Abstract
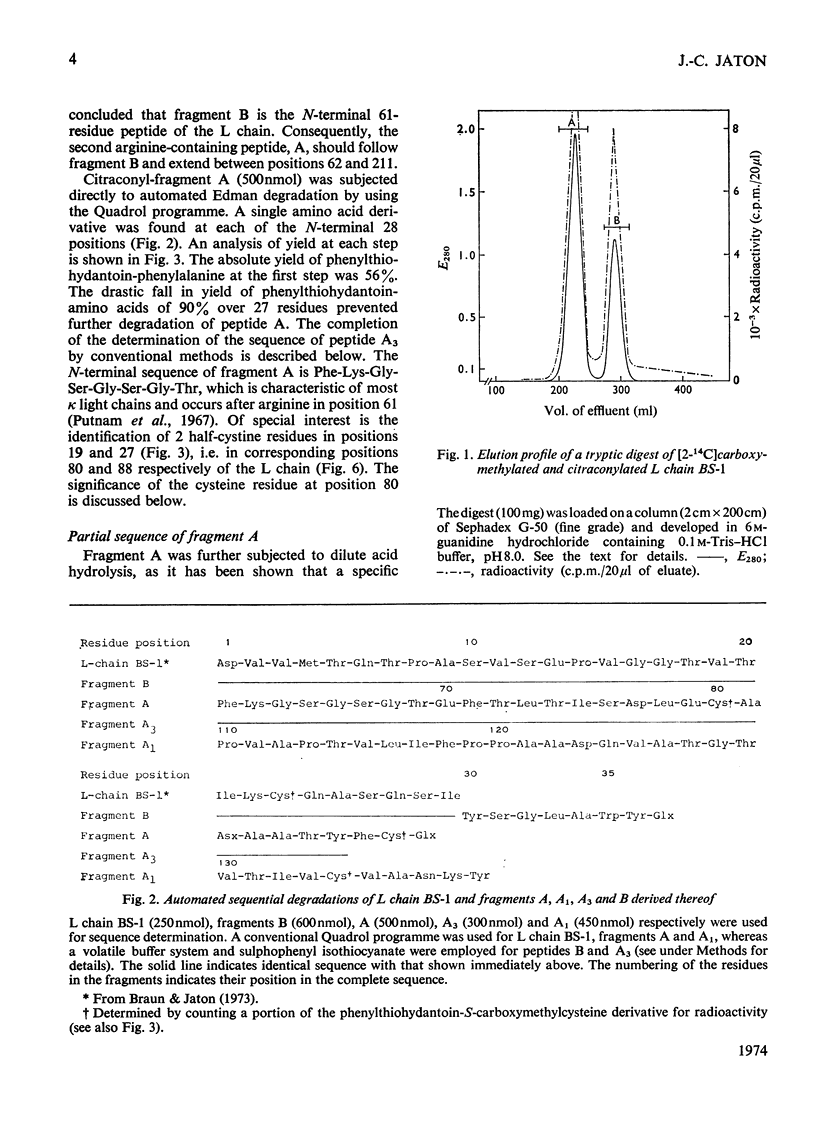
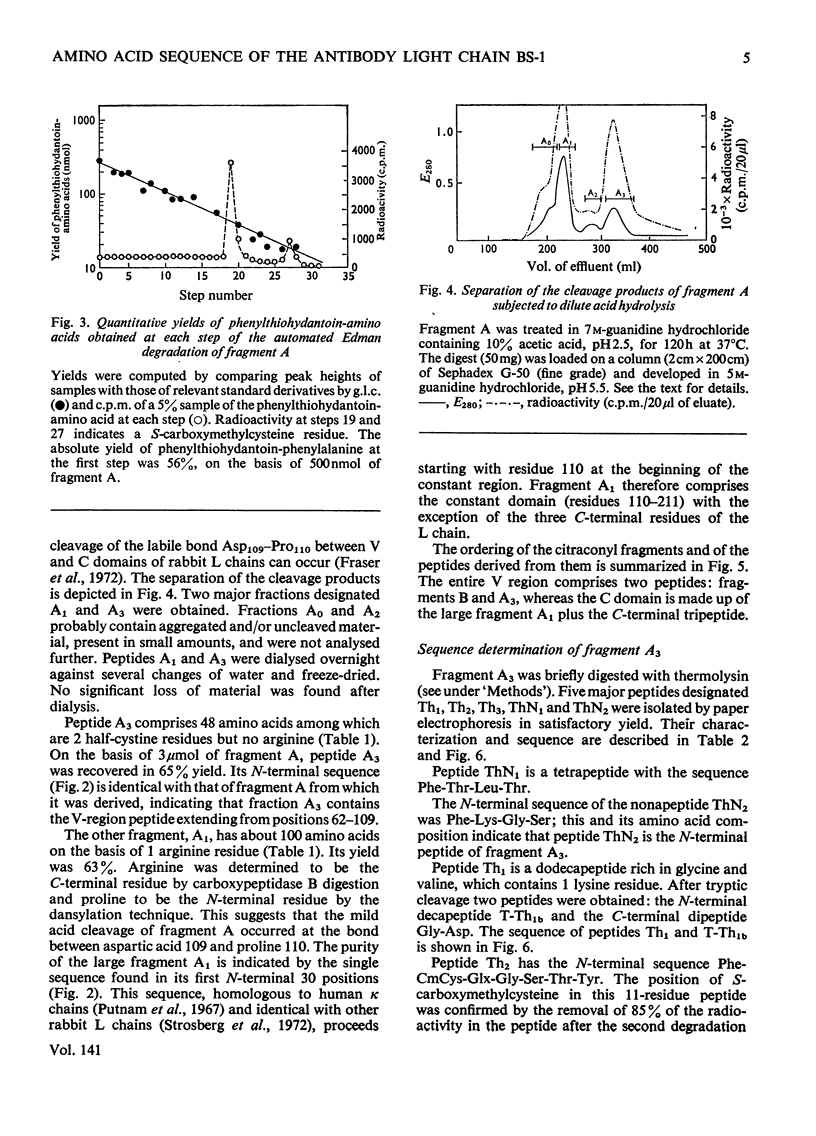
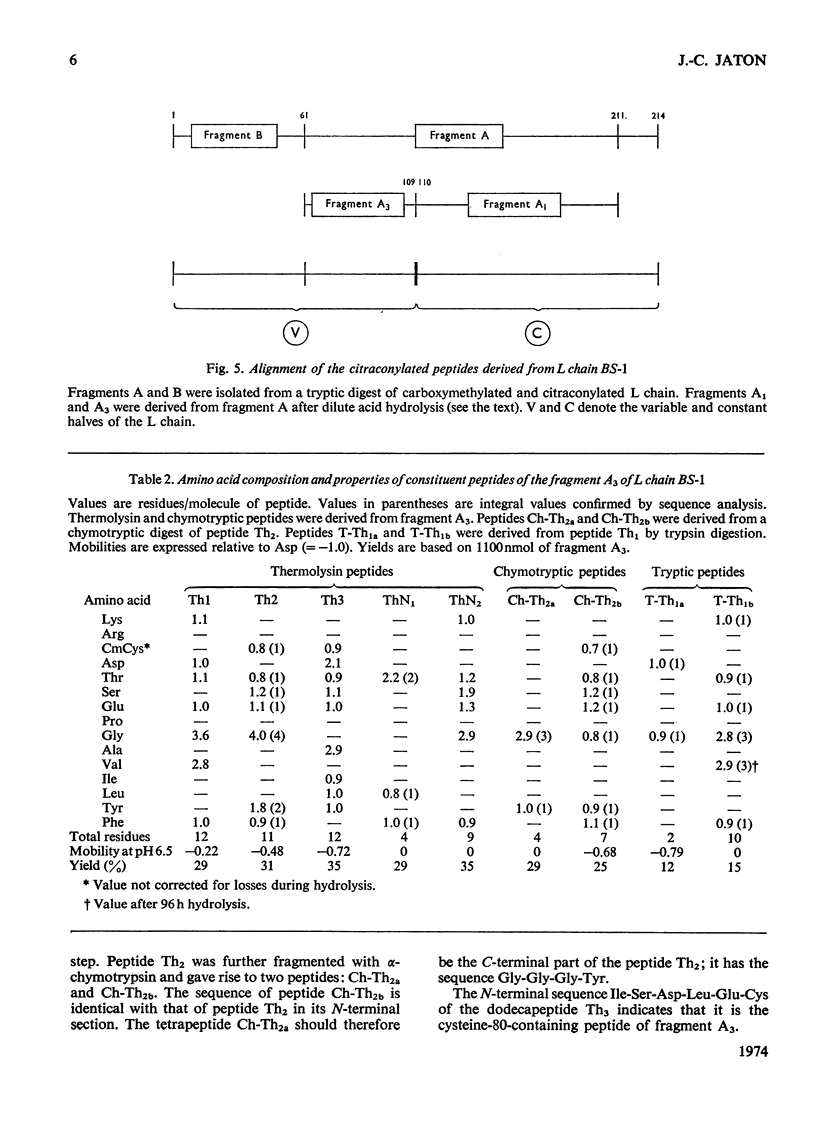
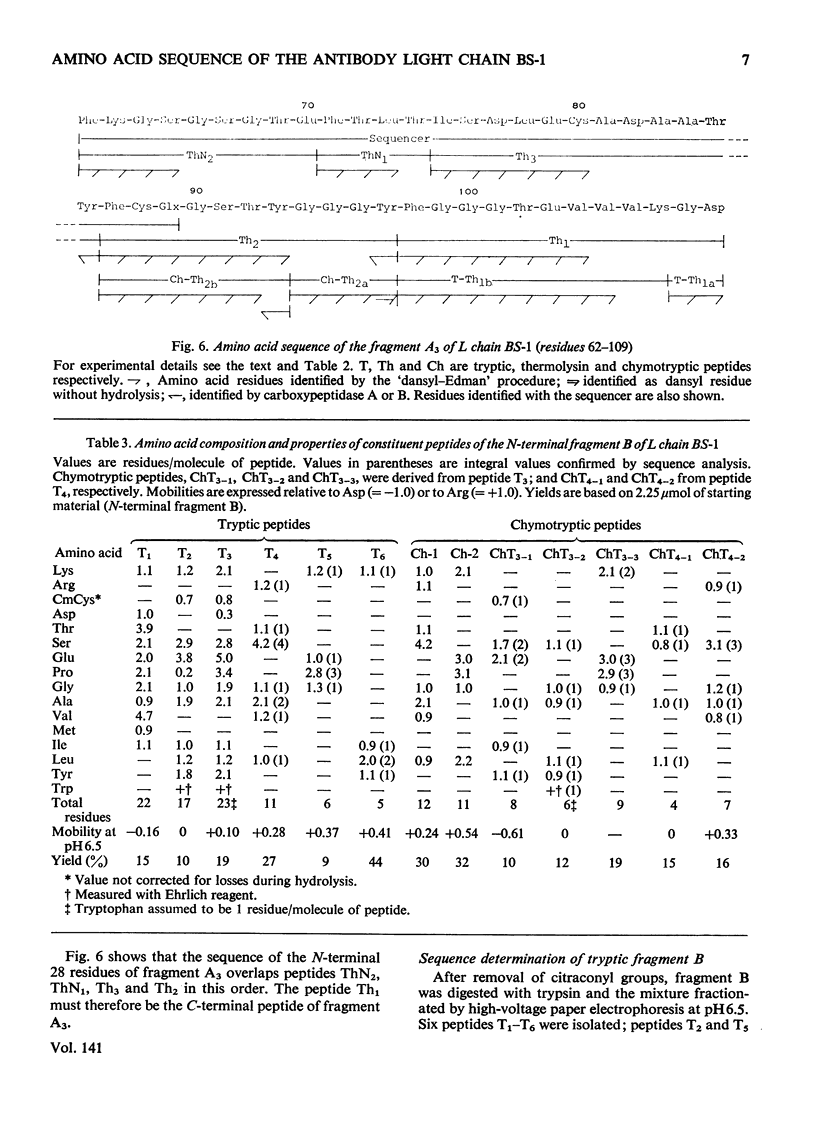
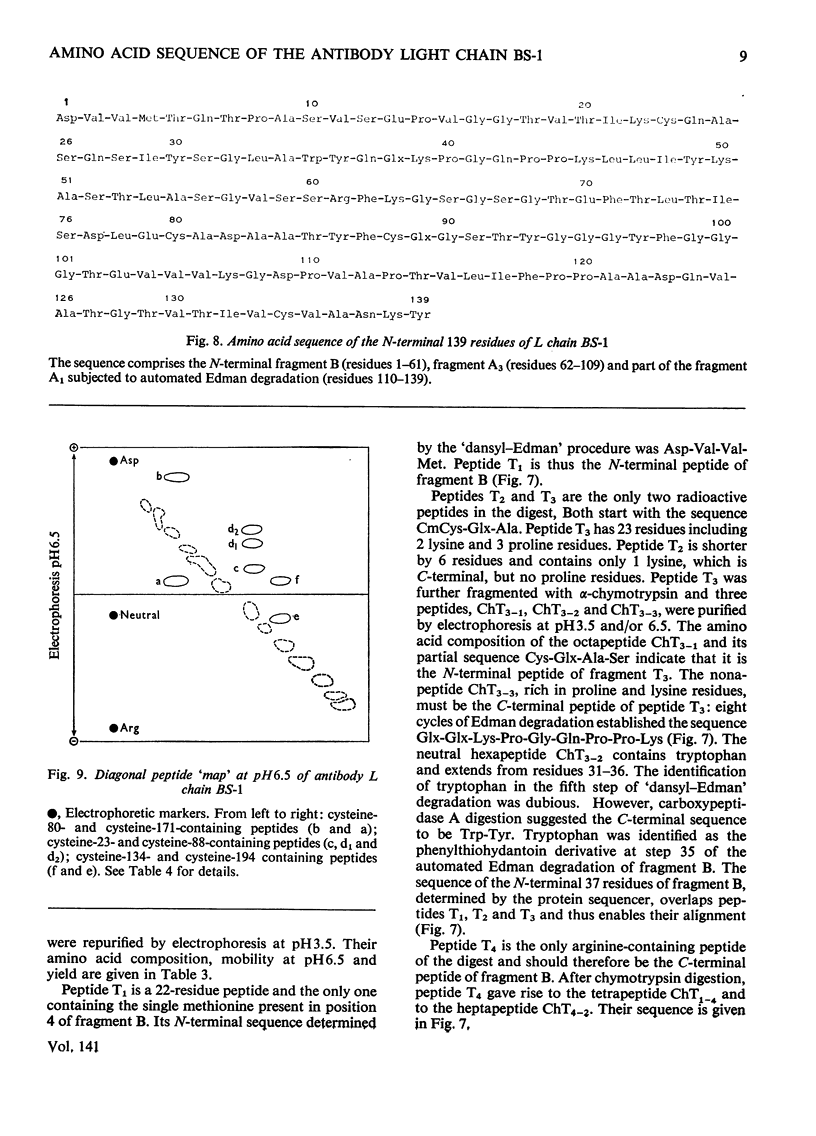
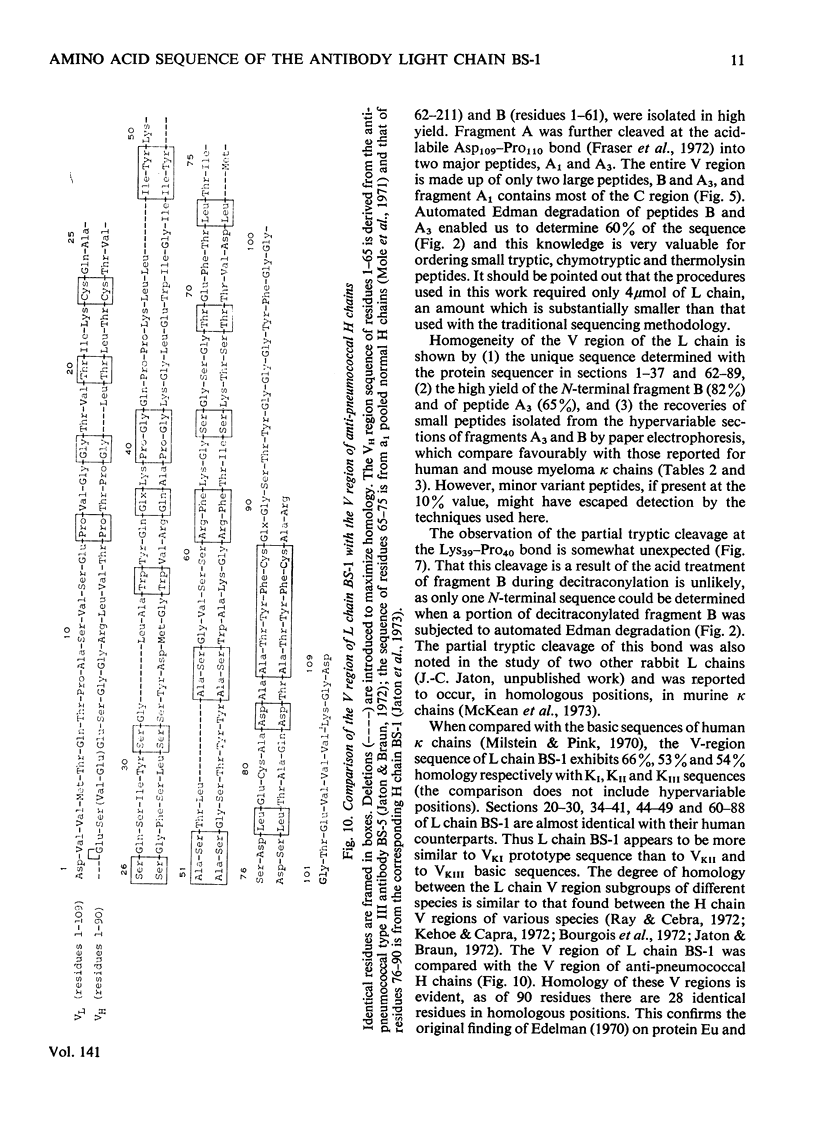
The amino acid sequence of the N-terminal 139 residues of the L (light) chain derived from a homogeneous rabbit antibody (designated BS-1) to type III pneumococci was determined. A combination of methods involving tryptic cleavage restricted to the 2 arginine residues of the molecule and mild acid hydrolysis of a labile peptide bond between the V (variable) and C (constant) regions of the L chain (Fraser et al., 1972) allowed the isolation of two large peptides comprising the entire V region (residues 1–109); these peptides were suitable for automated Edman degradation. The complete sequence analysis of the V region was carried out with only 4μmol of L chain. This material was homogeneous, although minor variant sequences, if present at the 10% value, would not have been detected. The L chain contains 3 intrachain disulphide bridges, whose pairing was established by diagonal electrophoresis: there is one V-region bridge between positions 23 and 88 and one C-region bridge between positions 134 and 194; the third one connects V and C domains between positions 80 and 171. When compared with the basic sequence of human κ chains, rabbit L chain BS-1 appears to be more similar to the VKI prototype sequence than to VKII or VKIII sequences, where VKI, VKII and VKIII represent subgroups I, II and III respectively of V regions of κ light chains. The V regions of rabbit heavy and light chains are homologous to each other. The presence of two clusters of 3 glycine residues in positions 94–96 and 99–101 respectively is remarkable. Residues 94–96 may be related to antibody complementarity whereas residues 99–101 function probably as a pivot permitting the combining region of the L chain to make optimal contact with the antigenic determinant (Wu & Kabat, 1970).
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Chersi A., Roholt O. A., Pressman D. Amino-acid sequences of light chains of a rabbit anti-p-azobenzoate antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2569–2573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appella E., Rejnek J., Reisfeld R. A. Variations at the carboxyl-terminal amino acid sequence of rabbit light chains with b4, b5 and b6 allotypic specificities. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgois A., Fougereau M., De Preval C. Sequence of amino acids of the NH 2 -terminal region of a mouse-clonal immunoglobulin heavy chain. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 21;24(3):446–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb19705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. G., Jaton J. C. The aminoterminal sequence of antibody light chains: evidence for possible inheritance of structural genes. Immunochemistry. 1973 Jun;10(6):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunitzer G., Schrank B., Ruhfus A. Zum vollständigen und autoatischen Abbau von Peptiden nach der Quadrolmethode. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Dec;351(12):1589–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R., Hartley B. S. Location of disulphide bridges by diagonal paper electrophoresis. The disulphide bridges of bovine chymotrypsinogen A. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):214–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1010214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M., Williams R. C., Jr, Feizi T., Kunkel H. G. Light chain sequences of human IgM cold agglutinins (variable-region subgroups amino-acid sequence-kappa light chain-N-terminal). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):40–43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A., Gall W. E., Gottlieb P. D., Rutishauser U., Waxdal M. J. The covalent structure of an entire gammaG immunoglobulin molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):78–85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Gall W. E. The antibody problem. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:415–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. XI. Functional implications. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 4;9(16):3197–3205. doi: 10.1021/bi00818a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman J. B. A partial amino acid sequence in the heavy chain of a rabbit antibody to group C streptococcal carbohydrate. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 6;10(14):2753–2761. doi: 10.1021/bi00790a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman J. B. Amino acid sequences in the Fd of a rabbit antibody heavy chain. Immunochemistry. 1973 Jun;10(6):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B. Correlation of the c-terminal sequence of rabbit light chains with allotypes. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jun;3(5):341–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser K. J., Pulsen K., Haber E. Specific cleavage between variable and constant domains of rabbit antibody light chains by dilute acid hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4974–4977. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedlender E. F., Haber E. A method for obtaining large variable-region peptides from rabbit light chains. Biochemistry. 1972 Jun 6;11(12):2362–2370. doi: 10.1021/bi00762a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Guyer R. B., Terry W. D. Isolation and characterization of electrophoretically homogeneous rabbit antihapten antibody populations. 3. NH 2 -terminal light chain sequence analyses of focused anti-p-azophenyltrimethylammonium and anti-p-azobenzenearsonate antibody fractions. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7051–7061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I., Perham R. N. The reaction of aldolase with 2-methylmaleic anhydride. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):843–849. doi: 10.1042/bj1160843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F., Atassi M. Z. Enzymic and immunochemical properties of lysozyme. Evaluation of several amino group reversible blocking reagents. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 8;9(25):4939–4944. doi: 10.1021/bi00827a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Eichmann K., Lackland H., Krause R. M., Ohms J. J. Rabbit antibody light chains and gene evolution. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1040–1044. doi: 10.1038/2281040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C., Braun D. G. Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal sixty-nine residues of heavy chain derived from a homogeneous rabbit antibody. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):539–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1300539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C., Braun D. G., Strosberg A. D., Haber E., Morris J. E. Restricted rabbit antibodies: amino acid sequences of rabbit H chains of allotype a1, a2, and a3 in the region 80 to 94. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1838–1843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the variable regions of light chains derived from two homogeneous rabbit anti-pneumococcal antibodies. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):15–25. doi: 10.1042/bj1410015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C., Waterfield M. D., Margolies M. N., Bloch K. J., Haber E. Variation in the primary structure of antibodies during the course of immunization. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1583–1587. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe J. M., Capra J. D. Sequence relationships among the variable regions of immunoglobulin heavy chains from various mammalian species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2052–2055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball J. W., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Jaton J. C. The response in rabbits to prolonged immunization with type 3 pneumococci. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1177–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J., Seide R. K., Lackland H., Thunberg A. L. Serologic identity of the b4 allotypic determinants present on homogeneous rabbit light chains with different N-terminal amino acid sequences. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):735–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm M. E., Frangione B. Intrachain disulphide bridges of rabbit immunoglobulin light chains of allotypes b4 and b5. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1357–1359. doi: 10.1042/bj1281357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Partial amino acid sequence of a kappa chain. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):749–759. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Pink J. R. Structure and evolution of immunoglobulins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1970;21:209–263. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(70)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole L. E., Jackson S. A., Porter R. R., Wilkinson J. M. Allotypically related sequences in the Fd fragment of rabbit immunoglobulin heavy chains. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(2):301–318. doi: 10.1042/bj1240301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell I. J., Frangione B., Porter R. R. The disulphide bonds of the heavy chain of rabbit immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):261–268. doi: 10.1042/bj1160261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J. Analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by gas chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5597–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J., Amzel L. M., Avey H. P., Becka L. N. Structure of Fab' New at 6 A resolution. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 2;235(57):137–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio235137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J., Amzel L. M., Avey H. P., Chen B. L., Phizackerley R. P., Saul F. Three-dimensional structure of the Fab' fragment of a human immunoglobulin at 2,8-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3305–3310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Fraser K. J., Haber E. An active derivative of rabbit antibody light chain composed of the constant and the variable domains held together only by a native disulfide bond. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press E. M., Piggot P. J., Porter R. R. The N- and c-terminal amino acid sequences of the heavy chain from a pathological human immunoglobulin IgG. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):356–366. doi: 10.1042/bj0990356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Cebra J. J. Localization of affinity-labeled residues in the primary structure of anti-dinitrophenyl antibody raised in strain 13 guinea pigs. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3647–3657. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rejnek J., Appella E., Mage R. G., Reisfeld R. A. Subtypes of rabbit kappa light polypeptide chains associated with the beta locus. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2712–2718. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Girling R. L., Ely K. R., Edmundson A. B. Structure of a lambda-type Bence-Jones protein at 3.5-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4620–4631. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strosberg A. D., Fraser K. J., Margolies M. N., Haber E. Amino acid sequence of rabbit pneumococcal antibody. I. Light-chain cysteine-containing peptides. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4978–4985. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



