Abstract
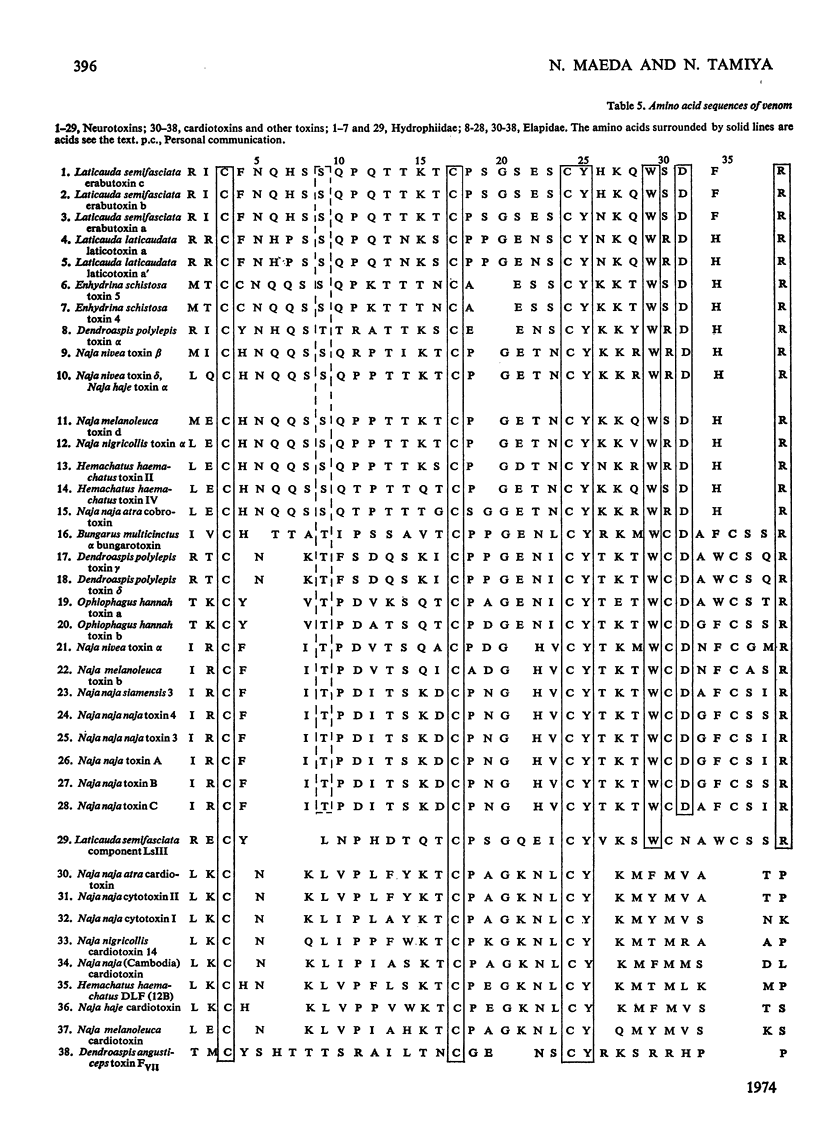
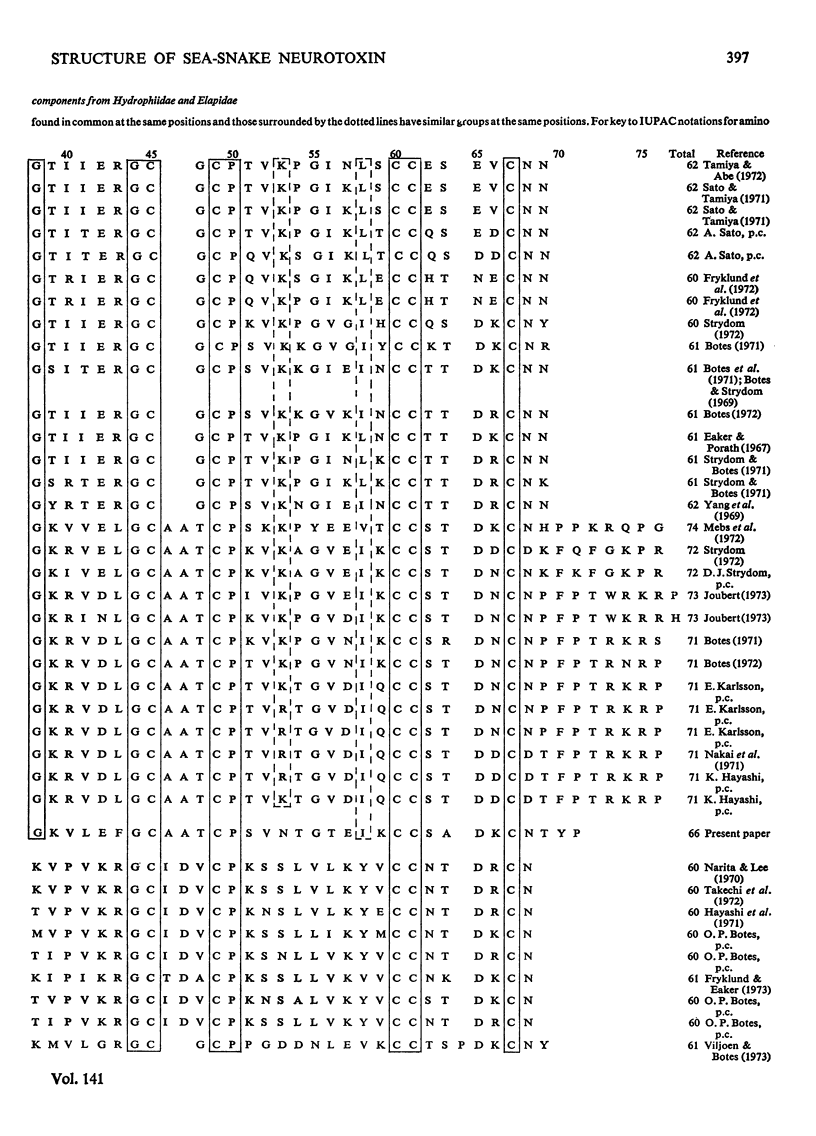
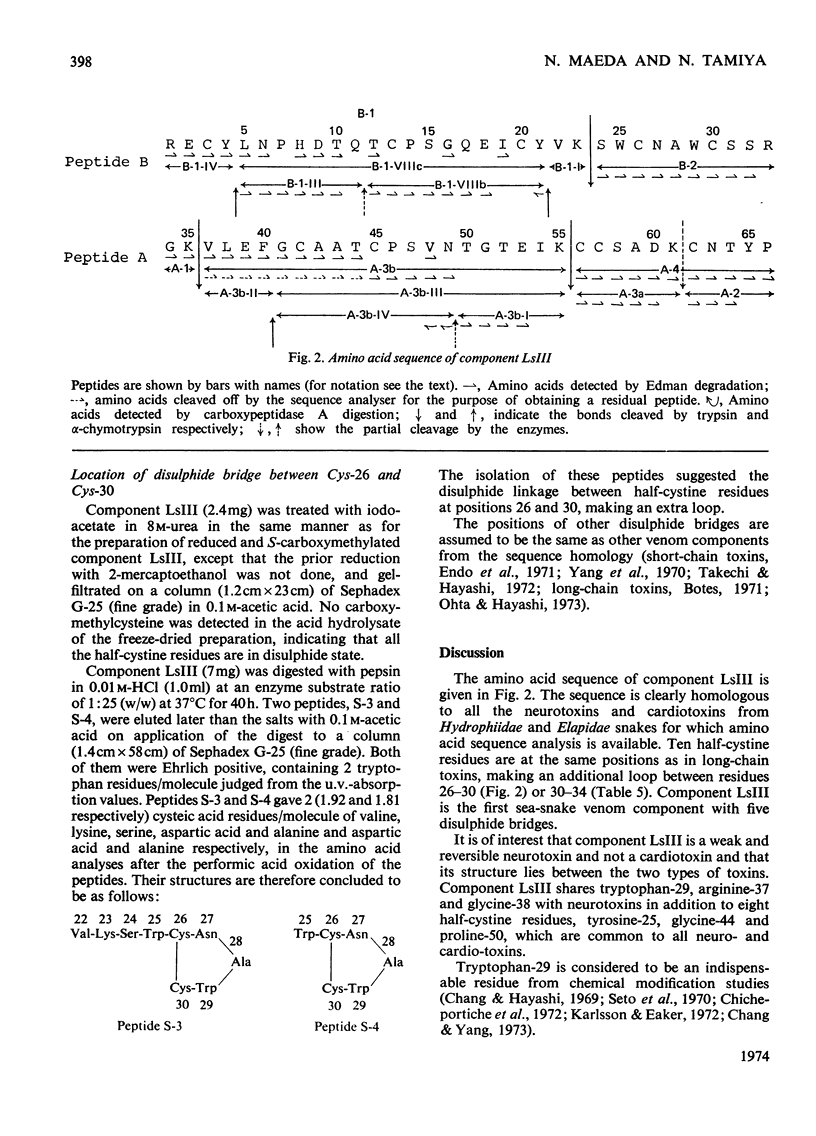
A weak and reversibly acting neurotoxic protein of Laticauda semifasciata venom, Laticauda semifasciata III (component LsIII), was sequenced. Component LsIII consists of 66 amino acid residues and has five disulphide bridges, one of which was located between residues 26 and 30. The weak and reversible neurotoxicity of component LsIII is discussed in relation to its structure, which falls between those of the neuro- and cardiotoxins of sea snakes and Elapidae snakes isolated and sequenced so far.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of toxins and from Naja nivea venom and the disulfide bonds of toxin . J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7383–7391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of toxins b and d from Naja melanoleuca venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2866–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P., Strydom D. J. A neurotoxin, toxin alpha, from Egyptian cobra (Naja haje haje) venom. I. Purification, properties, and complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4147–4157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P., Strydom D. J., Anderson C. G., Christensen P. A. Snake venom toxins. Purification and properties of three toxins from Naja nivea (Linnaeus) (Cape cobra) venom and the amino acid sequence of toxin delta. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3132–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Hayashi K. Chemical modification of the tryptophan residue in cobratoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Nov 20;37(5):841–846. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90968-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Yang C. C. Immunochemical studies on the tryptophan-modified cobrotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 21;295(2):595–604. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Yang C. C., Nakai K., Hayashi K. Studies on the status of free amino and carboxyl groups in cobrotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):334–344. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicheportiche R., Rochat C., Sampieri F., Lazdunski M. Structure-function relationships of neurotoxins isolated from Naja haje venom. Physiochemical properties and identification of the active site. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 25;11(9):1681–1691. doi: 10.1021/bi00759a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Sato S., Ishii S., Tamiya N. The disulphide bonds of erabutoxin a, a neurotoxic protein of a sea-snake (Laticauda semifasciata) venom. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):463–467. doi: 10.1042/bj1220463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryklund L., Eaker D. Complete amino acid sequence of a nonneurotoxic hemolytic protein from the venom of Haemachatus haemachates (African ringhals cobra). Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):661–667. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryklund L., Eaker D., Karlsson E. Amino acid sequences of the two principal neurotoxins of Enhydrina schistosa venom. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4633–4640. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I., Perham R. N. The reaction of aldolase with 2-methylmaleic anhydride. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):843–849. doi: 10.1042/bj1160843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Takechi M., Sasaki T. Amino acid sequence of cytotoxin I from the venom of the Indian cobra (Naja naja). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 3;45(5):1357–1362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Wallén P., Gröndahl N. J., Henschen A., Blombäck B. On the primary structure of human fibrinogen. Isolation and characterization of N-terminal fragments from plasmic digests. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(2):189–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEPSON J. B., SMITH I. Multiple dipping procedures in paper chromatography: a specific test for hydroxy-proline. Nature. 1953 Dec 12;172(4389):1100–1101. doi: 10.1038/1721100b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joubert F. J. Snake venom toxins the amino acid sequences of two toxins from Ophiophagus hannah (King cobra) venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 12;317(1):85–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson E., Eaker D. Chemical modifications of the postsynaptic Naja naja neurotoxins. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1972 Jun 28;71(6):358–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson E., Eaker D., Ponterius G. Modification of amino groups in Naja naja neurotoxins and the preparation of radioactive derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN T., LEONE E. Studies on the metabolism of semen. VIII. Ergothioneine as a normal constituent of boar seminal plasma; purification and crystallization; site of formation and function. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):140–148. doi: 10.1042/bj0530140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Takagi K., Tamiya N., Chen Y. M., Lee C. Y. The isolation of an easily reversible post-synaptic toxin from the venom of a sea snake, Laticauda semifasciata. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):383–387. doi: 10.1042/bj1410383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebs D., Narita K., Iwanaga S., Samejima Y., Lee C. Y. Purification, properties and amino acid sequence of -bungarotoxin from the venom of Bungarus multicinctus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Feb;353(2):243–262. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai K., Sasaki T., Hayashi K. Amino acid sequence of toxin A from the venom of the Indian cobra (Naja naja). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):893–897. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90795-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita K., Lee C. Y. The amino acid sequence of cardiotoxin from Formosan cobra (Naja naja atra) venom. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 23;41(2):339–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90509-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota M., Hayashi K. Localization of the five disulfide bridges in toxin B from the venom of the Indian cobra (Naja naja). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORATH J. Gel filtration of proteins, peptides and amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 8;39:193–207. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH I. Colour reactions on paper chromatograms by a dipping technique. Nature. 1953 Jan 3;171(4340):43–44. doi: 10.1038/171043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Tamiya N. The amino acid sequences of erabutoxins, neurotoxic proteins of sea-snake (Laticauda semifasciata) venom. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1220453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto A., Sato S., Tamiya N. The properties and modification of tryptophan in a sea snake toxin, erabutoxin a. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 29;214(3):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom A. J., Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. Purification, properties, and complete amino acid sequence of two toxins from Ringhals (Hemachatus haemachatus) venom. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1341–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J. Snake venom toxins. Structure-function relationships and phylogenetics. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1973 Jan 15;44(1):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(73)90364-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of two toxins from Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):4029–4042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takechi M., Hayashi K. Localization of the four disulfide bridges in cytotoxin II from the venom of the indian cobra (Naja naja). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):584–590. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90451-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takechi M., Hayashi K., Sasaki T. The amino acid sequence of cytotoxin II from the venom of the Indian cobra (Naja naja). Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;8(4):446–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamiya N., Abe H. The isolation, properties and amino acid sequence of erabutoxin c, a minor neurotoxic component of the venom of a sea snake Katicauda semifasciata. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):547–555. doi: 10.1042/bj1300547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamiya N., Arai H. Studies on sea-snake venoms. Crystallization of erabutoxins a and b from Laticauda semifasciata venom. Biochem J. 1966 Jun;99(3):624–630. doi: 10.1042/bj0990624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljoen C. C., Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. The purification and amino acid sequence of toxin F VII from Dendroaspis angusticeps venom. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4915–4919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Yang H. J., Chiu R. H. The position of disulfide bonds in cobrotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 21;214(2):355–363. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Yang H. J., Huang J. S. The amino acid sequence of cobrotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 12;188(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



