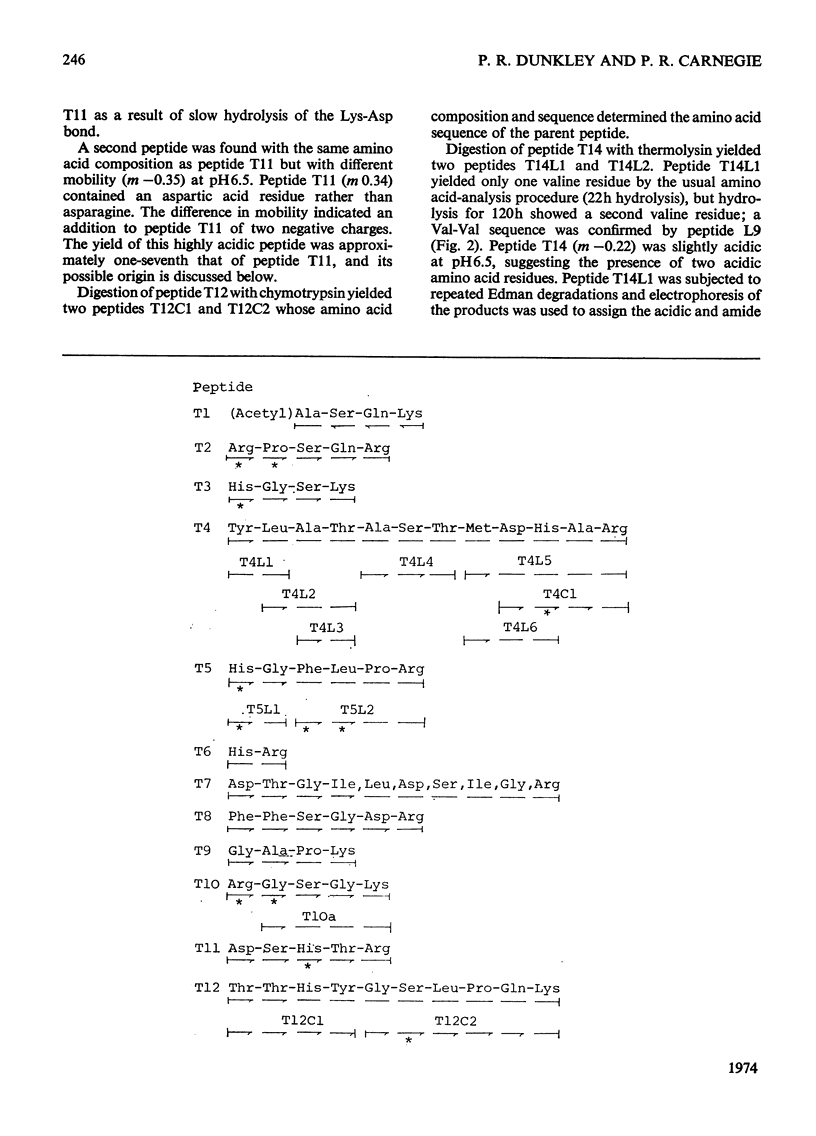
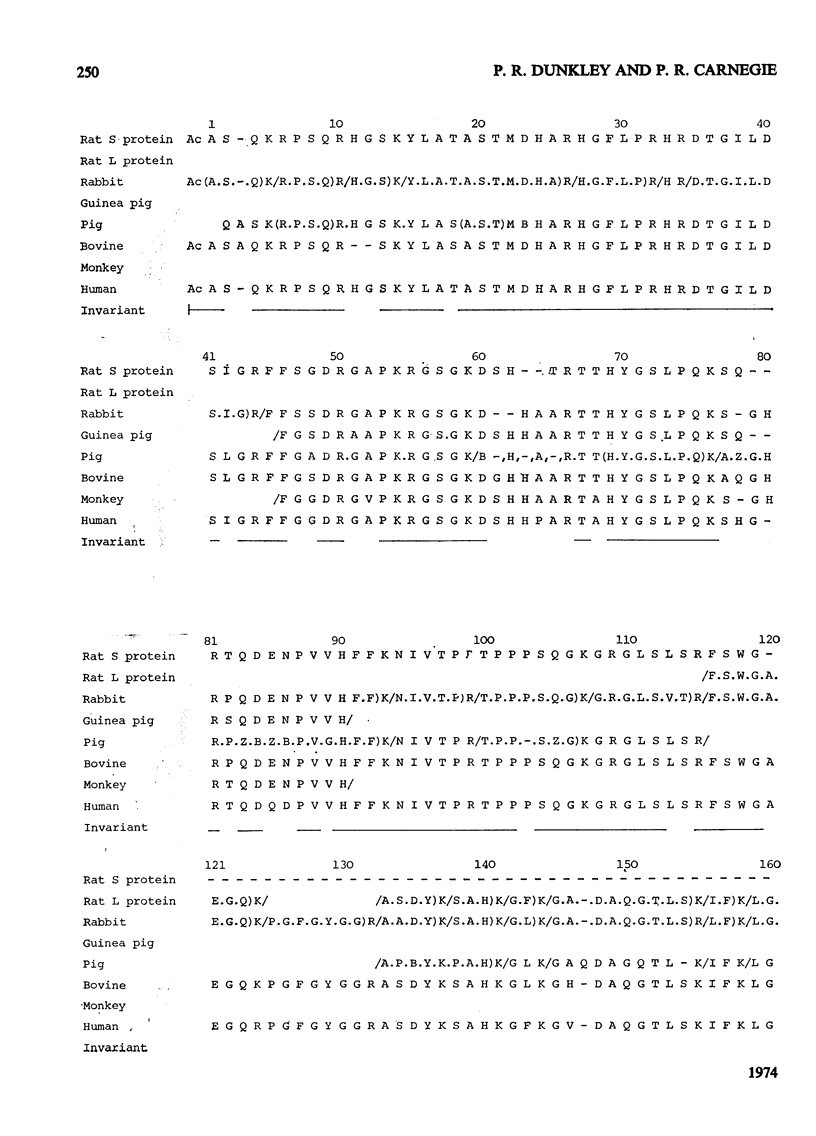
Abstract
1. The complete amino acid sequence of the smaller basic protein from rat brain myelin was determined. This protein differs from myelin basic proteins of other species in having a deletion of a polypeptide of 40 amino acid residues from the centre of the molecule. 2. A detailed comparison is made of the constant and variable regions in a group of myelin basic proteins from six species. 3. An arginine residue in the rat protein was found to be partially methylated. The ratio of methylated to unmethylated arginine at this position differed from that found for the human basic protein. 4. Three tryptic peptides were isolated in more than one form. The differences between the two forms of each peptide are discussed in relation to the electrophoretic heterogeneity of myelin basic proteins, which is known to occur at alkaline pH values. 5. Detailed evidence for the amino acid sequence of the protein has been deposited as Supplementary Publication SUP 50029 at the British Library (Lending Division) (formerly the National Lending Library for Science and Technology), Boston Spa, Yorks. LS23 7BQ, U.K., from whom copies may be obtained on the terms given in Biochem. J. (1973) 131, 5.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. H., Osborne J. A developmental study of the relationship between the protein components of rat CNS myelin. Neurobiology. 1973;3(2):91–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. S., Carnegie P. R. Isolation and partial characterization of methylated arginines from the encephalitogenic basic protein of myelin. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):69–74. doi: 10.1042/bj1230069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. S., Carnegie P. R. Specific enzymic methylation of an arginine in the experimental allergic encephalomyelitis protein from human myelin. Science. 1971 Feb 12;171(3971):579–581. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3971.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K. Evidence for the homology of the main determinant of the human encephalitogenic protein and an anecstral histone IV sequence. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1245–1248. doi: 10.1042/bj1261245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrand H. Isolation and partial characterization of some proteolytically and chemically derived fragments of bovine encephalitogenic protein. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 15;21(1):116–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S. W., Eylar E. H. The proposed amino acid sequence of the P1 protein of rabbit sciatic nerve myelin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):590–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90377-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S., Eylar E. H. Localization of methylated arginine in the A1 protein from myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R. Amino acid sequence of the encephalitogenic basic protein from human myelin. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):57–67. doi: 10.1042/bj1230057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R., Kemp B. E., Dunkley P. R., Murray A. W. Phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by an adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;135(3):569–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1350569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R., Lamoureux G., Bencina B. Proposed technique for classifying and identifying encephalitogens. Nature. 1967 Apr 22;214(5086):407–408. doi: 10.1038/214407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R. N-terminal sequence of an encephalitogenic protein form human myelin. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(2):240–242. doi: 10.1042/bj1110240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R. Properties, structure and possible neuroreceptor role of the encephalitogenic protein of human brain. Nature. 1971 Jan 1;229(5279):25–28. doi: 10.1038/229025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R., Symthies J. R., Caspary E. A., Field E. J. Interaction of hallucinogenic drugs with encephalitogenic protein of myelin. Nature. 1972 Dec 29;240(5383):561–563. doi: 10.1038/240561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Mahler H. R. Resolution of insoluble proteins in rat brain subcellular fractions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 May;120(2):384–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E. Chromatographic fractionation of myelin basic protein. Partial characterization and methylarginine contents of the multiple forms. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2392–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E. Determination of methylated basic amino acids with the amino acid analyzer. Application to total acid hydrolyzates of myelin basic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2387–2391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E., Kies M. W. Gel filtration of proteins at acid pH. Application to molecular weight estimation of myelin basic proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):342–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E., Kies M. W. Large scale preparation of myelin basic protein from central nervous tissue of several mammalian species. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(2):139–165. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley P. R., Coates A. S., Carnegie P. R. Communications. Encephalitogenic activity of peptides from the smaller basic protein of rat myelin. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1699–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easley C. W. Combinations of specific color reactions useful in the peptide mapping technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 13;107(2):386–388. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng L. F., Chao F. C., Gerstl B., Pratt D., Tavaststjerna M. G. The maturation of human white matter myelin. Fractionation of the myelin membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4455–4465. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H., Brostoff S., Hashim G., Caccam J., Burnett P. Basic A1 protein of the myelin membrane. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5770–5784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaitonde M. K., Dovey T. A rapid and direct method for the quantitative determination of tryptophan in the intact protein. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):907–911. doi: 10.1042/bj1170907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J. I., ROOS P. Studies on pituitary polypeptide hormones. I. The structure of beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone from pig pituitary glands. Biochem J. 1959 Mar;71(3):434–445. doi: 10.1042/bj0710434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagopian A., Westall F. C., Whitehead J. S., Eylar E. H. Glycosylation of the A1 protein from myelin by a polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. Identification of the receptor sequence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2519–2523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. L. Hydrolysis of proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1965;20:37–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60388-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth S. E., Kozel L. R., Smithies O. Probable identity of tissue specific histone with encephalitogenic protein. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 10;237(71):49–50. doi: 10.1038/newbio237049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London Y., Demel R. A., Geurts van Kessel W. S., Vossenberg F. G., van Deenen L. L. The protection of A1 myelin basic protein against the action of proteolytic enzymes after interaction of the protein with lipids at the air-water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 18;311(4):520–530. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E., Kies M. W. Comparison of amino-acid sequences of hypothalamic peptide, brain-specific histone and myelin basic protein. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 17;234(46):87–89. doi: 10.1038/newbio234087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E., Kies M. W. Electrophoretic characterization of basic proteins in acid extracts of central nervous system tissue. J Neurochem. 1971 Dec;18(12):2417–2426. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E., Kies M. W., McKneally S. S., Shapira R., Kibler R. F. Differences between the two myelin basic proteins of the rat central nervous system. A deletion in the smaller protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 15;263(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E., Kies M. W. Myelin basic proteins of the rat central nervous system. Purification, encephalitogenic properties, and amino acid compositions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E., Kies M. W. Rat myelin basic proteins: relationship between size differences and microheterogeneity. J Neurochem. 1970 Aug;17(8):1329–passim. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb03383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E., Kies M. W. The occurrence of two myelin basic proteins in the central nervous system of rodents in the suborders Myomorpha and Sciuromorpha. J Neurochem. 1971 Dec;18(12):2427–2433. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlin D. E., Blank S. E., Kibler R. F., McKneally S., Shapira R. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the rat: response to encephalitogenic proteins and peptides. Science. 1973 Feb 2;179(4072):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4072.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMANN G. E. Enzymatic dephosphorylation of ovalbumin and plakalbumin. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;35(5):711–726. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.5.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer S. E., Wechsler W. Biochemically differentiated neoplastic clone of Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2885–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammeck R., Martenson R. E., Brady R. O. Studies of the metabolism of myelin basic proteins in various regions of the central nervous system of immature and adult rats. Brain Res. 1971 Nov;34(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Hartley B. S. Evidence for the amino acid sequence of porcine pancreatic elastase. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):643–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1310643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D. M., Fanning E. M., Percy M. E., Parr D. M., Connell G. E. Deletions in immunoglobulin polypeptide chains as evidence for breakage and repair in DNA. Science. 1971 May 7;172(3983):574–577. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3983.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundarraj N., Pfeiffer S. E. Myelin basic protein arginine methyl transferase: wide distribution among both neurogenic and non-neurogenic tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 8;52(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



