Abstract
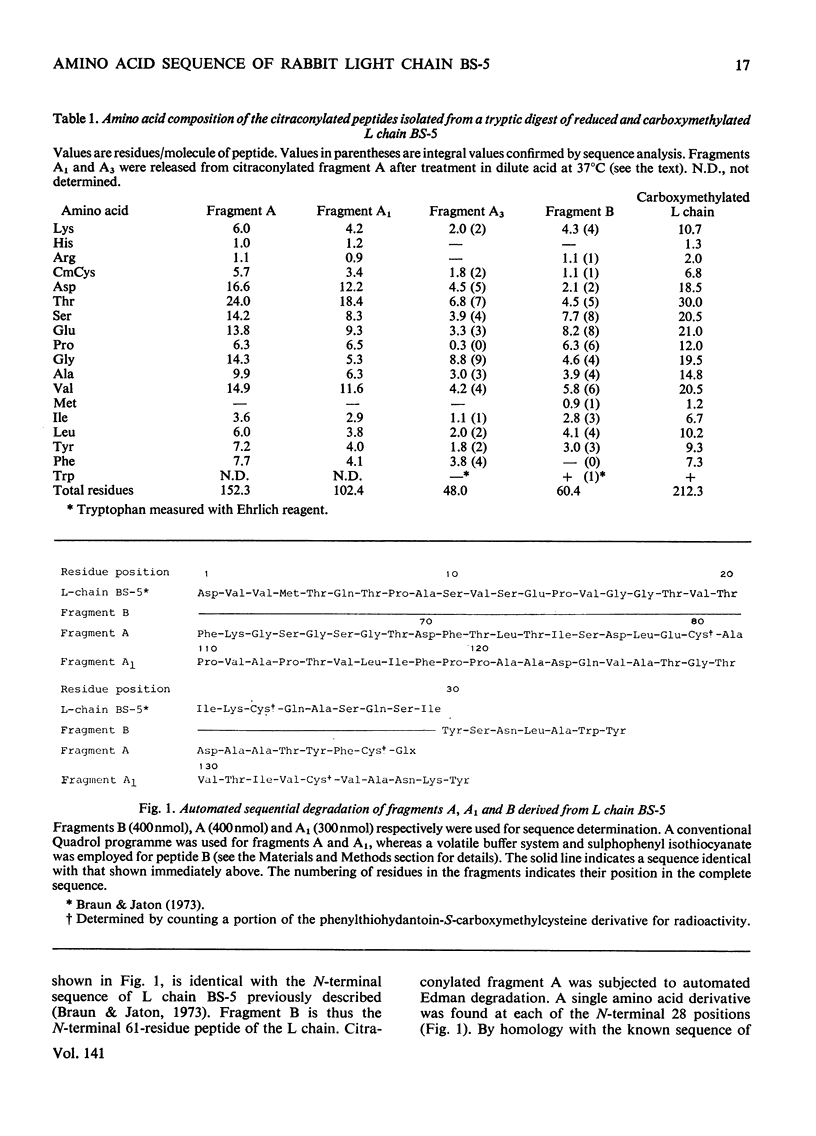
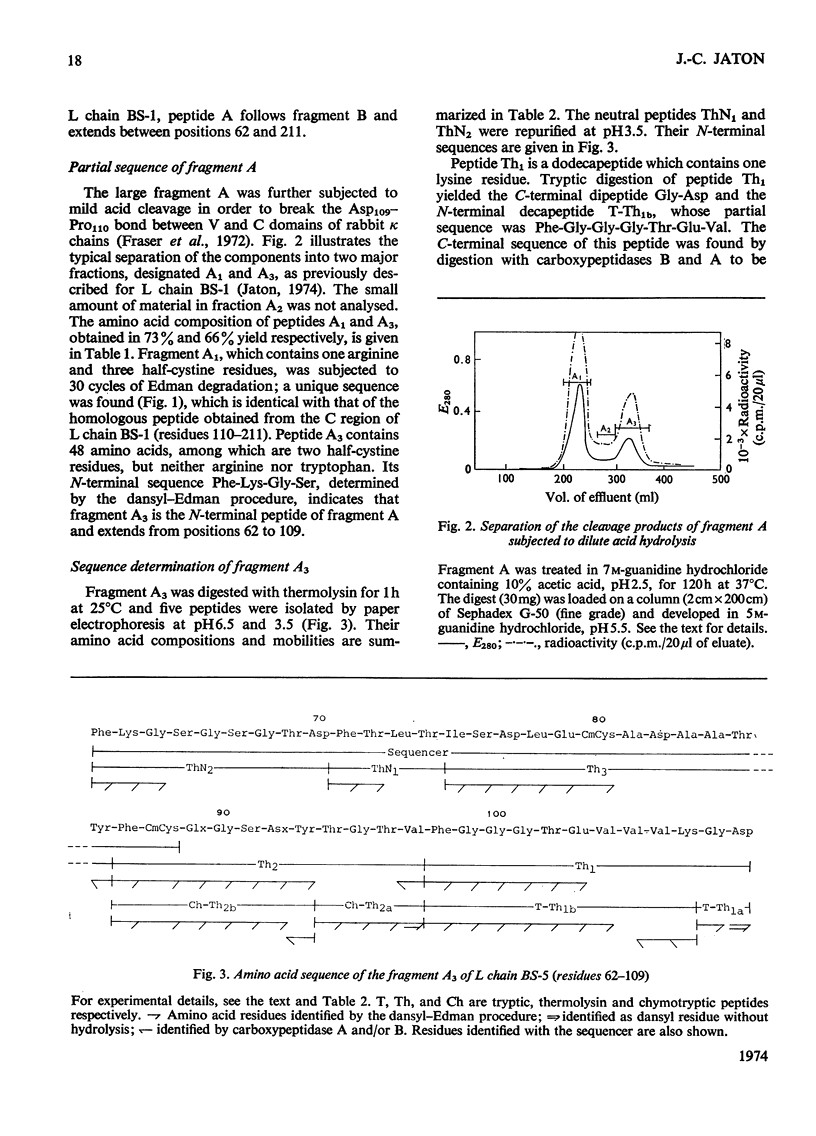
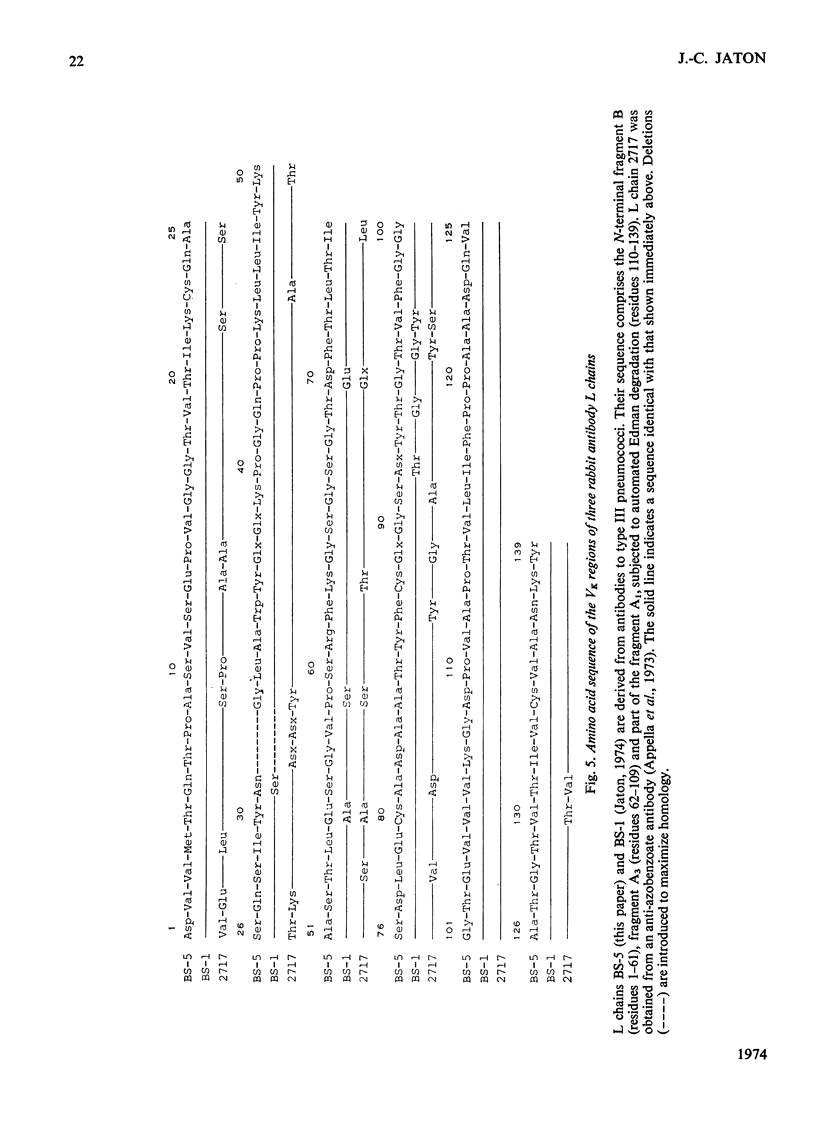
The amino acid sequence of the N-terminal 139 residues of the L (light) chain derived from a homogeneous rabbit antibody to type III pneumococci was determined. This L chain, designated BS-5, exhibits a greater degree of homology with the basic sequence of human κ chains of subgroup I (72%) than with subgroups II and III. L-chain BS-5 differs from another L chain (BS-1), also derived from an antibody to type III pneumococci (Jaton, 1974), by eight amino acid residues, even though the chains are identical within the N-terminal 30 residues. Six of these eight substitutions are located within the three hypervariable sections of the variable half: Asn/Ser in position 31, Glu/Ala in position 55, Asx/Thr, Thr/Gly, Thr/Gly and Val/Tyr in positions 92, 94, 96 and 97 respectively. The two anti-pneumococcal L chains BS-1 and BS-5 are much more similar to each other than to an anti-azobenzoate L chain (Appella et al., 1973), from which they differ by 30 and 29 residues respectively. Of these interchanges 13–15 are confined to the three hypervariable sections, and 11 occur within the N-terminal 27 positions. The three chains have an identical sequence from residue 98 to residue 139, except for a possible inversion of two residues in positions 130–131 of the anti-azobenzoate chain.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Rejnek J., Reisfeld R. A. Variations at the carboxyl-terminal amino acid sequence of rabbit light chains with b4, b5 and b6 allotypic specificities. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appella E., Roholt O. A., Chersi A., Radzimski G., Pressman D. Amino acid sequence of the light chain derived from a rabbit anti-p-azobenzoate antibody of restricted heterogeneity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 21;53(4):1122–1129. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90581-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. G., Jaton J. C. The aminoterminal sequence of antibody light chains: evidence for possible inheritance of structural genes. Immunochemistry. 1973 Jun;10(6):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunitzer G., Schrank B., Ruhfus A. Zum vollständigen und autoatischen Abbau von Peptiden nach der Quadrolmethode. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Dec;351(12):1589–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D., Weigert M. Immunochemical analysis of the cross-reacting idiotypes of mouse myeloma proteins with anti-dextran activity and normal anti-dextran antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):235–239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser K. J., Pulsen K., Haber E. Specific cleavage between variable and constant domains of rabbit antibody light chains by dilute acid hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4974–4977. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I., Perham R. N. The reaction of aldolase with 2-methylmaleic anhydride. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):843–849. doi: 10.1042/bj1160843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E. Homogeneous elicited antibodies: induction, characterization, isolation, and structure. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:285–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilschmann N., Craig L. C. Amino acid sequence studies with Bence-Jones proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1403–1409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilschmann N. Die molekularen Grundlagen der Antikörperbildung. Naturwissenschaften. 1969 Apr;56(4):195–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01166814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Eichmann K., Lackland H., Krause R. M., Ohms J. J. Rabbit antibody light chains and gene evolution. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1040–1044. doi: 10.1038/2281040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C. Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal 139 residues of light chain derived from a homogeneous rabbit antibody. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj1410001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C., Braun D. G. Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal sixty-nine residues of heavy chain derived from a homogeneous rabbit antibody. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):539–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1300539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C., Waterfield M. D., Margolies M. N., Bloch K. J., Haber E. Variation in the primary structure of antibodies during the course of immunization. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1583–1587. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball J. W., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Jaton J. C. The response in rabbits to prolonged immunization with type 3 pneumococci. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1177–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. Linked groups of residues in immunoglobulin k chains. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):330–332. doi: 10.1038/216330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Pink J. R. Structure and evolution of immunoglobulins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1970;21:209–263. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(70)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niall H. D., Edman P. Two structurally distinct classes of kappa-chains in human immunoglobulins. Nature. 1967 Oct 21;216(5112):262–263. doi: 10.1038/216262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell I. J., Frangione B., Porter R. R. The disulphide bonds of the heavy chain of rabbit immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):261–268. doi: 10.1042/bj1160261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J. Analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by gas chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5597–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R. The combining sites of antibodies. Harvey Lect. 1971;65:157–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam F. W. Immunoglobulin structure: variability and homology. Science. 1969 Feb 14;163(3868):633–644. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3868.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Girling R. L., Ely K. R., Edmundson A. B. Structure of a lambda-type Bence-Jones protein at 3.5-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4620–4631. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strosberg A. D., Fraser K. J., Margolies M. N., Haber E. Amino acid sequence of rabbit pneumococcal antibody. I. Light-chain cysteine-containing peptides. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4978–4985. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


