. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-5-1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vértes M., King R. J. The mechanism of oestradiol binding in rat hypothalamus: effect of androgenization. J Endocrinol. 1971 Oct;51(2):271–282. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0510271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. K. Characterization and assay of steroid hormone receptors and steroid-binding serum proteins by agargel electrophoresis at low temperature. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Aug;353(8):1235–1245. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.2.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D., Gorski J. Preparation and characterization of free cell suspensions from the immature rat uterus. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):297–306. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


